How Does A Digital Microscope Work ?
A digital microscope works by using a combination of optics and digital imaging technology to magnify and capture images of small objects. It typically consists of a lens system, a light source, and a digital camera. The lens system magnifies the object being observed, allowing for a closer look at its details. The light source illuminates the object, enhancing visibility. The digital camera captures the magnified image and converts it into a digital format. This image can then be displayed on a computer screen or other digital device, allowing for easy viewing and analysis. Some digital microscopes also offer additional features such as adjustable magnification levels, image capture and storage capabilities, and the ability to connect to a computer for further analysis or sharing of images.
1、 Optical magnification using lenses and light sources.
A digital microscope is a modern tool that allows for the magnification and visualization of objects at a microscopic level. It works by utilizing a combination of optical magnification using lenses and light sources, along with digital imaging technology.
The basic principle behind a digital microscope is similar to that of a traditional optical microscope. It uses lenses to magnify the object being observed, allowing for a closer look at its details. However, instead of using eyepieces to view the magnified image, a digital microscope captures the image using a digital camera and displays it on a computer screen or other digital device.
The magnification process begins with the objective lens, which is responsible for capturing the light reflected or transmitted through the object. This light is then focused onto the image sensor of the digital camera. The image sensor converts the light into an electrical signal, which is then processed and displayed as a digital image.
One of the advantages of a digital microscope is the ability to capture and store images or videos of the magnified objects. This allows for easy documentation, analysis, and sharing of the observed samples. Additionally, digital microscopes often come with software that enables further image enhancement, measurement, and analysis.
In recent years, advancements in digital microscope technology have led to the development of high-resolution cameras and improved image sensors. These advancements have resulted in higher image quality and increased magnification capabilities. Some digital microscopes also incorporate features such as autofocus, image stitching, and 3D imaging, further enhancing their functionality.
Overall, a digital microscope combines the principles of optical magnification with digital imaging technology to provide a powerful tool for scientific research, education, and various other applications.

2、 Digital image capture through a camera or sensor.
A digital microscope is a modern tool that allows users to capture and view magnified images of objects or specimens on a computer screen. It works by utilizing a combination of optics, digital imaging technology, and software.
The basic principle behind a digital microscope is the same as that of a traditional optical microscope. Light passes through the specimen and is magnified by a series of lenses. However, instead of using eyepieces to view the magnified image, a digital microscope uses a camera or sensor to capture the image and display it on a computer screen.
The camera or sensor in a digital microscope captures the light that passes through the specimen and converts it into a digital signal. This digital signal is then processed by the microscope's software, which enhances the image and allows for various adjustments such as zooming, focusing, and adjusting brightness and contrast.
The latest advancements in digital microscope technology have led to the development of high-resolution cameras and sensors, allowing for even greater magnification and image clarity. Additionally, some digital microscopes now offer features such as 3D imaging, fluorescence imaging, and real-time video capture.
Furthermore, digital microscopes often come with additional features like image analysis software, which enables users to measure and analyze the captured images. This can be particularly useful in scientific research, quality control, and educational settings.
In summary, a digital microscope works by capturing the light passing through a specimen using a camera or sensor, converting it into a digital signal, and displaying the magnified image on a computer screen. The latest advancements in digital microscope technology have greatly improved image quality and introduced new features, making them versatile tools in various fields.

