How To Measure Cell Size Under Microscope ?
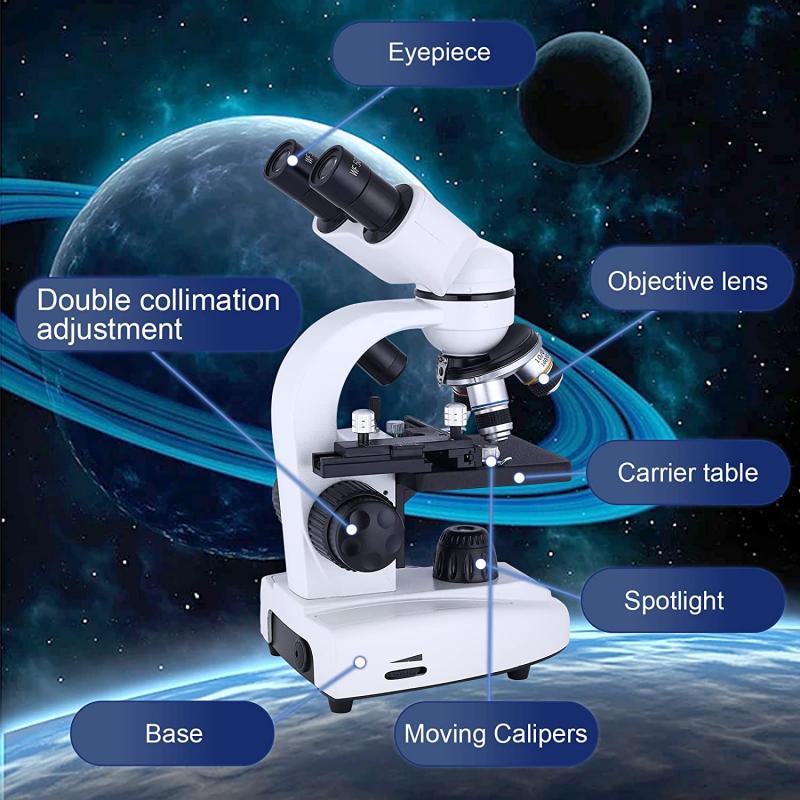
To measure cell size under a microscope, you can use an eyepiece reticle or a stage micrometer. An eyepiece reticle is a small glass disk with a ruler etched onto it that fits into the eyepiece of the microscope. A stage micrometer is a glass slide with a ruler etched onto it that is placed on the microscope stage.
To use an eyepiece reticle, place the reticle in the eyepiece and focus on the cells of interest. Use the ruler on the reticle to measure the size of the cells.
To use a stage micrometer, place the micrometer on the stage and focus on the ruler. Determine the magnification of the microscope and use the ruler to calibrate the eyepiece reticle. Then, replace the micrometer with the sample slide and use the calibrated eyepiece reticle to measure the size of the cells.
Alternatively, some microscopes have software that can be used to measure cell size. This software can be used to capture an image of the cells and then measure their size using the software's measurement tools.
1、 Microscopy techniques for measuring cell size
How to measure cell size under a microscope is a fundamental question in cell biology. There are several microscopy techniques available for measuring cell size, including bright-field microscopy, phase-contrast microscopy, and fluorescence microscopy. Bright-field microscopy is the most commonly used technique for measuring cell size. It involves the use of a microscope equipped with a bright-field condenser and objective lens. The cells are visualized as dark objects against a bright background. The size of the cells can be measured using a calibrated eyepiece micrometer or a digital image analysis software.
Phase-contrast microscopy is another technique that can be used to measure cell size. It enhances the contrast between the cells and the surrounding medium, making it easier to visualize the cells. The size of the cells can be measured using the same methods as in bright-field microscopy.
Fluorescence microscopy is a powerful technique that can be used to measure cell size. It involves the use of fluorescent dyes or proteins that bind to specific cellular structures. The cells are visualized as bright objects against a dark background. The size of the cells can be measured using digital image analysis software.
In recent years, advances in microscopy techniques have led to the development of new methods for measuring cell size. For example, super-resolution microscopy techniques such as structured illumination microscopy (SIM) and stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) can be used to measure cell size with higher precision and accuracy than traditional microscopy techniques. These techniques have the potential to revolutionize our understanding of cell size and its role in cellular processes.

