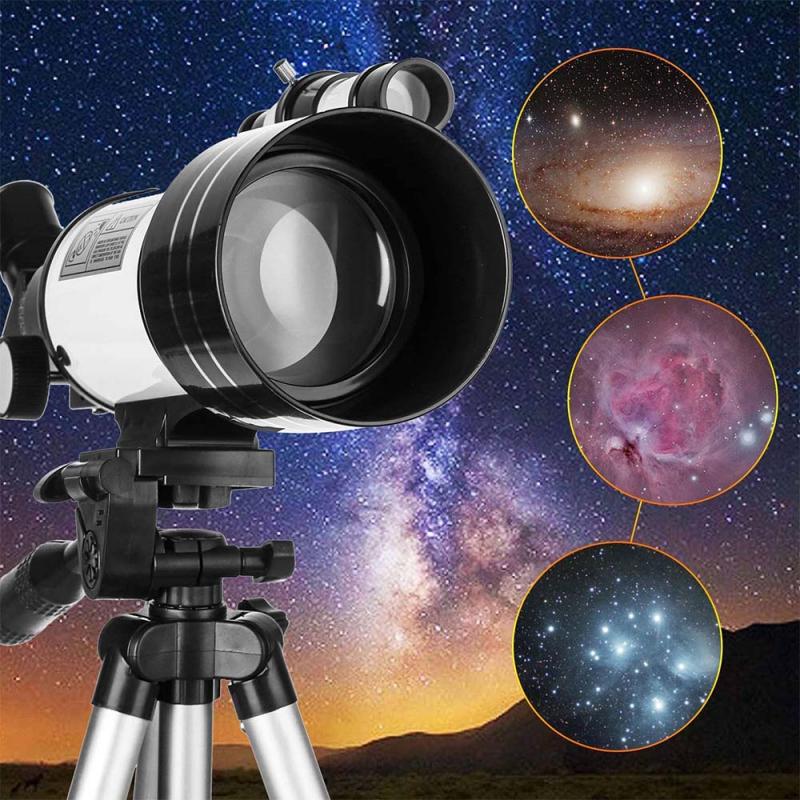
How To Buy A Telescope ?
To buy a telescope, you can start by researching different types and brands of telescopes to determine which one suits your needs and budget. Consider factors such as the telescope's aperture, focal length, and mount type. You can find telescopes at specialized astronomy stores, online retailers, or even second-hand through classified ads or online marketplaces. Read reviews and compare prices to make an informed decision. Once you have chosen a telescope, proceed with the purchase by following the retailer's instructions, which may involve adding the item to your cart, providing shipping information, and making a payment.
1、 Types of telescopes: Refractor, reflector, compound, and catadioptric telescopes.
Types of telescopes: Refractor, reflector, compound, and catadioptric telescopes.
If you are interested in exploring the wonders of the night sky, buying a telescope is a great investment. However, with so many options available, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. Here is a guide on how to buy a telescope and the different types available.
1. Determine your budget: Telescopes can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand. Decide how much you are willing to spend, keeping in mind that higher quality telescopes generally provide better views.
2. Research the different types: There are four main types of telescopes to choose from. Refractor telescopes use lenses to gather and focus light, while reflector telescopes use mirrors. Compound telescopes combine lenses and mirrors, and catadioptric telescopes use a combination of lenses and mirrors to fold the light path. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, so research which one suits your needs and preferences.
3. Consider the aperture: The aperture, or the diameter of the telescope's main lens or mirror, determines how much light the telescope can gather. A larger aperture allows for better image quality and the ability to see fainter objects.
4. Portability and ease of use: Consider where you will be using the telescope and how easy it is to transport. If you plan on traveling with it, a smaller and more portable option may be preferable.
5. Read reviews and seek advice: Look for reviews from reputable sources and seek advice from experienced astronomers or astronomy clubs. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their own experiences.
6. Purchase from a reputable dealer: Ensure that you buy from a reputable dealer who offers good customer service and warranties.
