How To See Moon From Telescope ?
To see the moon from a telescope, you will need to follow these steps:
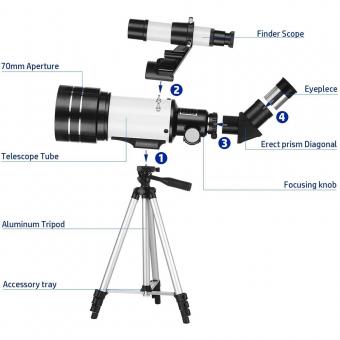
1. Set up your telescope in a location with a clear view of the sky. Make sure it is stable and securely mounted.
2. Align your telescope by pointing it towards a bright object on the horizon, such as a distant building or a bright star.
3. Use the telescope's finder scope or a low-power eyepiece to locate the moon. Look for a bright, round object in the sky.
4. Adjust the focus of your telescope until the moon appears sharp and clear. You may need to experiment with different eyepieces to achieve the desired magnification.
5. Take your time to observe the moon's surface features, such as craters, mountains, and maria (dark areas). Pay attention to the changing shadows and the overall texture of the lunar landscape.
Remember to be patient and allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness. Also, consider using a moon filter to reduce the brightness and enhance the details of the moon's surface. Enjoy your lunar observations!
1、 Lunar Surface Features: Craters, mountains, and other geological formations.
To see the moon from a telescope, you will need a few essential steps to ensure a successful viewing experience. Here's a guide on how to see the moon using a telescope:
1. Choose the right telescope: Select a telescope with a good magnification power and a large aperture. A telescope with a minimum of 60mm aperture and 100x magnification is recommended for lunar observations.
2. Set up your telescope: Find a stable location with minimal light pollution. Set up your telescope on a sturdy tripod or mount, ensuring it is properly aligned and balanced.
3. Use a lunar filter: Attach a lunar filter to your telescope's eyepiece. This filter helps reduce the brightness of the moon, making it easier to observe surface details.
4. Focus your telescope: Adjust the focus of your telescope until the moon appears sharp and clear. Fine-tune the focus to enhance the details of the lunar surface.
5. Observe lunar surface features: Once you have the moon in view, you can start exploring its surface features. Look for craters, mountains, and other geological formations. The moon's surface is covered in impact craters, caused by meteorite collisions over millions of years. You may also spot mountain ranges, such as the Apennine Mountains or the Montes Alpes.
6. Take advantage of the moon's phases: The moon goes through different phases, which can affect the visibility of its surface features. During a full moon, the surface may appear flat and less detailed due to the lack of shadows. However, during a crescent or half-moon phase, the shadows cast by mountains and craters create a more dramatic and visually appealing view.
It's worth noting that the latest point of view on lunar surface features can be obtained through various sources, including NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) mission. The LRO has provided high-resolution images and data that have significantly enhanced our understanding of the moon's geology and surface features.

2、 Lunar Phases: Waxing, waning, full, and new moon cycles.
To see the moon from a telescope, follow these steps:
1. Choose the right telescope: Select a telescope with a good magnification power and a stable mount. A refractor or reflector telescope with a minimum aperture of 70mm is recommended for lunar observations.
2. Find a suitable location: Set up your telescope in a location away from bright city lights to minimize light pollution. This will enhance your viewing experience and allow you to see more details on the moon's surface.
3. Align your telescope: Use the telescope's finder scope or a star chart to align it with the moon. This will help you locate the moon quickly and accurately.
4. Observe the lunar phases: The moon goes through different phases as it orbits the Earth. These phases include the waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, third quarter, and waning crescent. Each phase offers a unique view of the moon's surface.
5. Adjust the focus: Once you have located the moon, adjust the focus of your telescope to get a clear image. Experiment with different eyepieces to achieve the desired magnification level.
6. Observe the details: Look for craters, mountains, valleys, and other features on the moon's surface. The moon's topography is fascinating to explore, and a telescope can reveal intricate details that are not visible to the naked eye.
It's important to note that the moon's appearance changes throughout the lunar cycle. The latest point of view is that the moon's phases are caused by the relative positions of the sun, Earth, and moon. During a full moon, the moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the sun, and its entire illuminated side is visible. In contrast, during a new moon, the moon is between the Earth and the sun, and its illuminated side faces away from us, making it appear dark.
By following these steps and understanding the lunar phases, you can enjoy observing the moon through a telescope and gain a deeper appreciation for our celestial neighbor.

3、 Lunar Libration: Visible oscillation and tilting of the moon.
To see the moon from a telescope, you will need to follow a few steps:
1. Set up your telescope: Choose a location with minimal light pollution and a clear view of the sky. Set up your telescope on a stable surface and ensure it is properly aligned and focused.
2. Find the moon: Use the telescope's finder scope or low-power eyepiece to locate the moon in the night sky. Adjust the telescope's position until the moon is centered in the field of view.
3. Observe the moon: Once you have the moon in view, you can start exploring its features. The moon's surface is covered in craters, mountains, and dark plains called maria. Look for these distinct features and take note of their details.
Now, let's talk about lunar libration. Lunar libration refers to the visible oscillation and tilting of the moon as observed from Earth. Due to the moon's elliptical orbit and its slightly tilted axis, different parts of the moon's surface become visible over time. This phenomenon allows us to see around 59% of the moon's surface from Earth.
The libration of the moon can be observed through a telescope over a period of time. It is caused by the combined effects of the moon's rotation and its orbit around Earth. As a result, we can see a slight rocking motion and a shifting of the moon's east-west and north-south boundaries.
The latest point of view on lunar libration is that it provides astronomers with an opportunity to observe and study different regions of the moon's surface that would otherwise remain hidden. By observing the moon during different phases and libration angles, scientists can gather more comprehensive data about its topography, geology, and other characteristics.
In conclusion, to see the moon from a telescope, follow the steps mentioned above. Additionally, take advantage of lunar libration to explore different parts of the moon's surface and enhance your observations.

4、 Lunar Maria: Dark, flat regions on the moon's surface.
To see the moon from a telescope, you will need to follow a few steps:
1. Choose the right telescope: Select a telescope with a good magnification power and a large aperture. A telescope with a minimum of 70mm aperture is recommended for lunar observations.
2. Set up your telescope: Find a stable location with a clear view of the sky. Set up your telescope according to the manufacturer's instructions, ensuring it is properly aligned.
3. Locate the moon: Use a star chart or a smartphone app to locate the moon in the night sky. The moon is visible at different times of the month, so check the lunar phase to determine the best time for observation.
4. Focus your telescope: Adjust the focus knob on your telescope until the moon appears sharp and clear. Experiment with different eyepieces to find the best magnification for your viewing.
5. Explore the lunar surface: Once you have the moon in view, you can start observing its features. Lunar Maria, the dark, flat regions on the moon's surface, are easily visible through a telescope. These areas are ancient volcanic plains and appear darker due to their lower reflectivity compared to the surrounding highlands.
It's worth noting that the latest point of view on Lunar Maria is that they were formed by volcanic activity billions of years ago. Recent studies have also suggested that the dark regions might have been created by asteroid impacts that caused the moon's crust to crack and fill with lava. These findings provide valuable insights into the moon's geological history.
Remember to take your time and enjoy the experience of observing the moon through a telescope. It's a fascinating sight that reveals intricate details of our celestial neighbor.