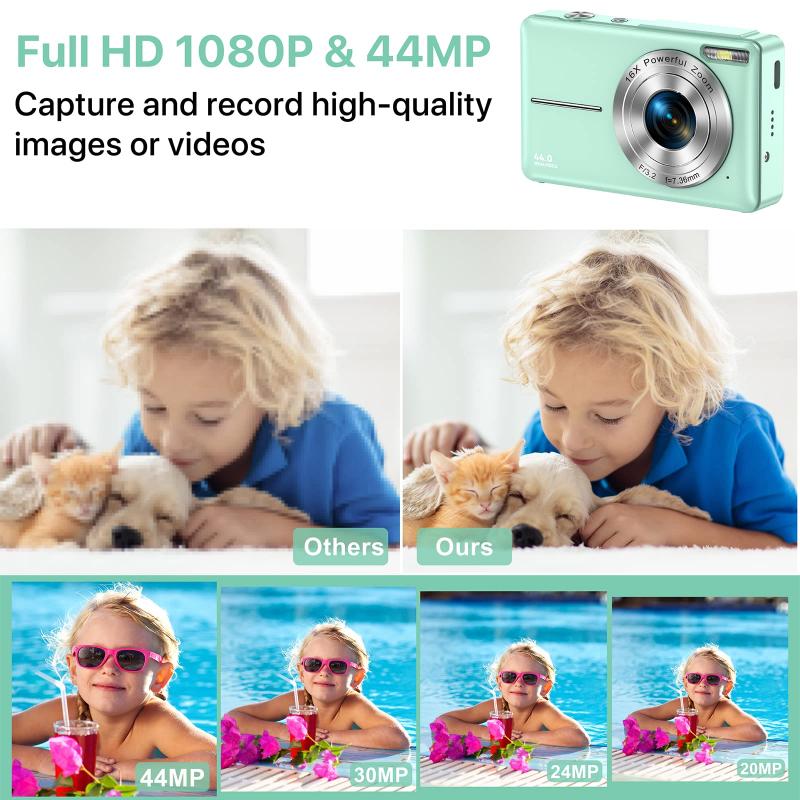
How Digital Camera Works ?
A digital camera works by capturing and recording images using electronic sensors instead of traditional film. When you press the shutter button, light enters through the camera lens and hits the image sensor, which is made up of millions of tiny photosensitive cells called pixels. Each pixel measures the intensity of light that falls on it and converts it into an electrical signal.
The electrical signals from the pixels are then processed by the camera's image processor, which applies various algorithms to enhance the image quality. The processor also converts the analog signals into digital data, which is then stored on a memory card.
Digital cameras also have various settings and features that allow users to control aspects such as exposure, focus, and white balance. Additionally, most digital cameras have an LCD screen that displays the captured image, allowing users to preview and review their photos instantly.
Overall, the combination of the lens, image sensor, image processor, and other components work together to capture, process, and store digital images in a convenient and efficient manner.
1、 Image Capture: Light enters through the lens and hits the image sensor.
How digital cameras work has evolved significantly over the years, but the fundamental principle remains the same. Image capture is the core function of a digital camera, and it involves the process of converting light into a digital image.
Light enters the camera through the lens, which focuses the light onto the image sensor. The image sensor is a crucial component that detects and records the light information. In most digital cameras, the image sensor is a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) sensor.
When light hits the image sensor, each pixel on the sensor converts the light into an electrical charge. The intensity of the charge depends on the amount of light that hits each pixel. The image sensor then converts these electrical charges into digital data, representing the colors and brightness levels of the captured image.
The latest advancements in digital camera technology have led to improvements in image sensors. CMOS sensors, in particular, have become more popular due to their lower power consumption and faster readout speeds. Additionally, manufacturers have increased the number of pixels on the image sensor, resulting in higher resolution images.
Once the digital data is captured, it is processed by the camera's image processor. The image processor applies various algorithms to enhance the image quality, reduce noise, and adjust colors and exposure levels. The processed image is then stored in the camera's memory card or internal storage.
In recent years, digital cameras have also incorporated features such as autofocus, image stabilization, and advanced shooting modes. These features utilize additional sensors and algorithms to improve the overall photography experience.
Overall, the process of how a digital camera works revolves around capturing light through the lens and converting it into a digital image using an image sensor. The latest advancements in technology have further refined this process, resulting in higher quality images and improved camera functionality.

