How Does A Variable Neutral Density Filter Work ?
A variable neutral density (ND) filter is a type of camera filter that allows you to adjust the amount of light entering the lens without affecting the color or quality of the image. It consists of two polarizing filters that are stacked together and can be rotated relative to each other. By rotating the filters, you can control the amount of light that passes through them.
The first polarizing filter blocks a certain amount of light, while the second filter can be rotated to either block or allow more light to pass through. When the filters are aligned, they allow maximum light transmission, and as they are rotated relative to each other, the amount of light passing through decreases. This adjustable light reduction is what makes the variable ND filter versatile and useful in various photography situations, such as capturing long exposures or achieving a shallow depth of field in bright conditions.
1、 Variable Neutral Density Filter: Definition and Function
A variable neutral density (ND) filter is a versatile tool used in photography and videography to control the amount of light entering the camera lens. It consists of two polarizing filters that can be rotated independently, allowing the user to adjust the density of the filter and thus control the exposure.
The primary function of a variable ND filter is to reduce the amount of light reaching the camera sensor without affecting the color or quality of the image. This is achieved by rotating the front and rear polarizing filters in opposite directions. When the filters are aligned, they allow maximum light transmission, but as they are rotated, they start to block the light, resulting in a darker image.
The variable ND filter works by selectively blocking certain wavelengths of light. As the filters rotate, they align or cross-polarize the light waves, allowing only a fraction of the light to pass through. This adjustable light reduction enables photographers and videographers to achieve longer exposure times, wider apertures, or use slower shutter speeds even in bright conditions.
The latest advancements in variable ND filters include improved optical coatings to minimize reflections and flare, as well as enhanced durability and ease of use. Some filters also feature a range of stops or density markings, allowing for precise adjustments and repeatability.
Overall, a variable ND filter is a valuable tool for photographers and videographers, providing them with greater creative control over exposure and allowing them to capture stunning images in various lighting conditions.

2、 Optical Principles Behind Variable Neutral Density Filters
A variable neutral density (ND) filter is a versatile tool used in photography and videography to control the amount of light entering the camera lens. It consists of two polarizing filters that are stacked together and can be rotated relative to each other. The optical principles behind variable ND filters involve the manipulation of light polarization and the reduction of light intensity.
When light passes through the first polarizing filter, it becomes polarized in a specific direction. As the light travels through the second polarizing filter, which is oriented perpendicular to the first, it encounters resistance. By rotating the second filter, the amount of resistance can be adjusted, allowing more or less light to pass through.
The variable ND filter works by selectively blocking certain wavelengths of light, resulting in a reduction of overall light intensity. This allows photographers and videographers to achieve longer exposure times or wider apertures in bright conditions without overexposing the image. It also enables the use of slower shutter speeds, which can create motion blur effects or smooth out water and clouds.
The latest advancements in variable ND filters have focused on improving image quality and reducing color cast. High-quality filters use multi-coating techniques to minimize reflections and flare, ensuring accurate color reproduction. Additionally, some filters employ advanced materials and manufacturing processes to maintain consistent density across the entire filter surface, avoiding any uneven light reduction.
In conclusion, the optical principles behind variable ND filters involve the manipulation of light polarization and the reduction of light intensity. By rotating two polarizing filters, photographers and videographers can control the amount of light entering the camera lens, allowing for creative exposure and aperture settings in various lighting conditions.
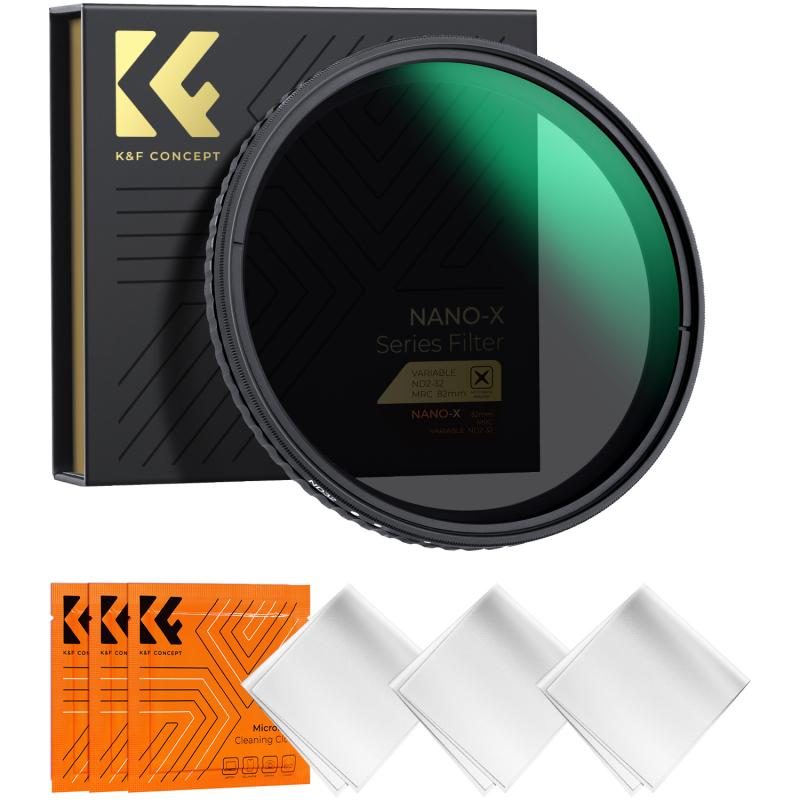