Remember, the best telescope for you will depend on your specific needs and interests. Take your time to research and make an informed decision. Happy stargazing!
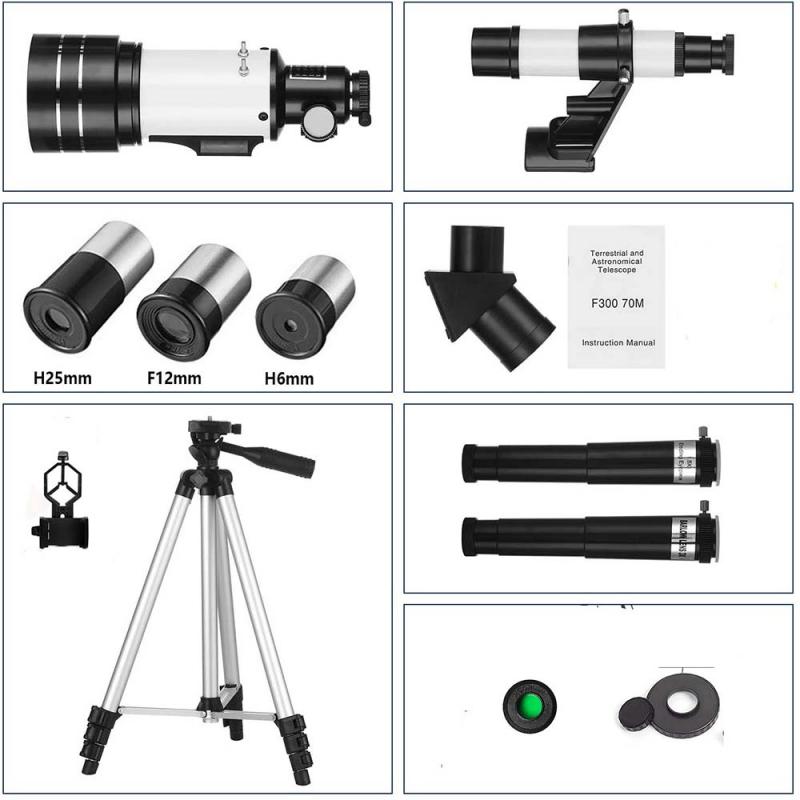

2、 Aperture size: Consider the diameter of the telescope's primary mirror or lens.
Aperture size: Consider the diameter of the telescope's primary mirror or lens.
When it comes to buying a telescope, one of the most important factors to consider is the aperture size. The aperture refers to the diameter of the telescope's primary mirror or lens, and it plays a crucial role in determining the telescope's light-gathering ability and overall image quality.
A larger aperture allows more light to enter the telescope, resulting in brighter and more detailed images. It also enables the telescope to gather more light from faint celestial objects, making it ideal for observing deep-sky objects like galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters. On the other hand, a smaller aperture may limit the telescope's ability to capture faint objects and may result in dimmer images.
The choice of aperture size depends on your observing goals and budget. If you are primarily interested in observing the Moon, planets, and brighter objects like star clusters, a telescope with a smaller aperture (around 70-90mm) can provide satisfactory views. These telescopes are often more portable and affordable, making them a good choice for beginners or those on a tight budget.
However, if you have a keen interest in deep-sky objects and want to explore the wonders of the universe in greater detail, a larger aperture telescope (around 150mm or more) is recommended. These telescopes offer superior light-gathering capabilities, allowing you to observe fainter objects and reveal more intricate details.
It's worth noting that larger aperture telescopes tend to be bulkier, heavier, and more expensive. Therefore, it's important to strike a balance between your observing goals, budget, and practical considerations such as portability and storage space.
In recent years, technological advancements have made telescopes with larger apertures more accessible and affordable. With the advent of computerized mounts and improved manufacturing techniques, it is now possible to find telescopes with larger apertures at relatively reasonable prices.
