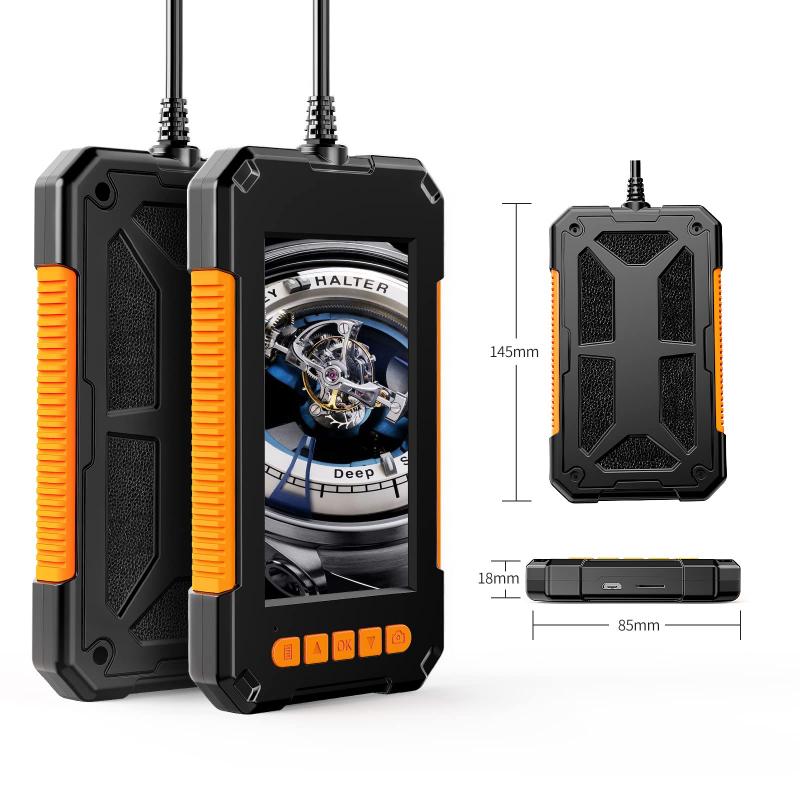
How Endoscope Works ?
An endoscope is a medical device used to examine the inside of the body. It consists of a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and camera at the end. The endoscope is inserted into the body through a natural opening or a small incision. The camera sends images to a monitor, allowing the doctor to see inside the body.
The endoscope is typically used to examine the digestive tract, respiratory system, urinary tract, and joints. It can also be used to perform minimally invasive surgeries.
To use an endoscope, the doctor first numbs the area where the endoscope will be inserted. The endoscope is then inserted into the body and guided to the area of interest. The camera sends images to a monitor, allowing the doctor to see inside the body and guide the endoscope to the correct location.
The endoscope can be used to take biopsies, remove polyps, and perform other procedures. After the procedure is complete, the endoscope is removed from the body.
1、 Optical System
An endoscope is a medical device that is used to examine the internal organs and tissues of the human body. The optical system is a critical component of an endoscope, as it allows the physician to see inside the body. The optical system consists of a series of lenses, mirrors, and fibers that transmit light and images from the body to the physician's eye or a camera.
The endoscope's optical system works by using a light source to illuminate the area being examined. The light is transmitted through a fiber optic cable to the end of the endoscope, where it is directed into the body. The light reflects off the internal organs and tissues and is transmitted back through the endoscope to the physician's eye or camera.
The lenses and mirrors in the endoscope's optical system are designed to magnify and focus the image, allowing the physician to see the internal structures of the body in detail. The fibers in the endoscope's optical system are also designed to transmit the image without distortion or loss of clarity.
The latest point of view on endoscope technology is the development of high-definition and 3D imaging systems. These systems use advanced optics and digital technology to provide physicians with even more detailed and accurate images of the internal structures of the body. This technology has revolutionized the field of endoscopy, allowing physicians to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions with greater precision and accuracy.

2、 Light Source
A light source is an essential component of an endoscope, which is a medical device used to examine the internal organs and tissues of the body. The light source provides illumination to the endoscope's camera, allowing doctors to see inside the body. The light source is typically located outside the body and connected to the endoscope via a fiber optic cable.
The light source used in endoscopes is usually a high-intensity LED or xenon bulb. The light is transmitted through the fiber optic cable to the endoscope's camera, which captures the images and sends them to a monitor for viewing. The light source can be adjusted to provide different levels of illumination, depending on the area being examined.
The latest point of view on endoscope light sources is the use of LED technology. LED lights are more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan than traditional xenon bulbs. They also produce less heat, which reduces the risk of tissue damage during the examination. Additionally, LED lights can be adjusted to provide different colors of light, which can be useful in identifying specific tissues or abnormalities.
In conclusion, the light source is a crucial component of an endoscope, providing the necessary illumination for doctors to examine the internal organs and tissues of the body. The latest advancements in LED technology have improved the efficiency and safety of endoscopes, making them an increasingly valuable tool in modern medicine.

3、 Fiber Optic Cable
How Endoscope Works with Fiber Optic Cable:
Endoscopes are medical devices that allow doctors to see inside the human body without making large incisions. They are used for a variety of procedures, including colonoscopies, bronchoscopies, and laparoscopies. One of the key components of an endoscope is the fiber optic cable.
Fiber optic cables are made up of thin strands of glass or plastic that transmit light signals over long distances. In an endoscope, the fiber optic cable is used to transmit light from a source outside the body to the tip of the endoscope. The light is then reflected off the tissue inside the body and back through the cable to a camera or eyepiece, allowing the doctor to see the internal organs or tissues.
The latest point of view on endoscopes with fiber optic cables is the development of new materials and technologies that improve the image quality and flexibility of the devices. For example, some endoscopes now use high-definition cameras and advanced image processing software to provide clearer and more detailed images. Others use flexible fiber optic cables that can bend and twist to navigate through the body's curves and corners.
In addition, researchers are exploring the use of new materials for fiber optic cables, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene, which could offer even greater flexibility and durability. These advancements are helping to make endoscopes safer, more effective, and more comfortable for patients, while also improving the accuracy and precision of medical diagnoses and treatments.

4、 Camera System
An endoscope is a medical device that is used to examine the inside of the body. It is a camera system that consists of a long, thin tube with a camera and light source at the end. The camera sends images to a monitor, allowing doctors to see inside the body without making large incisions.
The endoscope works by using a series of lenses and mirrors to transmit light and images from the tip of the scope to the monitor. The light source at the end of the scope illuminates the area being examined, while the camera captures images and sends them to the monitor. The images can be viewed in real-time, allowing doctors to see any abnormalities or issues that may be present.
The latest advancements in endoscope technology have led to the development of high-definition cameras and 3D imaging capabilities. This allows for even greater detail and accuracy in diagnosing and treating medical conditions.
In addition, some endoscopes now have the ability to perform minimally invasive procedures, such as removing polyps or taking tissue samples for biopsy. This reduces the need for more invasive surgeries and can lead to faster recovery times for patients.
Overall, the endoscope is a crucial tool in modern medicine, allowing doctors to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions with minimal invasiveness and maximum accuracy.