How Does Slope Rangefinder Work ?
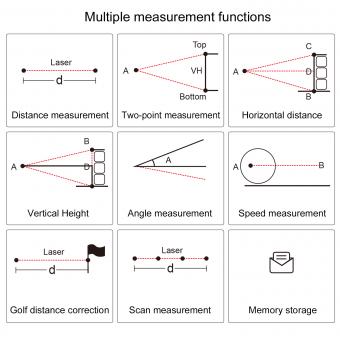
A slope rangefinder, also known as a laser rangefinder with slope compensation, works by using a laser beam to measure the distance between the device and a target object. It calculates the slope or incline of the terrain and adjusts the distance measurement accordingly to provide an accurate reading. This is done by incorporating an inclinometer or tilt sensor into the rangefinder, which detects the angle of elevation or decline. The device then uses this information to calculate the actual horizontal distance to the target, taking into account the slope. This feature is particularly useful in golfing and hunting, where knowing the adjusted distance can help in making more precise shots.
1、 Optical principles of slope rangefinders
A slope rangefinder is a device used to measure the slope or gradient of a surface. It utilizes optical principles to determine the angle of inclination between the device and the surface being measured.
The basic working principle of a slope rangefinder involves the use of a laser or infrared beam emitted from the device. This beam is directed towards the surface and reflected back to the rangefinder. By measuring the time it takes for the beam to travel to the surface and back, the device can calculate the distance between itself and the surface.
To determine the slope, the rangefinder also measures the vertical distance between the device and the surface. This is typically done using a built-in inclinometer or by analyzing the change in position of the reflected beam over a known distance.
By combining the distance measurement with the vertical distance measurement, the slope rangefinder can calculate the angle of inclination or slope of the surface. This information is then displayed on a screen or provided as a numerical value.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more accurate and compact slope rangefinders. Some devices now incorporate multiple sensors and algorithms to improve accuracy and reduce errors. Additionally, the use of digital signal processing techniques has allowed for faster and more precise calculations.
Overall, slope rangefinders provide a convenient and efficient way to measure slopes in various applications such as construction, surveying, and outdoor sports. They offer a reliable and accurate method for determining the angle of inclination of a surface, aiding in decision-making and ensuring safety in various fields.
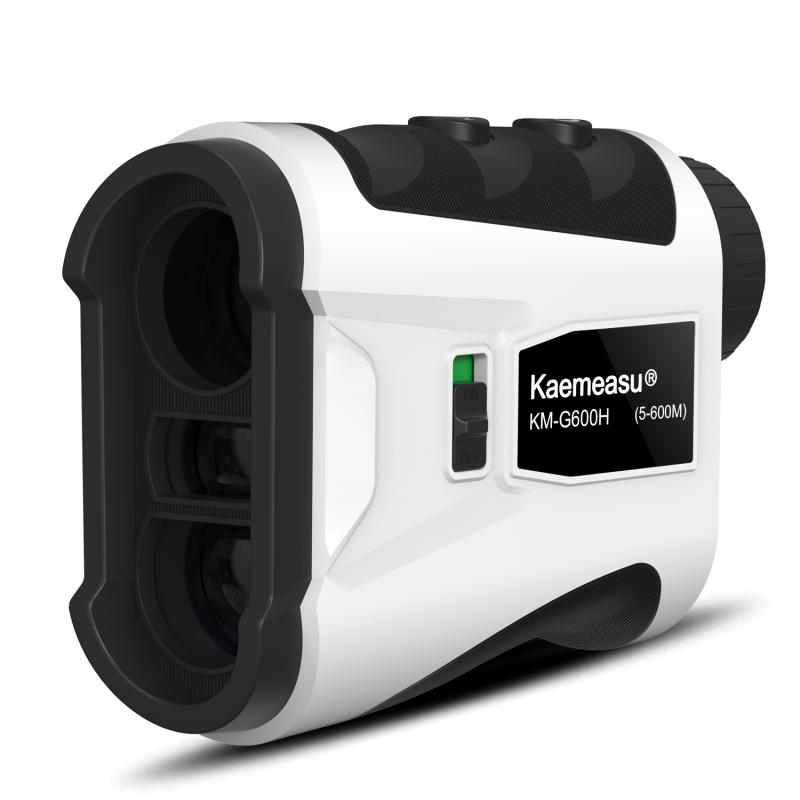

