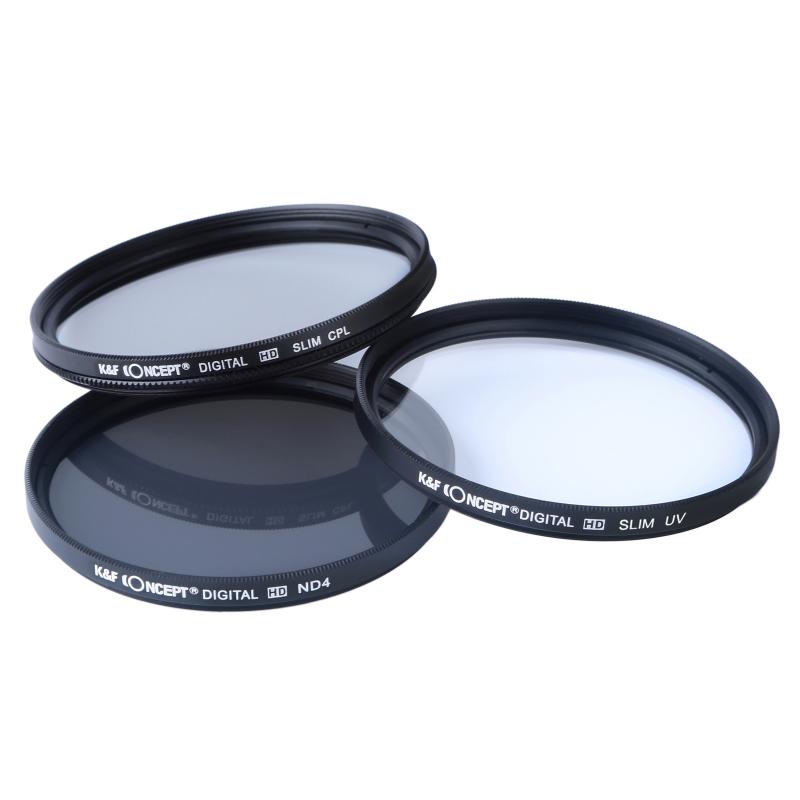
How Do Circular Polarizing Filters Work ?
Circular polarizing filters work by selectively blocking certain polarized light waves from entering the camera lens. They consist of a polarizing material that is sandwiched between two layers of glass or plastic. When light enters the filter, it is polarized in a specific direction. The filter then allows only the light waves that are polarized in a perpendicular direction to pass through, while blocking the waves that are polarized in the same direction as the filter.
This selective blocking of light waves helps to reduce glare and reflections from non-metallic surfaces such as water or glass. It also enhances color saturation and contrast in the resulting image. By rotating the filter, photographers can adjust the amount of polarization effect to achieve the desired outcome. Circular polarizing filters are commonly used in landscape photography to capture vibrant skies, reduce reflections on water surfaces, and enhance overall image quality.
1、 Light polarization and its properties
Circular polarizing filters work by selectively blocking certain polarized light waves from entering the camera lens. Light waves can vibrate in different directions, and when they vibrate in a specific plane, they are said to be polarized. Polarizing filters are designed to allow only light waves vibrating in a particular direction to pass through, while blocking light waves vibrating in other directions.
When light reflects off non-metallic surfaces such as water, glass, or foliage, it becomes partially polarized. This means that the light waves align in a specific plane, resulting in glare or reflections. Circular polarizing filters are used to reduce or eliminate this glare by blocking the polarized light waves that cause it.
The filter consists of a layer of material that contains microscopic linear polarizing molecules. These molecules are aligned in a specific direction, allowing only light waves vibrating in that direction to pass through. The filter is then mounted on a rotating ring, which allows the photographer to adjust the angle of polarization.
By rotating the filter, the photographer can selectively block or allow certain polarized light waves to enter the lens. This helps to reduce reflections and glare, enhance color saturation, and improve overall image quality. Circular polarizing filters are commonly used in landscape photography to capture vibrant colors and reduce unwanted reflections from water or glass.
It is important to note that circular polarizing filters are different from linear polarizing filters. Circular polarizing filters are designed specifically for use with autofocus cameras, as they do not interfere with the camera's autofocus and metering systems. Linear polarizing filters, on the other hand, can cause issues with autofocus and metering in modern cameras.
In recent years, there have been advancements in polarizing filter technology. Some filters now incorporate multiple layers of polarizing material, allowing for even greater control over the polarization effect. Additionally, some filters are now designed to be more resistant to water, oil, and scratches, making them more durable and easier to clean.
Overall, circular polarizing filters are a valuable tool for photographers, allowing them to control and manipulate light polarization to achieve desired effects in their images.