When buying a telescope, it's crucial to consider the aperture size as it directly impacts the quality of your observations. Assess your observing goals, budget, and practical requirements to determine the ideal aperture size for your needs. Remember, a larger aperture can open up a whole new world of celestial wonders, but it's important to find the right balance that suits your individual circumstances.
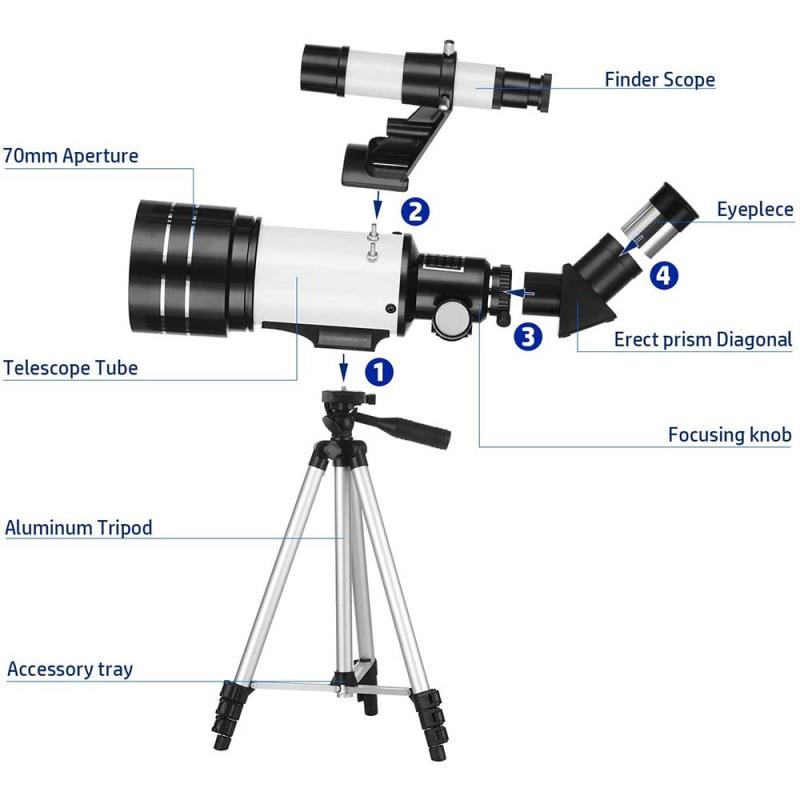
3、 Mount type: Equatorial or alt-azimuth mount for stability and tracking.
Mount type: Equatorial or alt-azimuth mount for stability and tracking.
When it comes to buying a telescope, one of the most important factors to consider is the mount type. The mount is responsible for providing stability and tracking capabilities to ensure a smooth viewing experience. There are two main types of mounts to choose from: equatorial and alt-azimuth.
An equatorial mount is designed to align with the Earth's axis, allowing for easy tracking of celestial objects as they move across the sky. This type of mount is ideal for astrophotography and observing objects that require long exposure times. Equatorial mounts can be motorized, which further enhances tracking accuracy and convenience. However, they tend to be more complex to set up and operate, requiring some knowledge of celestial coordinates.
On the other hand, alt-azimuth mounts offer simplicity and ease of use. They move in vertical (altitude) and horizontal (azimuth) directions, making them intuitive for beginners. Alt-azimuth mounts are great for observing the moon, planets, and other bright objects in the sky. They are also more portable and lightweight compared to equatorial mounts, making them suitable for on-the-go stargazing.
The choice between equatorial and alt-azimuth mounts ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences. If you are interested in astrophotography or tracking faint deep-sky objects, an equatorial mount would be the better option. However, if you prioritize simplicity and portability, an alt-azimuth mount would be more suitable.
It's worth noting that recent advancements in technology have led to the development of computerized mounts that combine the benefits of both types. These computerized mounts, often referred to as GoTo mounts, utilize GPS and databases of celestial objects to automatically locate and track targets. They are a popular choice among both beginners and experienced astronomers due to their convenience and accuracy.