2、 Laser technology in slope rangefinders
A slope rangefinder is a device used to measure the slope or incline of a particular surface or terrain. It utilizes laser technology to accurately determine the angle of the slope.
The basic principle behind the operation of a slope rangefinder is the measurement of the distance between the device and the target surface. The rangefinder emits a laser beam towards the target, and the time it takes for the beam to bounce back to the device is measured. By knowing the speed of light, the device can calculate the distance between itself and the target.
To determine the slope, the rangefinder also measures the change in height between the device and the target. This is done by comparing the initial height reading with the final height reading after the laser beam has bounced back. By combining the distance and height measurements, the device can calculate the slope angle using trigonometry.
The latest advancements in laser technology have greatly improved the accuracy and precision of slope rangefinders. These devices now have the ability to measure slopes with high levels of accuracy, often within a few degrees. Additionally, some slope rangefinders also incorporate GPS technology, allowing for more precise measurements by taking into account the user's location and elevation.
Overall, laser technology in slope rangefinders has revolutionized the way slopes are measured. These devices provide quick and accurate slope measurements, making them invaluable tools for a variety of applications such as construction, landscaping, and outdoor sports.

3、 Calculation algorithms used in slope rangefinders
A slope rangefinder is a device used to measure the slope or gradient of a surface. It is commonly used in various fields such as construction, surveying, and sports. The device works by utilizing calculation algorithms to determine the angle of inclination between the device and the surface being measured.
The calculation algorithms used in slope rangefinders typically involve the use of trigonometry. The device measures the vertical distance and the horizontal distance between two points on the surface. By using these measurements, the device can calculate the angle of inclination using trigonometric functions such as tangent or arctangent.
In more advanced slope rangefinders, additional sensors and technologies may be incorporated to enhance accuracy and precision. For example, some devices may use accelerometers to measure the tilt or inclination of the device itself, which can then be used to calculate the slope of the surface.
The latest advancements in slope rangefinders include the use of laser technology. Laser rangefinders can provide highly accurate distance measurements, which can then be used in conjunction with the device's calculation algorithms to determine the slope. This combination of laser technology and calculation algorithms allows for more precise and efficient slope measurements.
Overall, slope rangefinders work by utilizing calculation algorithms, often involving trigonometry, to determine the angle of inclination between the device and the surface being measured. The incorporation of additional sensors and technologies, such as accelerometers and laser rangefinders, further enhances the accuracy and efficiency of these devices.

4、 Integration of slope rangefinders with other devices
A slope rangefinder is a device used to measure the slope or gradient of a surface. It works by utilizing various sensors and algorithms to calculate the angle of inclination between the device and the surface being measured. The most common type of slope rangefinder is a digital inclinometer, which uses an accelerometer to measure changes in the device's orientation.
The device typically consists of a display screen that shows the measured slope angle, as well as buttons or controls to calibrate and adjust the settings. Some slope rangefinders also have additional features such as a laser pointer or a built-in compass.
Integration of slope rangefinders with other devices has become increasingly popular in recent years. This integration allows for more advanced functionality and improved accuracy in measuring slopes. For example, slope rangefinders can be integrated with smartphones or tablets, enabling users to capture and store slope measurements digitally. This integration also allows for the use of GPS technology to provide precise location information along with the slope measurements.
Furthermore, slope rangefinders can be integrated with other surveying or mapping equipment, such as total stations or GPS receivers. This integration enables the direct transfer of slope measurements to these devices, streamlining the data collection process and improving overall efficiency.
In addition, advancements in technology have led to the development of wireless connectivity options for slope rangefinders. This allows for real-time data sharing and remote control capabilities, making it easier for multiple users to collaborate on a project or for supervisors to monitor progress from a distance.
Overall, the integration of slope rangefinders with other devices has greatly enhanced their functionality and usability. It has opened up new possibilities for data collection, analysis, and collaboration in various fields such as construction, engineering, and land surveying.






























There are no comments for this blog.