3、 Construction and Components of Variable Neutral Density Filters
A variable neutral density (ND) filter is a versatile tool used in photography and videography to control the amount of light entering the camera lens. It consists of two polarizing filters that are stacked together and can be rotated relative to each other. The construction and components of variable ND filters play a crucial role in their functionality.
The two polarizing filters are made of high-quality optical glass and are mounted in a rotating frame. The front filter is fixed, while the rear filter can be rotated to adjust the density of the filter. As the rear filter is rotated, it changes the angle at which light passes through the filters, thus altering the amount of light that reaches the camera sensor.
The polarizing filters work by selectively blocking certain wavelengths of light. When the filters are aligned, they allow maximum light transmission, resulting in a lower density. As the rear filter is rotated, it starts to block more light, increasing the density. This allows photographers and videographers to have precise control over the exposure by adjusting the amount of light entering the lens.
Variable ND filters are particularly useful in situations where the lighting conditions change rapidly or when shooting in bright environments. They eliminate the need for carrying multiple fixed ND filters of different densities, providing convenience and flexibility.
It is important to note that variable ND filters may introduce some color cast or image degradation, especially at extreme density settings. However, advancements in filter technology have significantly reduced these issues in modern variable ND filters.
In conclusion, the construction and components of variable ND filters, including the two polarizing filters and their rotating frame, allow photographers and videographers to control the amount of light entering the lens. This versatility makes them an essential tool for achieving the desired exposure in various shooting conditions.

4、 Variable Neutral Density Filter Operation and Adjustment Mechanisms
A variable neutral density (ND) filter is a versatile tool used in photography and videography to control the amount of light entering the camera lens. It consists of two polarizing filters that are stacked together and can be rotated relative to each other. The rotation of these filters allows for the adjustment of the amount of light that passes through the lens.
The first polarizing filter is fixed and acts as a base. The second filter is rotatable and can be adjusted to control the intensity of light passing through the lens. When the two filters are aligned, they allow maximum light transmission, resulting in a low ND value. As the second filter is rotated, it starts to block some of the light, gradually increasing the ND value.
The variable ND filter works by selectively blocking certain wavelengths of light. When light passes through the first polarizing filter, it becomes polarized in a specific direction. As it reaches the second filter, the orientation of the polarized light determines how much of it is allowed to pass through. By rotating the second filter, the orientation of the polarized light changes, thus controlling the amount of light that reaches the camera sensor.
The latest advancements in variable ND filters include improved coatings to reduce reflections and flare, as well as better color accuracy and image quality. Some filters also feature a range scale or markings to help photographers and videographers precisely adjust the ND value.
Overall, a variable ND filter provides photographers and videographers with a convenient and flexible way to control exposure in various lighting conditions, allowing for creative effects such as motion blur or shallow depth of field.