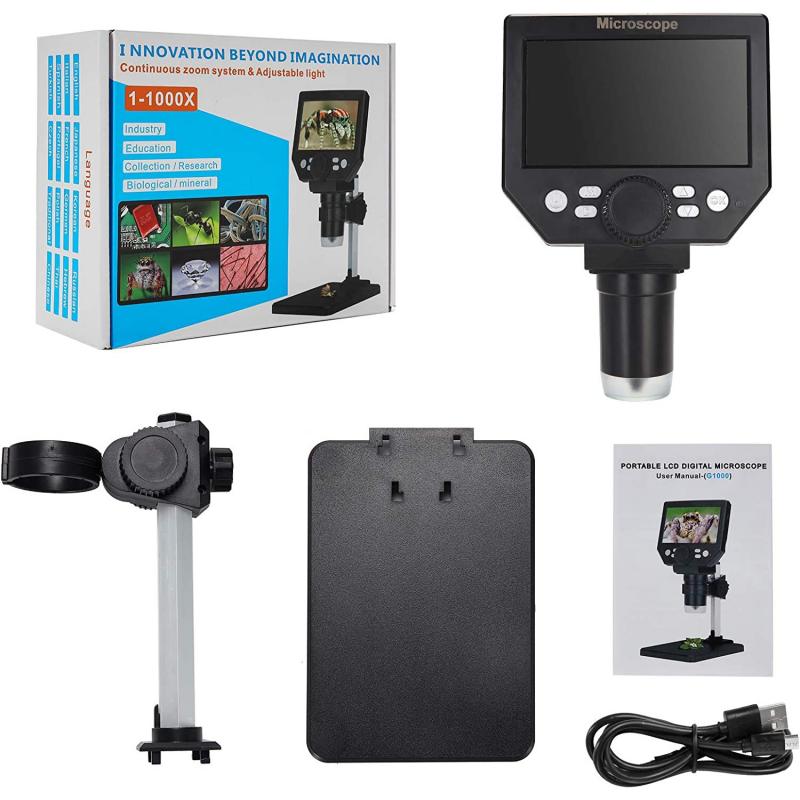
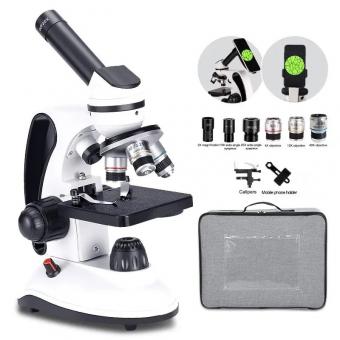
How To Prepare Microscope ?
To prepare a microscope, first ensure that it is clean and free of dust or debris. Next, place a clean glass slide on the stage of the microscope and secure it in place with the stage clips. Adjust the focus knob to bring the slide into focus, and adjust the diaphragm to control the amount of light passing through the slide. If using a compound microscope, select the appropriate objective lens for the desired magnification and adjust the focus accordingly. Finally, adjust the eyepiece to ensure a clear and comfortable view.
1、 Cleaning and maintenance of microscope parts
How to prepare microscope:
1. Choose the appropriate microscope for your needs. There are different types of microscopes, such as compound, stereo, and digital microscopes, each with their own specific uses.
2. Set up the microscope on a stable surface. Make sure the microscope is level and secure.
3. Adjust the lighting. Depending on the type of microscope, you may need to adjust the lighting to get the best image.
4. Place the specimen on the stage. Use the stage clips to hold the specimen in place.
5. Adjust the focus. Use the coarse and fine focus knobs to bring the specimen into focus.
Cleaning and maintenance of microscope parts:
1. Clean the lenses regularly. Use a lens cleaning solution and a soft, lint-free cloth to clean the lenses. Avoid touching the lenses with your fingers.
