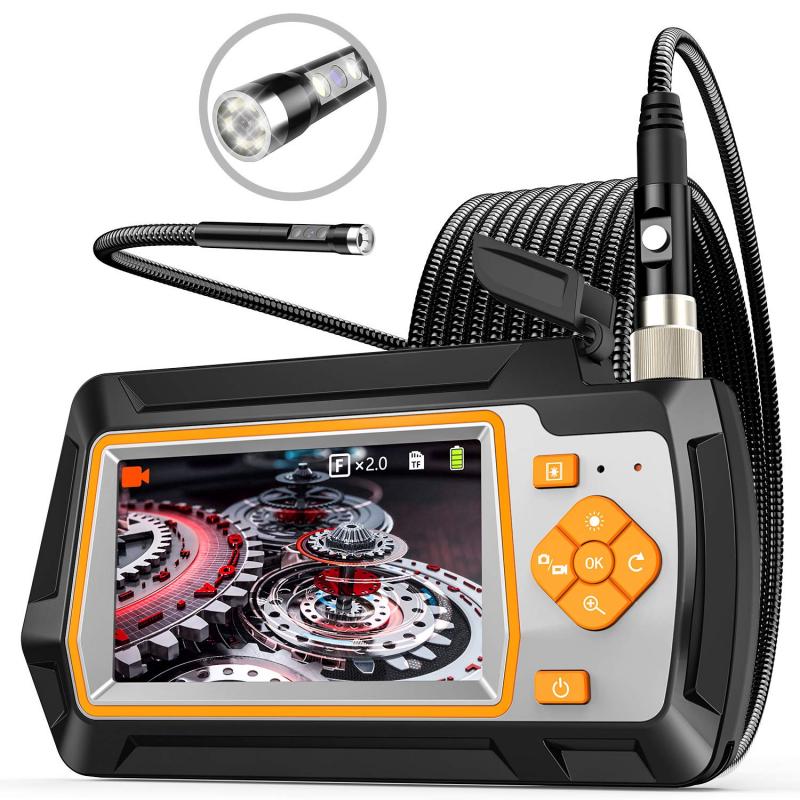
How Are Endoscope Sterilized ?
Endoscopes are typically sterilized using a combination of manual cleaning and high-level disinfection. After each use, the endoscope is carefully cleaned to remove any visible debris or organic material. This is usually done by flushing the channels with enzymatic detergent and brushing the surfaces.
Once the endoscope is cleaned, it undergoes high-level disinfection to eliminate any remaining microorganisms. This is typically achieved by immersing the endoscope in a liquid disinfectant solution or using an automated endoscope reprocessor (AER). The disinfectant solution or AER is designed to kill a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
It is important to follow strict protocols and guidelines provided by regulatory bodies and manufacturers to ensure effective sterilization and prevent the transmission of infections. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the sterilization process are also crucial to ensure the endoscope remains in a sterile condition for safe use in medical procedures.
1、 Chemical sterilization methods for endoscopes
Endoscopes are medical devices used for visualizing and examining internal body cavities or organs. Due to their direct contact with patients, it is crucial to ensure that endoscopes are properly sterilized to prevent the transmission of infections. Chemical sterilization methods are commonly employed to achieve this.
One of the most widely used chemical sterilization methods for endoscopes is high-level disinfection (HLD). HLD involves the use of chemical agents, such as glutaraldehyde, peracetic acid, or hydrogen peroxide, to kill or inactivate microorganisms on the endoscope. These agents are effective against a wide range of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. HLD is typically performed by immersing the endoscope in the disinfectant solution for a specified period, followed by rinsing and drying.
However, recent studies have raised concerns about the effectiveness of HLD in completely eliminating certain pathogens, such as multidrug-resistant bacteria. Some studies have reported the presence of residual bacteria on endoscopes even after undergoing HLD. This has led to the exploration of alternative chemical sterilization methods.
One emerging method is the use of advanced oxidizing agents, such as peracetic acid and ozone. These agents have shown promising results in effectively sterilizing endoscopes and eliminating resistant pathogens. Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of automated endoscope reprocessors (AERs) that can provide standardized and consistent HLD or sterilization processes.
In conclusion, chemical sterilization methods, particularly high-level disinfection, are commonly used for endoscope sterilization. However, there is ongoing research and development to improve the effectiveness of these methods and address concerns regarding the elimination of resistant pathogens. The use of advanced oxidizing agents and automated reprocessing systems are some of the latest advancements in endoscope sterilization.