In conclusion, when buying a telescope, consider the mount type that best suits your needs. Equatorial mounts are ideal for astrophotography and precise tracking, while alt-azimuth mounts offer simplicity and portability. Additionally, computerized mounts provide advanced features for automated tracking and locating celestial objects.
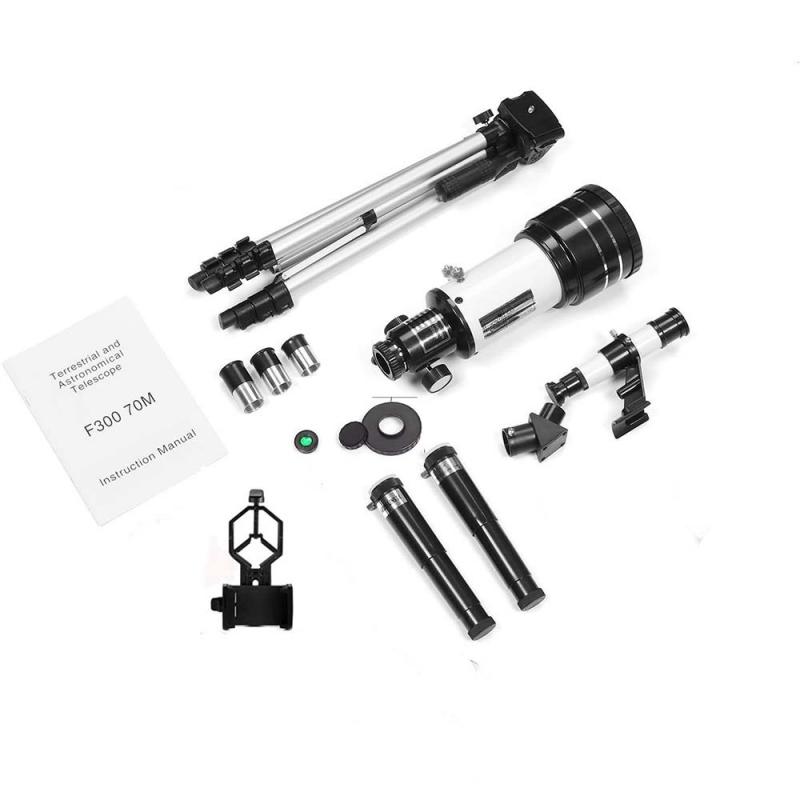

4、 Magnification and focal length: Determine the telescope's potential for zooming in.
How to buy a telescope:
1. Determine your budget: Telescopes can range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand. Decide how much you are willing to spend before beginning your search.
2. Research different types of telescopes: There are three main types of telescopes - refractor, reflector, and compound. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it's important to understand which one suits your needs best.
3. Consider the aperture size: The aperture size determines how much light the telescope can gather. A larger aperture allows for better image quality and the ability to see fainter objects. However, larger apertures also mean larger and more expensive telescopes.
4. Magnification and focal length: Determine the telescope's potential for zooming in. Magnification is not the most important factor when choosing a telescope, as it depends on the atmospheric conditions and the quality of the optics. Focal length, on the other hand, affects the field of view and the level of detail you can observe.
5. Portability and ease of use: Consider where you plan to use the telescope and how easy it is to transport. If you want to take it on camping trips or to remote locations, a compact and lightweight telescope may be more suitable.
6. Read reviews and seek expert advice: Look for reviews from other users to get an idea of the telescope's performance and reliability. Additionally, consult with experts or visit a local astronomy club to get personalized recommendations based on your specific needs.
7. Accessories and warranties: Check if the telescope comes with any additional accessories such as eyepieces, filters, or a tripod. Also, consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer to ensure you are protected against any potential defects.
Remember, buying a telescope is an investment in your passion for astronomy. Take your time, do thorough research, and choose a telescope that aligns with your interests and budget.









