3、 Image processing and enhancement for improved visibility.
A digital microscope works by utilizing advanced imaging technology to capture and display magnified images of objects. It combines the principles of traditional microscopy with digital imaging to provide enhanced visibility and analysis capabilities.
The basic working principle of a digital microscope involves capturing light from the object being observed and converting it into digital signals. This is achieved through a combination of lenses, sensors, and image processing algorithms. The lenses in the microscope system focus the light onto a sensor, which converts the light into electrical signals. These signals are then processed and converted into a digital image that can be displayed on a computer or other digital device.
Image processing and enhancement play a crucial role in improving the visibility and quality of the captured images. Advanced algorithms are used to enhance contrast, adjust brightness and color, reduce noise, and improve overall image clarity. These techniques help to reveal finer details and make the images more visually appealing and informative.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in digital microscope technology. For example, some digital microscopes now incorporate features such as 3D imaging, fluorescence imaging, and real-time video capture. These advancements have expanded the capabilities of digital microscopy and made it a valuable tool in various fields, including biology, medicine, materials science, and forensics.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms has opened up new possibilities for digital microscopy. AI-powered image analysis algorithms can automatically detect and classify objects, measure dimensions, and identify patterns or anomalies. This enables faster and more accurate analysis of samples, making digital microscopes even more valuable in research and industrial applications.
Overall, the working of a digital microscope involves a combination of optics, sensors, and image processing techniques to capture and enhance images for improved visibility and analysis. The latest advancements in technology continue to push the boundaries of digital microscopy, making it an indispensable tool in scientific research and various industries.
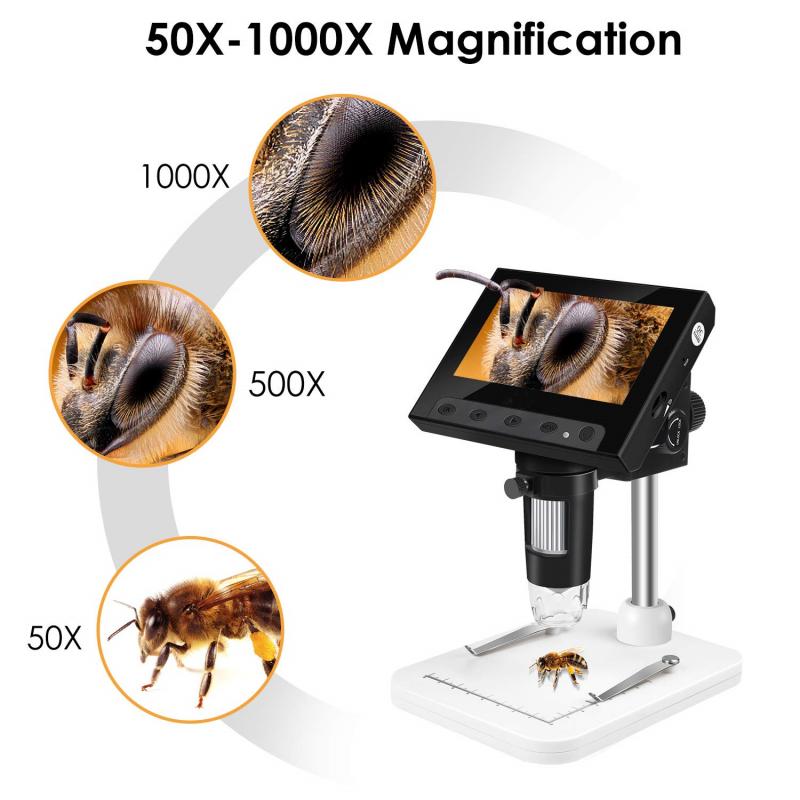

4、 Display and analysis of the captured images on a screen.
A digital microscope is a modern tool that allows for the magnification and visualization of objects at a microscopic level. It works by utilizing advanced imaging technology to capture high-resolution images of the specimen and displaying them on a screen for analysis.
The process begins with the placement of the specimen under the microscope's lens. The lens system of a digital microscope consists of multiple lenses that work together to magnify the object. These lenses are designed to provide a high level of clarity and detail, allowing for precise examination of the specimen.
Once the specimen is in focus, the digital microscope uses a digital camera to capture images of the magnified object. The camera is equipped with a sensor that converts the light signals into digital data. This data is then processed by the microscope's software, which enhances the image quality and adjusts the color and contrast as needed.
The captured images are then displayed on a screen, which can be a computer monitor or a dedicated display unit. This allows for real-time observation and analysis of the specimen. The digital microscope often includes additional features such as zooming, measurement tools, and image capturing capabilities, which further enhance the user's ability to examine and document the specimen.
From a latest point of view, advancements in digital microscope technology have led to the development of more compact and portable devices. These portable digital microscopes offer the convenience of being able to capture and analyze microscopic images on the go. Additionally, some digital microscopes now incorporate advanced imaging techniques such as fluorescence microscopy, which allows for the visualization of specific structures or molecules within the specimen.
In conclusion, a digital microscope works by capturing high-resolution images of a magnified specimen using a digital camera and displaying them on a screen for analysis. The latest advancements in digital microscope technology have made these devices more portable and have expanded their capabilities, allowing for more detailed and specialized examination of microscopic objects.