How To Draw Microscope Images ?
To draw microscope images, you will need a microscope, a slide with a specimen, and drawing materials such as paper and pencils. Start by placing the slide on the microscope stage and adjusting the focus to get a clear view of the specimen. Use the microscope's magnification and focus controls to zoom in on the area you want to draw. Take your time to observe the details and features of the specimen carefully. Then, using your drawing materials, begin sketching what you see through the microscope. Pay attention to the shapes, textures, and patterns of the specimen. You can use different shading techniques to add depth and dimension to your drawing. Remember to be patient and practice regularly to improve your skills in drawing microscope images.
1、 Understanding Microscope Anatomy and Function
To draw microscope images, it is important to have a good understanding of microscope anatomy and function. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to draw microscope images:
1. Start by drawing the basic shape of the microscope. It typically consists of a base, an arm, and a stage. The base provides stability, the arm holds the optical components, and the stage holds the specimen.
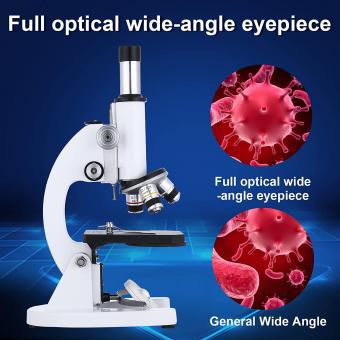
2. Add the eyepiece or ocular lens at the top of the arm. This is where the viewer looks through to observe the specimen. It is usually a cylindrical shape with a lens at one end.
3. Draw the objective lenses on a rotating nosepiece. These lenses are located just above the stage and are used to magnify the specimen. They come in different magnification powers, such as 4x, 10x, and 40x.
4. Include the stage, which is a flat platform where the specimen is placed. It often has clips or a mechanical stage to hold the specimen in place.
5. Draw the condenser, which is located beneath the stage. It focuses the light onto the specimen, improving the image quality.
6. Add the light source, which can be a built-in lamp or an external light. It provides illumination for the specimen.
7. Finally, add any additional features such as focus knobs, fine adjustment knobs, and diaphragm controls. These allow for precise focusing and control of light intensity.
Understanding the latest point of view in microscope anatomy and function, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated microscopes. For example, electron microscopes use a beam of electrons instead of light to magnify the specimen, resulting in higher resolution images. Additionally, confocal microscopes use laser beams to scan the specimen, allowing for three-dimensional imaging. These advancements may require additional components and adjustments in the drawing of microscope images.
In conclusion, drawing microscope images requires a good understanding of microscope anatomy and function. By following the steps outlined above and considering the latest advancements in microscopy, one can accurately depict the various components of a microscope.

2、 Preparing Specimens for Microscopic Imaging
To draw microscope images, follow these steps:
1. Obtain a microscope: Start by acquiring a light microscope suitable for your needs. There are various types available, such as compound microscopes for high magnification or stereo microscopes for three-dimensional imaging.
2. Prepare the specimen: Choose the specimen you want to observe under the microscope. It can be a biological sample, a thin slice of a material, or any other object of interest. Ensure the specimen is small enough to fit on a microscope slide.
3. Fixation and staining: Depending on the nature of the specimen, you may need to fix it to preserve its structure and stain it to enhance visibility. Fixation involves treating the specimen with chemicals to prevent decay or alteration. Staining involves adding dyes or fluorescent markers to highlight specific structures or components.
4. Mount the specimen: Place a small drop of mounting medium, such as water or a specialized mounting fluid, on a clean microscope slide. Carefully transfer the specimen onto the drop, ensuring it is properly oriented for observation.
5. Cover slip: Gently lower a cover slip onto the specimen, taking care to avoid trapping air bubbles. The cover slip protects the specimen and flattens it for better imaging.
6. Adjust the microscope: Place the slide on the microscope stage and secure it in place. Start with the lowest magnification objective lens and gradually increase the magnification until you achieve the desired level of detail. Adjust the focus using the coarse and fine focus knobs.
7. Observe and draw: Look through the eyepiece and observe the specimen. Pay attention to the details and structures you want to capture in your drawing. Use a pencil or a fine-tipped pen to sketch the observed features on a separate sheet of paper.
8. Add annotations: Label the different structures or components in your drawing, indicating their names and any relevant measurements or observations.
When drawing microscope images, it is important to accurately represent what you see. Take your time, be patient, and practice to improve your skills in capturing the microscopic world.
From a modern perspective, advancements in technology have led to the development of digital microscopes and imaging software. These tools allow for more precise and detailed imaging, as well as the ability to capture and analyze images digitally. Additionally, techniques such as confocal microscopy and electron microscopy provide even higher resolution and three-dimensional imaging capabilities. These advancements have revolutionized the field of microscopy and expanded our understanding of the microscopic world.