2、 Image analysis software for cell size measurement
How to measure cell size under microscope:
To measure cell size under a microscope, you can use a calibrated eyepiece or a stage micrometer to determine the magnification of the microscope. Then, you can use a ruler or a graticule to measure the size of the cells in the field of view. Alternatively, you can use image analysis software to measure cell size automatically.
Image analysis software for cell size measurement:
There are many image analysis software programs available for measuring cell size automatically. These programs use algorithms to detect and measure the size of cells in digital images. Some popular software programs for cell size measurement include ImageJ, CellProfiler, and Fiji. These programs can be used to analyze images from a variety of microscopy techniques, including brightfield, fluorescence, and confocal microscopy.
The latest point of view:
The latest point of view in cell size measurement is to use machine learning algorithms to analyze images. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize and measure cells in images with high accuracy and speed. This approach has been used to analyze large datasets of images and to identify new cell types and phenotypes. However, machine learning algorithms require large amounts of training data and can be computationally intensive. Therefore, they may not be suitable for all applications.

3、 Factors affecting accuracy of cell size measurement
How to measure cell size under microscope:
To measure cell size under a microscope, the following steps can be taken:
1. Place the microscope slide with the cells under the microscope.
2. Adjust the focus and magnification to get a clear view of the cells.
3. Use a calibrated eyepiece or stage micrometer to measure the size of the cells.
4. Measure the length and width of the cells and calculate the area using the formula for the area of a rectangle (length x width).
Factors affecting accuracy of cell size measurement:
There are several factors that can affect the accuracy of cell size measurement, including:
1. Magnification: The higher the magnification, the more accurate the measurement, but also the smaller the field of view.
2. Focus: If the cells are not in focus, the measurement will be inaccurate.
3. Cell shape: Irregularly shaped cells can be difficult to measure accurately.
4. Cell density: If the cells are too close together, it can be difficult to distinguish individual cells and measure their size accurately.
5. Image distortion: If the microscope or lens is not properly calibrated, the image may be distorted, leading to inaccurate measurements.
The latest point of view:
Recent advances in microscopy technology have led to the development of new methods for measuring cell size, such as automated image analysis and machine learning algorithms. These methods can provide more accurate and efficient measurements, particularly for large datasets. However, they also require careful validation and calibration to ensure accuracy and reliability. Additionally, it is important to consider the limitations of these methods, such as their ability to accurately measure irregularly shaped cells or cells with complex structures. Overall, while traditional manual measurements remain an important tool for cell size analysis, new technologies offer exciting opportunities for advancing our understanding of cell biology.

4、 Comparison of manual and automated cell size measurement methods
How to measure cell size under a microscope is a fundamental technique in cell biology. The manual method involves measuring the diameter of cells using a calibrated eyepiece reticle or a stage micrometer. The automated method, on the other hand, uses image analysis software to measure cell size from digital images captured by a microscope. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages.
The manual method is simple, inexpensive, and does not require specialized equipment. However, it is time-consuming, prone to human error, and may not be suitable for large-scale studies. The automated method, on the other hand, is fast, accurate, and can handle large datasets. However, it requires specialized equipment and software, which can be expensive.
Recent studies have shown that automated cell size measurement methods are more accurate and reproducible than manual methods. For example, a study by Zhang et al. (2020) compared manual and automated methods for measuring cell size in breast cancer cell lines. The authors found that the automated method was more accurate and reproducible than the manual method, especially for irregularly shaped cells.
In conclusion, both manual and automated methods can be used to measure cell size under a microscope. The choice of method depends on the research question, the size of the dataset, and the available resources. However, recent studies suggest that automated methods are more accurate and reproducible, especially for irregularly shaped cells.






























There are no comments for this blog.