2、 Circular polarization and its distinction from linear polarization
Circular polarizing filters work by selectively blocking certain polarized light waves from entering the camera lens. They consist of a layer of material that contains microscopic linear polarizing filters arranged in a circular pattern. This circular pattern allows the filter to rotate freely on the lens, which is crucial for achieving the desired effect.
When light enters the filter, it encounters the linear polarizing filters. These filters are designed to only allow light waves oscillating in a specific direction to pass through, while blocking light waves oscillating in other directions. As a result, the filter only permits light waves that are linearly polarized in a specific direction to pass through.
However, circular polarizing filters take this a step further. They have an additional quarter-wave plate that converts the linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light. Circularly polarized light consists of two perpendicular components rotating in opposite directions. This conversion is necessary because many modern cameras and auto-focus systems require circularly polarized light to function properly.
The distinction between circular polarization and linear polarization lies in the way the light waves are oriented. Linearly polarized light waves oscillate in a single plane, while circularly polarized light waves rotate in a circular motion. This circular motion allows the light to maintain its polarization even after passing through the filter and bouncing off various surfaces.
The latest point of view on circular polarizing filters is that they are essential tools for photographers, especially when shooting outdoors. They help reduce glare and reflections from non-metallic surfaces such as water or glass, enhance color saturation, and improve overall image quality. Additionally, circular polarizing filters can also darken skies, making clouds stand out more prominently.
In conclusion, circular polarizing filters work by selectively blocking certain polarized light waves and converting linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light. This distinction from linear polarization allows photographers to achieve various creative effects and improve the quality of their images.

3、 Mechanism of circular polarizing filters
Circular polarizing filters work by selectively blocking certain polarized light waves from entering the camera lens. Light waves can vibrate in different directions, and when they are reflected off a non-metallic surface such as water or glass, they become polarized. This polarization causes glare and reflections, which can significantly reduce the clarity and contrast of an image.
Circular polarizing filters consist of a layer of material that contains microscopic linear polarizing filters. These filters are aligned in a specific direction, allowing only light waves vibrating in that direction to pass through. When the filter is rotated, it aligns with the polarized light waves in the scene, blocking them and reducing glare and reflections.
The mechanism of circular polarizing filters involves two main components: a linear polarizer and a quarter-wave plate. The linear polarizer filters out the unwanted polarized light waves, while the quarter-wave plate converts the linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light. This circularly polarized light then passes through the linear polarizer again, allowing only a specific orientation of light waves to reach the camera sensor.
The latest point of view on circular polarizing filters is that they are essential tools for photographers, especially in outdoor and landscape photography. They not only reduce glare and reflections but also enhance color saturation and contrast, resulting in more vibrant and detailed images. Additionally, circular polarizing filters can also improve the overall image quality by reducing atmospheric haze and increasing the clarity of distant objects.
In conclusion, circular polarizing filters work by selectively blocking polarized light waves, reducing glare and reflections. They consist of a linear polarizer and a quarter-wave plate, which together convert linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light. The latest perspective highlights the importance of circular polarizing filters in enhancing image quality and achieving desired photographic effects.

4、 Function of the quarter-wave plate in circular polarizers
Circular polarizing filters work by selectively blocking certain polarized light waves from entering the camera lens. They consist of two main components: a linear polarizer and a quarter-wave plate.
The linear polarizer is the first element of the filter and is responsible for blocking light waves that are polarized in a specific direction. It only allows light waves vibrating in a single plane to pass through, while blocking waves vibrating in other planes. This linear polarizer helps reduce glare and unwanted reflections from non-metallic surfaces such as water or glass.
The quarter-wave plate is the second component and is placed behind the linear polarizer. Its function is to convert linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light. It achieves this by delaying one of the two perpendicular components of the linearly polarized light by a quarter of a wavelength. This phase shift causes the light waves to rotate as they pass through the quarter-wave plate, resulting in circular polarization.
Circular polarization is important in photography because it allows the camera to autofocus and meter accurately. When light passes through the quarter-wave plate, it becomes circularly polarized and can be transmitted through the camera's autofocus and metering sensors without losing its polarization state. This is crucial for modern autofocus systems that rely on polarized light to accurately detect and track subjects.
In recent years, there have been advancements in circular polarizing filters, such as the use of multi-coatings to enhance light transmission and reduce reflections. Additionally, some filters now incorporate nano-coatings that repel water, oil, and dirt, making them easier to clean and maintain.
Overall, circular polarizing filters are essential tools for photographers, allowing them to control reflections, enhance colors, and improve image quality in various lighting conditions.