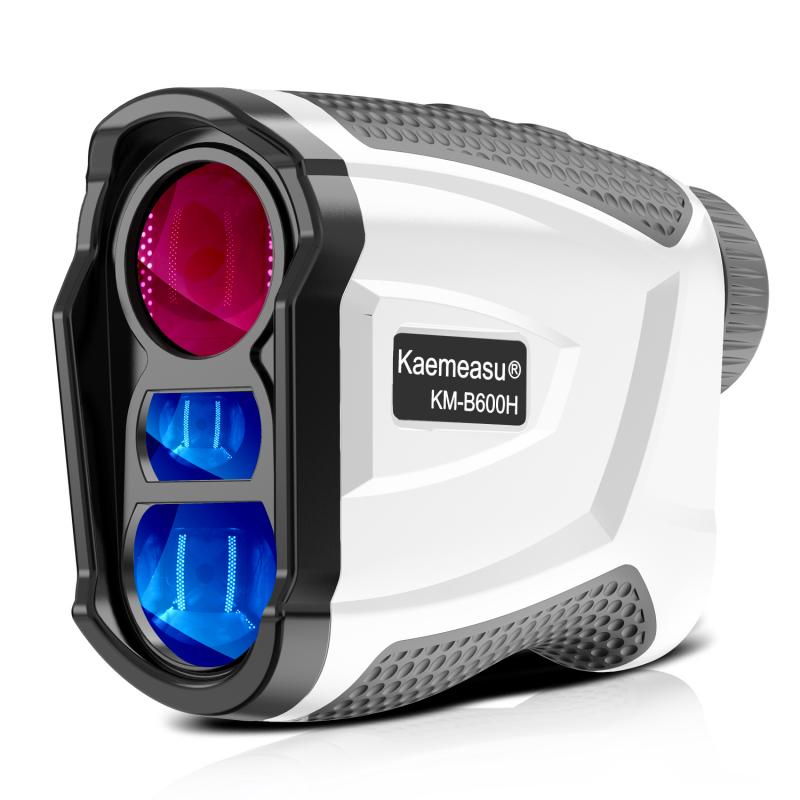
How Are Laser Rangefinder Slope Adjustments Calculated ?
Laser rangefinder slope adjustments are typically calculated using trigonometry. The rangefinder measures the distance to the target, and then uses the angle of inclination or decline to calculate the adjusted distance. By applying the principles of right-angle trigonometry, the rangefinder can determine the horizontal distance to the target, taking into account the slope. This adjusted distance is often referred to as the "slope-adjusted distance" or "true horizontal distance." The specific calculations may vary depending on the rangefinder model and its features, but the underlying principle remains the same.
1、 Laser rangefinder slope adjustment: Angle of Inclination
Laser rangefinder slope adjustments are calculated by taking into account the angle of inclination or slope of the target area. This adjustment is necessary because the distance measured by the rangefinder is affected by the angle at which the laser beam is projected and the angle at which it hits the target.
To calculate the slope adjustment, the rangefinder uses trigonometry principles. It measures the angle of inclination between the rangefinder and the target area. This angle is then used to determine the actual horizontal distance to the target.
The rangefinder uses a built-in inclinometer or tilt sensor to measure the angle of inclination. This sensor detects the tilt of the rangefinder and provides the necessary data for the calculation. Some rangefinders also have a built-in compass to determine the direction of the slope, which can further refine the slope adjustment calculation.
Once the angle of inclination is determined, the rangefinder applies a mathematical formula to calculate the slope adjustment. This formula takes into account the angle, the distance measured by the rangefinder, and other factors such as the speed of light and the time it takes for the laser beam to travel to the target and back.
It is important to note that different rangefinders may use slightly different algorithms or formulas to calculate the slope adjustment. Manufacturers continuously improve their rangefinder technology, so the latest point of view may involve more advanced algorithms or additional sensors to enhance accuracy.
Overall, laser rangefinder slope adjustments are calculated using trigonometry principles and the angle of inclination to provide a more accurate measurement of the horizontal distance to the target.
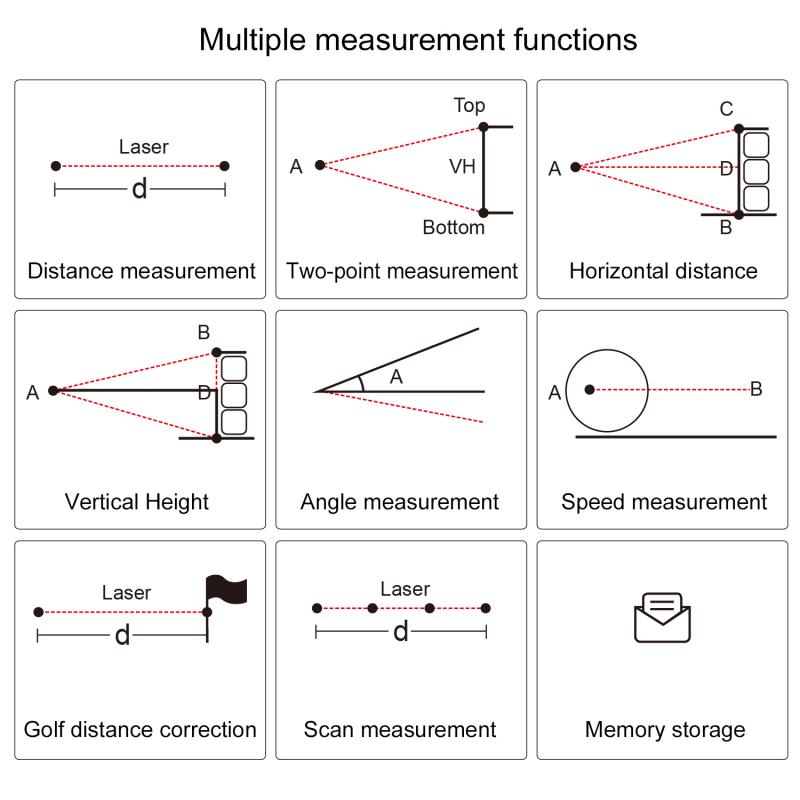
2、 Laser rangefinder slope adjustment: Trigonometric Calculations
Laser rangefinder slope adjustments are calculated using trigonometric calculations. Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. In the case of laser rangefinders, these calculations are used to determine the slope angle and adjust the distance measurement accordingly.