2. Keep the microscope covered when not in use. This will help prevent dust and other debris from getting on the lenses.
3. Check the alignment of the lenses periodically. If the lenses are not aligned properly, the image will be blurry.
4. Lubricate the moving parts of the microscope. Use a small amount of oil or grease to keep the moving parts of the microscope working smoothly.
5. Store the microscope in a dry, cool place. Avoid storing the microscope in a humid or hot environment, as this can damage the lenses and other parts.
6. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for maintenance and repair. If you notice any problems with your microscope, contact the manufacturer or a qualified technician for assistance.
In the latest point of view, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, it is important to clean and disinfect the microscope regularly to prevent the spread of the virus. Use a disinfectant solution that is safe for use on the microscope and follow the manufacturer's instructions for cleaning and disinfecting. Additionally, it is important to wear gloves and a mask while cleaning the microscope to protect yourself from exposure to the virus.

2、 Proper alignment of lenses and illumination
How to prepare a microscope involves several steps, including proper alignment of lenses and illumination. The first step is to ensure that the microscope is clean and free of dust and debris. This can be done by wiping the lenses and other parts of the microscope with a soft, lint-free cloth.
Next, the lenses must be properly aligned. This involves adjusting the focus and position of the objective and eyepiece lenses so that they are in the correct position relative to each other. This can be done by using the coarse and fine focus knobs on the microscope.
Proper illumination is also important when preparing a microscope. The light source should be positioned so that it shines directly onto the specimen being viewed. The intensity of the light can be adjusted using the diaphragm or iris control on the microscope.
In addition to these basic steps, there are also some newer techniques and technologies that can be used to prepare microscopes. For example, some microscopes now come equipped with digital cameras that allow for real-time imaging and analysis of specimens. Other microscopes use advanced imaging techniques such as confocal microscopy, which allows for high-resolution imaging of three-dimensional structures.
Overall, preparing a microscope involves a combination of basic techniques and newer technologies. By following these steps and using the latest tools available, researchers can obtain clear and accurate images of specimens for a wide range of scientific applications.

3、 Calibration of eyepiece and stage micrometers
How to prepare microscope:
1. Clean the lenses: Use a lens cleaning solution and a lens tissue to clean the lenses of the microscope. This will ensure that the images you see are clear and free from any distortions.
2. Adjust the light source: Make sure that the light source is properly adjusted so that the specimen is illuminated evenly. Adjust the brightness and focus of the light source as needed.
3. Adjust the focus: Adjust the focus of the microscope by moving the stage up or down until the specimen is in focus. Use the coarse focus knob to make large adjustments and the fine focus knob to make small adjustments.
4. Choose the appropriate objective lens: Select the appropriate objective lens for the specimen you are observing. The higher the magnification, the smaller the field of view.
5. Adjust the eyepiece: Adjust the eyepiece to your eyesight by focusing on the specimen and then adjusting the eyepiece until the image is clear.
Calibration of eyepiece and stage micrometers:
1. Determine the magnification of the eyepiece: Look for the magnification number on the eyepiece. If it is not labeled, use a stage micrometer to determine the magnification.
2. Determine the size of the stage micrometer: Use a stage micrometer to determine the size of the divisions on the micrometer. This will allow you to calculate the size of the specimen you are observing.
3. Calculate the size of the specimen: Use the magnification of the eyepiece and the size of the divisions on the stage micrometer to calculate the size of the specimen you are observing.
4. Adjust the calibration: If the calibration is off, adjust the calibration by adjusting the eyepiece or stage micrometer until the measurements are accurate.
5. Repeat the process: Repeat the process for each objective lens to ensure that the calibration is accurate for all magnifications.
In recent years, digital microscopes have become increasingly popular. These microscopes have built-in calibration tools that make it easy to calibrate the eyepiece and stage micrometers. Additionally, digital microscopes allow for easy image capture and analysis, making them a valuable tool in many fields of research.