2、 High-level disinfection techniques for endoscope sterilization
High-level disinfection techniques are used for endoscope sterilization to ensure the elimination of all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The process involves several steps to ensure the endoscope is thoroughly cleaned and disinfected before its next use.
The first step in endoscope sterilization is manual cleaning. This involves the removal of any visible debris or organic material from the endoscope using enzymatic cleaners and brushes. Manual cleaning is crucial as it helps to remove the biofilm, which can harbor microorganisms and make disinfection less effective.
After manual cleaning, the endoscope undergoes a series of disinfection steps. One commonly used method is high-level disinfection using chemical solutions. These solutions, such as glutaraldehyde or peracetic acid, are highly effective in killing a wide range of microorganisms. The endoscope is immersed in the disinfectant solution for a specific period, as recommended by the manufacturer, to ensure complete disinfection.
Another method gaining popularity is the use of automated endoscope reprocessors (AERs). These machines provide a standardized and controlled process for endoscope disinfection. AERs typically use a combination of cleaning, rinsing, and disinfection cycles to ensure thorough sterilization. Some AERs also incorporate advanced technologies like ultrasonic cleaning or hydrogen peroxide vapor to enhance the disinfection process.
It is important to note that the latest point of view in endoscope sterilization emphasizes the need for strict adherence to manufacturer's instructions and guidelines. This includes proper handling, cleaning, and disinfection techniques specific to each type of endoscope. Additionally, regular monitoring of the disinfection process through microbiological testing is recommended to ensure the effectiveness of the sterilization procedures.
In conclusion, high-level disinfection techniques, including manual cleaning, chemical disinfection, and automated endoscope reprocessors, are used for endoscope sterilization. Adherence to manufacturer's guidelines and regular monitoring of the disinfection process are essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of endoscope sterilization.

3、 Automated endoscope reprocessing (AER) systems for sterilization
Automated endoscope reprocessing (AER) systems are commonly used for the sterilization of endoscopes. These systems are designed to ensure that endoscopes are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected between uses, minimizing the risk of cross-contamination and infection transmission.
The AER process typically involves several steps. First, the endoscope is manually pre-cleaned to remove any visible debris or organic material. Then, it is placed in the AER system, which automatically flushes the endoscope's channels with detergent and water to remove any remaining contaminants. This is followed by a disinfection step, where the endoscope is exposed to a high-level disinfectant solution, such as glutaraldehyde or peracetic acid, to kill any remaining microorganisms.
To ensure the effectiveness of the sterilization process, AER systems are equipped with various monitoring and validation features. These include automated leak testing to check for any damage or leaks in the endoscope's channels, as well as temperature and chemical concentration monitoring to ensure that the disinfection parameters are met.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on improving the effectiveness of endoscope sterilization. One area of concern has been the potential for biofilm formation within the endoscope's channels, which can harbor bacteria and other microorganisms. To address this issue, new technologies and protocols have been developed, such as the use of enzymatic cleaners and the implementation of more rigorous cleaning and disinfection procedures.
Additionally, there has been an increased emphasis on the importance of proper training and education for healthcare professionals involved in endoscope reprocessing. This includes ensuring that staff are knowledgeable about the latest guidelines and best practices for endoscope sterilization, as well as providing ongoing training and competency assessments.
Overall, automated endoscope reprocessing systems play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and effective sterilization of endoscopes. Ongoing advancements in technology and protocols continue to improve the reliability and efficiency of these systems, helping to minimize the risk of infection transmission during endoscopic procedures.

4、 Sterilization guidelines for flexible endoscopes
Flexible endoscopes are essential medical devices used for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. However, they can pose a risk of infection if not properly sterilized. Sterilization guidelines for flexible endoscopes have been established to ensure patient safety and prevent the transmission of infectious diseases.
The process of sterilizing flexible endoscopes involves several steps. First, the endoscope is thoroughly cleaned to remove any organic material, such as blood or tissue, using enzymatic cleaners and detergents. This step is crucial as it helps to remove the majority of microorganisms present on the surface of the endoscope.
After cleaning, the endoscope undergoes high-level disinfection, which kills or inactivates most microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This is typically achieved by immersing the endoscope in a liquid disinfectant solution, such as glutaraldehyde or peracetic acid, for a specified period of time. The disinfectant solution must be prepared and used according to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure its effectiveness.
In recent years, there has been growing concern about the potential for endoscope-associated infections, particularly related to the transmission of multidrug-resistant organisms. As a result, additional measures have been recommended to enhance the sterilization process. These include the use of automated endoscope reprocessors (AERs), which provide standardized and consistent disinfection cycles, and the implementation of quality control measures, such as regular monitoring of the disinfection process and periodic testing of endoscope channels for residual contamination.
Furthermore, there has been a shift towards the use of sterilization methods that go beyond high-level disinfection. Some healthcare facilities have started implementing sterilization techniques, such as hydrogen peroxide gas plasma or ethylene oxide gas sterilization, for certain types of endoscopes. These methods provide a higher level of microbial kill and can be particularly useful for endoscopes used in high-risk procedures or in cases where there is a known or suspected infection.
In conclusion, the sterilization guidelines for flexible endoscopes involve a thorough cleaning followed by high-level disinfection. Additional measures, such as the use of AERs and quality control measures, have been recommended to enhance the sterilization process. There is also a growing trend towards the use of sterilization methods that provide a higher level of microbial kill. It is important for healthcare facilities to stay updated with the latest guidelines and recommendations to ensure the safe and effective sterilization of flexible endoscopes.