To understand how slope adjustments are calculated, let's consider a simple example. Imagine you are standing on a hill and using a laser rangefinder to measure the distance to a target at the bottom of the slope. The laser rangefinder will provide you with the line-of-sight distance, which is the straight-line distance between you and the target.
However, this line-of-sight distance does not take into account the slope of the hill. To calculate the slope adjustment, you need to determine the angle of the slope. This can be done by measuring the vertical distance between you and the target and the horizontal distance between you and the target.
Using trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent, you can then calculate the slope angle. Once you have the slope angle, you can apply it to the line-of-sight distance to calculate the adjusted distance, which takes into account the slope of the terrain.
It is important to note that different laser rangefinders may use slightly different algorithms or methods to calculate slope adjustments. Some rangefinders may also take into account other factors such as temperature, air pressure, and altitude to provide more accurate slope-adjusted measurements.
In recent years, there have been advancements in laser rangefinder technology that allow for more precise slope adjustments. Some rangefinders now incorporate built-in inclinometers or tilt sensors that directly measure the slope angle, eliminating the need for manual calculations. These advancements have made laser rangefinders even more reliable and accurate for various applications, including golfing, hunting, and surveying.

3、 Laser rangefinder slope adjustment: Distance and Elevation Measurements
Laser rangefinder slope adjustments are calculated using a combination of distance and elevation measurements. The purpose of these adjustments is to account for the angle or slope of the terrain between the rangefinder and the target, which can affect the actual distance to the target.
To calculate the slope adjustment, the laser rangefinder measures the line-of-sight distance to the target. This is the straight-line distance between the rangefinder and the target, without taking into account any elevation changes. The rangefinder also measures the angle or slope between the rangefinder and the target. This angle is typically measured using an inclinometer or an internal sensor within the rangefinder.
Using these measurements, the rangefinder applies a mathematical formula to calculate the slope adjustment. The formula takes into account the distance to the target and the angle or slope between the rangefinder and the target. By factoring in the angle, the rangefinder can determine the actual horizontal distance to the target, which is the distance along the ground.
The latest point of view on laser rangefinder slope adjustments involves advancements in technology and algorithms. Some modern rangefinders use advanced algorithms that take into account not only the angle but also other factors such as temperature, air pressure, and humidity. These factors can affect the speed of the laser beam and therefore the accuracy of the distance measurement. By considering these variables, the rangefinder can provide more precise slope adjustments.
Additionally, some rangefinders offer customizable slope adjustments based on the user's preferences or the specific conditions of the terrain. This allows the user to fine-tune the slope adjustment to match their playing style or the particular course they are on.
Overall, laser rangefinder slope adjustments are calculated using distance and elevation measurements, and advancements in technology continue to improve the accuracy and customization options of these adjustments.
4、 Laser rangefinder slope adjustment: Slope Compensation Algorithms
Laser rangefinder slope adjustments are calculated using slope compensation algorithms. These algorithms take into account the angle of the slope between the rangefinder and the target to provide an accurate distance measurement.
The basic principle behind slope compensation algorithms is trigonometry. By measuring the angle of the slope, the algorithm can calculate the vertical distance between the rangefinder and the target. This vertical distance is then added or subtracted from the measured horizontal distance to provide the adjusted distance.
There are different methods used to calculate slope adjustments, and the specific algorithm used can vary between different laser rangefinder models. Some algorithms may use simple trigonometric calculations, while others may incorporate more advanced mathematical models.
In recent years, there have been advancements in laser rangefinder technology that have improved the accuracy of slope adjustments. For example, some rangefinders now use inclinometers or tilt sensors to directly measure the angle of the slope. This eliminates the need for manual input of slope angle and improves the accuracy of the slope adjustment.
Additionally, some laser rangefinders now incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to continuously improve the accuracy of slope adjustments. These algorithms can analyze large amounts of data and make adjustments based on various factors such as terrain, weather conditions, and target characteristics.
Overall, laser rangefinder slope adjustments are calculated using slope compensation algorithms that take into account the angle of the slope. Advancements in technology have led to improved accuracy and the incorporation of features such as inclinometers and artificial intelligence to further enhance the performance of laser rangefinders in slope measurement.





































