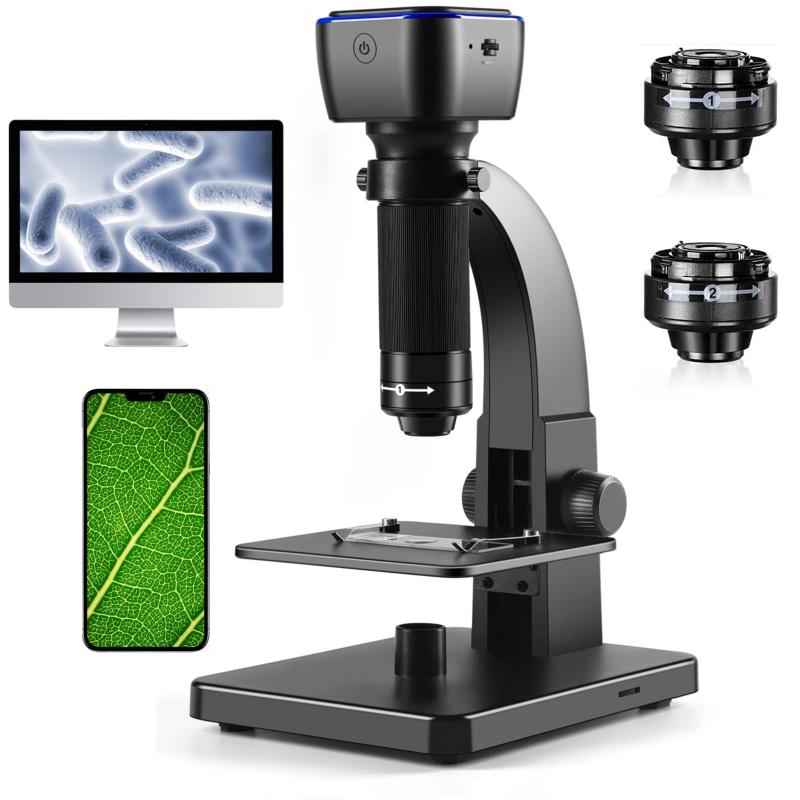
Algae Which Type Of Microscope To Use ?
To observe algae, a compound microscope is typically used. This type of microscope uses multiple lenses to magnify the specimen and provide a clear image. A brightfield microscope is commonly used to observe live or preserved algae specimens. However, if the algae is too small or transparent, a phase contrast microscope or a differential interference contrast microscope may be used to enhance the contrast and visibility of the specimen. Additionally, a fluorescence microscope can be used to observe specific pigments or proteins within the algae. The choice of microscope depends on the type of algae being observed and the specific research question being addressed.
1、 Bright-field microscope
Algae can be observed using a bright-field microscope. This type of microscope is commonly used in biological research and is ideal for observing live or stained specimens. Bright-field microscopes use a simple lens system to produce a bright image of the specimen against a dark background. This type of microscope is easy to use and provides a clear image of the specimen.
However, with the advancement of technology, other types of microscopes such as fluorescence and confocal microscopes have become more popular in the study of algae. Fluorescence microscopy uses fluorescent dyes to label specific structures within the cell, allowing for more detailed observation of the specimen. Confocal microscopy, on the other hand, uses a laser to scan the specimen and produce a 3D image.
Despite the availability of these advanced microscopes, bright-field microscopy remains a valuable tool in the study of algae. It is still widely used in research and education due to its simplicity and affordability. Additionally, bright-field microscopy can be used to observe a wide range of specimens, including those that are too small or too delicate for other types of microscopes.
In conclusion, while other types of microscopes have become more popular in recent years, a bright-field microscope is still a suitable option for observing algae. It remains a valuable tool in the study of biological specimens and is widely used in research and education.

2、 Phase-contrast microscope
When studying algae, a phase-contrast microscope is the most suitable type of microscope to use. This is because algae are unicellular organisms that are often transparent and difficult to see under a regular light microscope. A phase-contrast microscope uses a special optical technique that enhances the contrast of transparent specimens, making them easier to observe.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the study of algae due to their potential as a source of biofuels and other valuable products. As a result, there has been a renewed focus on developing new imaging techniques to better understand the structure and behavior of these organisms. One such technique is called super-resolution microscopy, which allows researchers to observe structures at a much higher resolution than was previously possible.
Super-resolution microscopy has already been used to study the structure of algal cells and their organelles, providing new insights into their biology. For example, researchers have used this technique to study the structure of the chloroplasts in algae, which are responsible for photosynthesis. By understanding the structure of these organelles, researchers hope to develop new ways to improve the efficiency of photosynthesis in algae, which could have important implications for the development of biofuels.
In conclusion, while a phase-contrast microscope is currently the most suitable type of microscope to use when studying algae, new imaging techniques such as super-resolution microscopy are providing researchers with new tools to better understand these organisms. As our understanding of algae continues to grow, it is likely that new imaging techniques will play an increasingly important role in advancing our knowledge of these important organisms.
3、 Fluorescence microscope
Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that can be found in a wide range of environments, from freshwater to marine ecosystems. To study algae, researchers typically use a variety of microscopy techniques, including brightfield, phase contrast, and fluorescence microscopy.
Fluorescence microscopy is particularly useful for studying algae because it allows researchers to visualize specific molecules and structures within the cells. This technique involves labeling the target molecules with fluorescent dyes or proteins, which emit light when excited by a specific wavelength of light. The emitted light can then be visualized using a fluorescence microscope.
One of the latest developments in fluorescence microscopy is super-resolution microscopy, which allows researchers to visualize structures at a much higher resolution than traditional microscopy techniques. This technique has been used to study the structure and function of various organelles within algae cells, including chloroplasts and mitochondria.
Overall, fluorescence microscopy is a powerful tool for studying algae and has contributed significantly to our understanding of their biology and ecology. As new microscopy techniques continue to be developed, we can expect to gain even more insights into the fascinating world of algae.

4、 Confocal microscope
Confocal microscope is the ideal type of microscope to use for studying algae. This is because it allows for the visualization of the internal structures of the algae with high resolution and clarity. The confocal microscope uses a laser beam to scan the sample and create a 3D image of the internal structures of the algae. This type of microscope is particularly useful for studying the chloroplasts of the algae, which are responsible for photosynthesis.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using confocal microscopy to study the interactions between algae and their environment. For example, researchers have used confocal microscopy to study the effects of environmental stressors such as temperature and light intensity on the growth and development of algae. This has led to a better understanding of how algae respond to changes in their environment and has important implications for the development of sustainable algae-based biofuels.
Overall, the confocal microscope is an essential tool for studying algae and has revolutionized our understanding of these important organisms. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that new applications of confocal microscopy will emerge, further expanding our knowledge of algae and their role in the environment.








