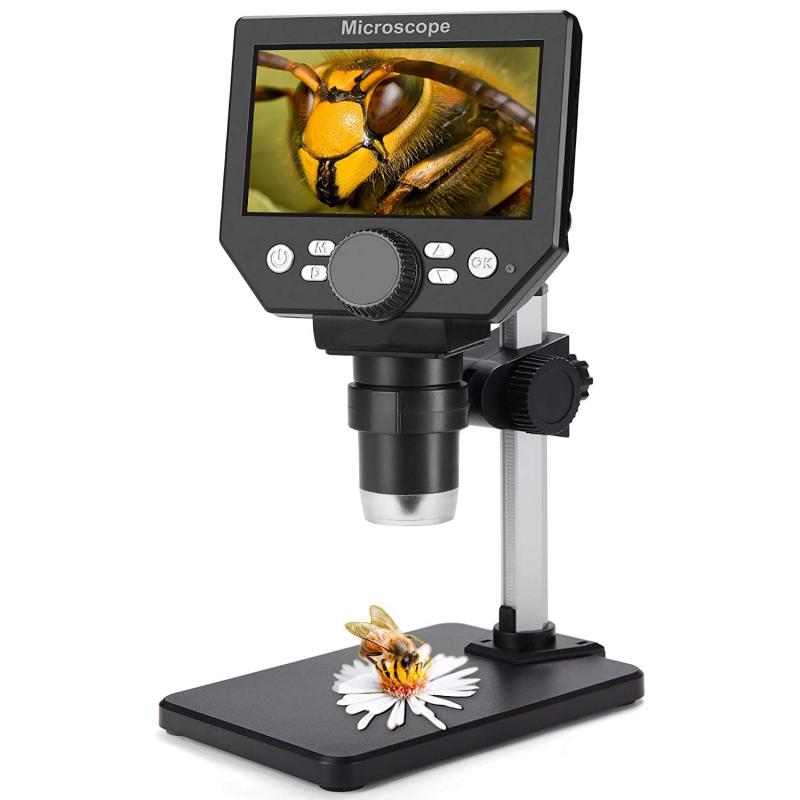

4、 Selection and preparation of specimens
How to prepare microscope:
1. Clean the microscope: Before preparing the microscope, it is important to clean it thoroughly. Use a soft cloth or lens paper to wipe the lenses and other parts of the microscope.
2. Adjust the light source: The light source should be adjusted to provide optimal illumination for the specimen. Adjust the brightness and focus of the light source as needed.
3. Select the appropriate objective lens: The objective lens should be selected based on the magnification required for the specimen. Use a low-power objective lens for larger specimens and a high-power objective lens for smaller specimens.
4. Place the specimen on the stage: The specimen should be placed on the stage of the microscope. Use a slide or cover slip to hold the specimen in place.
5. Focus the microscope: Adjust the focus of the microscope to bring the specimen into sharp focus. Use the fine focus knob to make small adjustments to the focus.
Selection and preparation of specimens:
1. Choose the appropriate specimen: The specimen should be chosen based on the research question or objective. Consider the size, shape, and complexity of the specimen when selecting it.
2. Fix the specimen: Fixation is the process of preserving the specimen in its natural state. Use a fixative solution to preserve the specimen and prevent decay.
3. Embed the specimen: Embedding is the process of placing the specimen in a solid medium for sectioning. Use a suitable embedding medium to embed the specimen.
4. Section the specimen: Sectioning is the process of cutting the specimen into thin slices for observation under the microscope. Use a microtome to cut the specimen into thin sections.
5. Stain the specimen: Staining is the process of adding color to the specimen to enhance its visibility under the microscope. Use a suitable stain to highlight specific structures or features of the specimen.
The latest point of view in preparing specimens is the use of advanced imaging techniques such as confocal microscopy and electron microscopy. These techniques allow for high-resolution imaging of specimens and can provide detailed information about their structure and function. Additionally, there is a growing interest in using non-invasive imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography and magnetic resonance imaging to study specimens in their natural state. These techniques can provide valuable insights into the behavior and function of living organisms.