2、 Image Processing: Sensor converts light into digital data.
How digital cameras work can be explained through the process of image processing. The primary function of a digital camera is to capture light and convert it into digital data that can be stored and manipulated. This process begins with the camera's sensor, which is typically a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) sensor.
When light enters the camera through the lens, it falls onto the sensor's surface. Each pixel on the sensor measures the intensity of the light that hits it and converts it into an electrical charge. The sensor then converts these charges into digital data by sampling and quantizing the charges into discrete values. This data is then processed by the camera's image processor, which applies various algorithms to enhance the image quality, adjust colors, and reduce noise.
The latest advancements in digital camera technology have focused on improving sensor performance. Manufacturers have been increasing the number of pixels on sensors to capture more detail and improve image resolution. Additionally, sensor technology has evolved to enhance low-light performance, dynamic range, and overall image quality.
Furthermore, advancements in image processing algorithms have allowed for more sophisticated features in digital cameras. These include face detection, image stabilization, and high dynamic range (HDR) imaging. Image processing algorithms can also be used to apply various filters and effects to images in real-time, giving users more creative control over their photographs.
In conclusion, digital cameras work by converting light into digital data through the use of sensors. The latest advancements in sensor technology and image processing algorithms have significantly improved the capabilities and image quality of digital cameras, providing users with more options and creative possibilities.

3、 Storage: Data is stored on a memory card or internal storage.
How digital cameras work has evolved significantly over the years, but the basic principle remains the same. A digital camera captures and stores images in a digital format, allowing for easy viewing, editing, and sharing. One crucial aspect of a digital camera is its storage system.
Storage: Data is stored on a memory card or internal storage. In the past, digital cameras primarily used memory cards such as CompactFlash or Secure Digital (SD) cards to store images. These cards have limited storage capacity, typically ranging from a few gigabytes to a few terabytes in the latest models. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of cameras with larger internal storage capacities, reducing the reliance on external memory cards.
The latest point of view on storage in digital cameras is the increasing use of solid-state drives (SSDs) or flash memory as internal storage. SSDs offer faster read and write speeds, allowing for quicker image processing and continuous shooting. Additionally, they are more durable and resistant to shock, making them ideal for use in rugged environments.
Furthermore, some cameras now offer the option to connect to cloud storage services, enabling users to automatically back up their images and access them from anywhere with an internet connection. This feature provides an extra layer of security and convenience, ensuring that precious memories are not lost even if the camera is damaged or lost.
In conclusion, the storage system of a digital camera plays a crucial role in capturing, storing, and accessing images. From traditional memory cards to internal storage and cloud connectivity, advancements in technology have revolutionized the way we store and manage our digital photographs.

4、 Display: Image is displayed on the camera's LCD screen.
How digital cameras work has evolved significantly over the years, but the basic principles remain the same. A digital camera captures and stores images electronically, eliminating the need for film. The process begins with the camera's lens, which focuses light onto a sensor called a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) sensor.
When light enters the camera through the lens, it hits the sensor, which converts the light into electrical signals. These signals are then processed by the camera's image processor, which applies various algorithms to enhance the image quality. The processor also converts the analog signals into digital data, which is then stored on a memory card.
One of the key components of a digital camera is the LCD screen. After the image is captured and processed, it is displayed on the camera's LCD screen. This allows the photographer to preview the image and make adjustments if necessary. The LCD screen also serves as a playback tool, allowing users to review the images they have taken.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of high-resolution LCD screens with improved color accuracy and brightness. Some cameras even feature touchscreens, making it easier for users to navigate through menus and settings.
Additionally, wireless connectivity has become a common feature in digital cameras. This allows users to transfer images directly from the camera to a computer or mobile device without the need for cables. Some cameras also offer the ability to instantly share images on social media platforms.
In conclusion, the display on a digital camera's LCD screen plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of the device. It allows photographers to preview and review their images, making it an essential component of the modern digital camera.






































There are no comments for this blog.