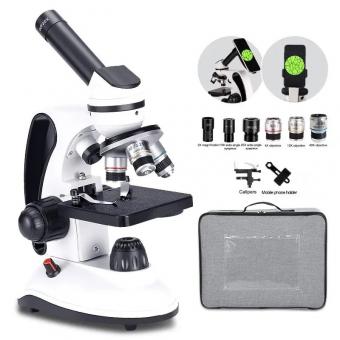
How To Calculate Magnification On Microscope ?
To calculate the magnification on a microscope, you can use the formula: Magnification = (Magnification of the objective lens) x (Magnification of the eyepiece lens). The magnification of the objective lens is usually indicated on the lens itself (e.g., 4x, 10x, 40x, etc.), while the magnification of the eyepiece lens is typically 10x. Multiply these two values together to obtain the total magnification. For example, if the objective lens is 40x and the eyepiece lens is 10x, the total magnification would be 400x. Keep in mind that this formula assumes that the microscope is properly calibrated and in focus.
1、 Total magnification formula for a compound microscope
To calculate the magnification on a microscope, you need to consider both the magnification of the objective lens and the eyepiece. The total magnification is the product of these two magnifications.
The magnification of the objective lens is usually marked on the lens itself. It is typically written as a number followed by an "x" symbol, such as 4x, 10x, or 40x. This number represents how many times larger the image appears compared to the actual size of the object.
The eyepiece, or ocular lens, also has a magnification value marked on it. This value is usually 10x, but it can vary depending on the microscope.
To calculate the total magnification, simply multiply the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece. For example, if the objective lens is 40x and the eyepiece is 10x, the total magnification would be 40x multiplied by 10x, which equals 400x.
It is important to note that the total magnification is not the only factor that determines the quality of the image. Other factors, such as the numerical aperture of the lens and the resolution of the microscope, also play a role in determining the level of detail that can be observed.
Additionally, it is worth mentioning that some modern microscopes have additional features, such as digital cameras or smartphone adapters, which allow for further magnification and image capture. These features can enhance the overall viewing experience and provide the ability to share images or videos with others.
In conclusion, calculating the magnification on a microscope involves multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece. However, it is important to consider other factors that contribute to the quality of the image and to be aware of any additional features that may enhance the viewing experience.

2、 Calculating magnification using objective and eyepiece lens powers
To calculate the magnification on a microscope, you need to consider the powers of both the objective lens and the eyepiece lens. The magnification of a microscope is the product of the magnification of these two lenses.
First, determine the magnification of the objective lens. This information is usually provided by the manufacturer and is typically engraved on the lens itself. It is usually written as a number followed by an "x" symbol, such as 10x or 40x. This number represents the magnification power of the objective lens.
Next, determine the magnification of the eyepiece lens. Similar to the objective lens, the magnification power of the eyepiece lens is also usually engraved on it. It is commonly 10x, but it can vary depending on the microscope model.
To calculate the total magnification, simply multiply the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece lens. For example, if the objective lens has a magnification of 40x and the eyepiece lens has a magnification of 10x, the total magnification would be 40x multiplied by 10x, which equals 400x.
It is important to note that the total magnification is not the only factor that determines the quality of the image. Other factors, such as the numerical aperture and resolution of the lenses, also play a significant role in the clarity and detail of the observed specimen.
In recent years, advancements in microscope technology have led to the development of digital microscopes. These microscopes use digital cameras and software to capture and display images on a computer screen. The magnification of digital microscopes is often calculated automatically by the software, eliminating the need for manual calculations.

3、 Determining magnification by measuring the size of an object
To calculate the magnification on a microscope, one common method is by measuring the size of an object. This method involves comparing the size of the object as seen through the microscope to its actual size. Here's how you can do it:
1. Choose an object with a known size, such as a ruler or a stage micrometer slide, which has a scale etched onto it.
2. Place the object on the microscope stage and focus on it using the lowest magnification objective lens.
3. Measure the size of the object as it appears under the microscope. This can be done by counting the number of divisions on the microscope's eyepiece scale that the object spans.
4. Measure the actual size of the object using a ruler or a known reference scale.
5. Divide the actual size of the object by the measured size under the microscope. This will give you the magnification of the microscope.
It is important to note that the magnification calculated using this method represents the total magnification of the microscope, which is the product of the magnification of the objective lens and the eyepiece lens.
It is worth mentioning that advancements in technology have led to the development of digital microscopes that can calculate magnification automatically. These microscopes use built-in software and image analysis algorithms to measure the size of objects and calculate magnification accurately.
In conclusion, determining magnification by measuring the size of an object is a straightforward method to calculate the magnification on a microscope. However, it is essential to consider the latest advancements in technology that offer more precise and automated ways of calculating magnification.

4、 Calculating magnification with a digital microscope or camera attachment
To calculate magnification on a microscope, you need to know the magnification power of the objective lens and the eyepiece. The total magnification is the product of these two values. However, when using a digital microscope or camera attachment, the process is slightly different.
With a digital microscope or camera attachment, the magnification is determined by the size of the image sensor and the resolution of the camera. The image sensor captures the image, and the resolution determines the level of detail that can be seen. The magnification is then calculated based on the size of the image on the sensor and the size of the object being viewed.
To calculate the magnification, you need to know the size of the object being viewed and the size of the image on the sensor. The magnification can be calculated using the formula:
Magnification = Size of object / Size of image on sensor
The size of the object can be measured using a ruler or a stage micrometer, while the size of the image on the sensor can be determined by examining the captured image and measuring the dimensions.
It is important to note that the magnification calculated using a digital microscope or camera attachment may not be the same as the magnification stated on the microscope itself. This is because the magnification on the microscope is determined by the optical system, while the magnification calculated using a digital microscope or camera attachment is based on the image sensor and camera resolution.
In conclusion, when using a digital microscope or camera attachment, the magnification is calculated based on the size of the object and the size of the image on the sensor. This provides a more accurate representation of the magnification compared to the traditional method of using the magnification power of the objective lens and eyepiece.