3、 Adjusting Microscope Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Drawing microscope images requires careful observation and attention to detail. Here are some steps to help you draw microscope images accurately:
1. Set up your microscope: Ensure that your microscope is properly set up and calibrated. Clean the lenses and adjust the lighting to provide optimal illumination.
2. Choose a specimen: Select a specimen that you want to observe under the microscope. It could be a prepared slide or a sample you have collected.
3. Focus on the specimen: Adjust the focus knob to bring the specimen into clear view. Start with the coarse adjustment knob to roughly focus, then use the fine adjustment knob for precise focusing.
4. Observe the details: Take your time to carefully observe the specimen. Pay attention to its shape, color, and any specific features you want to capture in your drawing.
5. Start sketching: Begin by lightly sketching the basic outline of the specimen using a pencil. Use simple shapes and lines to represent the main features.
6. Add details: Gradually add more details to your drawing, such as textures, patterns, and specific structures. Take note of any variations in color or shading.
7. Use shading and hatching: To create depth and dimension in your drawing, use shading techniques like cross-hatching or stippling. This will help to accurately represent the different areas of the specimen.
8. Finalize your drawing: Once you are satisfied with your sketch, go over the lines with a darker pencil or pen to make them more defined. Erase any unnecessary guidelines or smudges.
Remember, practice is key to improving your microscope drawing skills. Take your time, be patient, and keep experimenting with different techniques to achieve the best results.
In terms of adjusting microscope settings for optimal image quality, the latest point of view emphasizes the importance of using advanced imaging technologies. Digital microscopes with high-resolution cameras and software allow for real-time image processing and analysis. These systems often have automated settings that optimize image quality, such as adjusting brightness, contrast, and focus. Additionally, advanced microscopy techniques like confocal microscopy and super-resolution microscopy provide enhanced resolution and clarity, enabling researchers to capture more detailed and accurate images. It is also crucial to consider factors like sample preparation, staining techniques, and proper calibration of the microscope to achieve the best image quality. Continuous advancements in microscopy technology and techniques are constantly improving the ability to capture and analyze microscopic images with greater precision and detail.

4、 Techniques for Capturing Microscope Images
Techniques for Capturing Microscope Images
Capturing microscope images is a crucial aspect of scientific research and analysis. It allows scientists to observe and document microscopic structures and processes. Here are some techniques to help you draw microscope images effectively:
1. Prepare the sample: Before capturing images, ensure that the sample is properly prepared. This may involve fixing, staining, or mounting the specimen on a slide to enhance visibility and contrast.
2. Adjust microscope settings: Set the appropriate magnification and focus on the area of interest. Adjust the lighting conditions, such as brightness and contrast, to optimize image quality.
3. Use a camera attachment: Many microscopes have camera attachments that allow direct image capture. These attachments can be connected to a computer or a separate camera to capture high-resolution images.
4. Image stacking: For complex samples, capturing multiple images at different focal planes and combining them using image stacking software can result in a clearer and more detailed final image.
5. Image processing: After capturing the images, post-processing techniques can be applied to enhance the image quality. This may involve adjusting brightness, contrast, and color balance, as well as removing noise or artifacts.
6. 3D imaging: Advanced techniques like confocal microscopy or electron microscopy can provide three-dimensional images of microscopic structures. These techniques require specialized equipment and expertise.
7. Stay updated: With advancements in technology, new imaging techniques and equipment are constantly emerging. Stay informed about the latest developments in microscopy to ensure you are using the most effective techniques for capturing microscope images.
In conclusion, capturing microscope images requires careful preparation, adjustment of microscope settings, and the use of camera attachments. Image stacking, post-processing, and staying updated with the latest techniques are also important for obtaining high-quality microscope images.