How To Use Digital Cameras For Beginners ?
Using a digital camera for beginners involves a few basic steps. First, familiarize yourself with the camera's controls and settings. Next, ensure the camera is charged and insert a memory card. To take a photo, aim the camera at the subject, press the shutter button halfway to focus, and fully press it to capture the image. Review the photo on the camera's LCD screen and adjust settings as needed. To transfer photos to a computer, connect the camera using a USB cable or remove the memory card and insert it into a card reader. Finally, organize and edit the photos using software or apps. Practice and experimentation will help improve your photography skills over time.
1、 Camera Basics: Understanding the key components and functions.
Camera Basics: Understanding the key components and functions
Digital cameras have become increasingly popular in recent years, offering users the ability to capture high-quality images with ease. If you're a beginner looking to get started with digital photography, understanding the key components and functions of a camera is essential. Here's a guide to help you get started:
1. Megapixels: The number of megapixels determines the resolution of the image. Higher megapixels result in sharper and more detailed photos.
2. Lens: The lens is a crucial component that determines the quality of your images. Different lenses offer various focal lengths and aperture settings, allowing you to capture different types of shots.
3. Shutter Speed: Shutter speed refers to the length of time the camera's shutter remains open. It affects the amount of light entering the camera and can be adjusted to freeze motion or create motion blur.
4. Aperture: Aperture controls the amount of light that enters the camera through the lens. It also affects the depth of field, determining how much of the image is in focus.
5. ISO: ISO measures the camera's sensitivity to light. Higher ISO settings are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise or graininess to the image.
6. White Balance: White balance ensures that colors appear accurate in different lighting conditions. It can be set manually or adjusted automatically by the camera.
7. Exposure Compensation: Exposure compensation allows you to adjust the brightness of your images. It is useful when the camera's automatic exposure settings don't produce the desired results.
8. Autofocus: Most digital cameras have autofocus capabilities, which automatically adjust the focus to ensure sharp images. Understanding the different autofocus modes and how to use them effectively is essential.
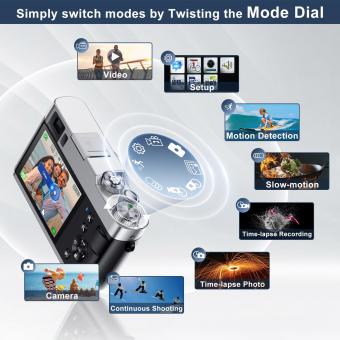
9. Shooting Modes: Digital cameras offer various shooting modes, such as auto, manual, aperture priority, and shutter priority. These modes allow you to have more control over your images or let the camera make decisions for you.
10. Composition: While not a technical aspect of the camera, composition plays a crucial role in creating visually appealing images. Experiment with different angles, perspectives, and framing techniques to enhance your photographs.
As technology advances, new features and functions are continually being introduced to digital cameras. It's essential to stay updated with the latest developments and explore how they can enhance your photography experience. Remember, practice is key to improving your skills, so get out there and start capturing beautiful moments with your digital camera!

2、 Shooting Modes: Exploring different modes for various photography situations.
Shooting Modes: Exploring different modes for various photography situations.
Digital cameras offer a wide range of shooting modes that can help beginners capture stunning photos in different situations. Understanding these modes and knowing when to use them is essential for maximizing the potential of your camera. Here is a beginner's guide to using shooting modes effectively:
1. Auto Mode: This is the default mode that most beginners start with. It allows the camera to make all the decisions regarding exposure, focus, and other settings. While it is convenient, it limits your creative control.
2. Program Mode (P): This mode gives you more control over settings like ISO, white balance, and exposure compensation while still allowing the camera to handle other aspects. It is a good step up from Auto mode as it allows you to experiment with different settings.
3. Aperture Priority Mode (A/Av): In this mode, you can manually set the aperture while the camera adjusts the other settings accordingly. It is great for controlling depth of field and is commonly used in portrait and landscape photography.
4. Shutter Priority Mode (S/Tv): This mode allows you to set the shutter speed while the camera adjusts the other settings. It is useful for capturing fast-moving subjects or creating motion blur effects.
5. Manual Mode (M): This mode gives you full control over all settings, including aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and more. It requires some knowledge and practice but offers the most creative freedom.
6. Scene Modes: Many cameras come with pre-set scene modes like portrait, landscape, sports, night, etc. These modes optimize the settings for specific situations, making it easier for beginners to capture great shots without much technical knowledge.
It is important to note that the latest digital cameras often come with additional shooting modes and features. For example, some cameras now have a dedicated "night mode" that enhances low-light photography, or a "panorama mode" for capturing wide-angle shots. Exploring these new features can help beginners expand their photography skills and experiment with different creative possibilities.
In conclusion, understanding and utilizing the various shooting modes on your digital camera is crucial for capturing high-quality photos in different situations. As a beginner, it is recommended to start with Auto or Program mode and gradually progress to more manual modes as you gain confidence and knowledge. Experimenting with different modes will allow you to discover your own style and unleash your creativity.

3、 Composition Techniques: Tips for framing and creating visually appealing photos.
How to Use Digital Cameras for Beginners: Composition Techniques
When it comes to using digital cameras for beginners, understanding composition techniques is essential for creating visually appealing photos. Composition refers to how elements are arranged within the frame to create a balanced and aesthetically pleasing image. Here are some tips to help you improve your composition skills:
1. Rule of Thirds: Divide your frame into a grid of nine equal parts by imagining two horizontal and two vertical lines. Place your subject along these lines or at their intersections to create a more dynamic and visually interesting composition.
2. Leading Lines: Utilize natural or man-made lines in your scene to guide the viewer's eye towards the main subject. Leading lines can be roads, fences, or even the curves of a river.
3. Framing: Use elements within the scene to frame your subject. This can be archways, windows, or even tree branches. Framing adds depth and draws attention to the main subject.
4. Symmetry and Patterns: Look for symmetrical scenes or patterns to create a sense of balance and harmony in your photos. This can be found in architecture, nature, or even everyday objects.
5. Point of View: Experiment with different angles and perspectives to add interest to your composition. Get low to the ground for a unique viewpoint or try shooting from above for a different perspective.
6. Negative Space: Don't be afraid to leave empty space around your subject. Negative space can help emphasize the main subject and create a sense of simplicity and elegance.
7. Depth of Field: Play with the depth of field to create a sense of depth in your photos. Use a wide aperture (small f-number) to blur the background and make your subject stand out.
Remember, these composition techniques are not strict rules but rather guidelines to help you create visually appealing photos. Experiment, practice, and develop your own style. With time and experience, you will become more confident in using your digital camera and capturing stunning images.

4、 Exposure Control: Mastering aperture, shutter speed, and ISO settings.
Exposure Control: Mastering aperture, shutter speed, and ISO settings.
For beginners looking to use digital cameras, understanding exposure control is essential to capture stunning photographs. Exposure control refers to the manipulation of three key settings: aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. These settings determine the amount of light that enters the camera and ultimately affect the brightness, sharpness, and overall quality of the image.
Aperture: Aperture refers to the size of the opening in the lens through which light enters the camera. It is measured in f-stops, with smaller numbers indicating larger openings. A wider aperture (smaller f-stop) allows more light to enter, resulting in a shallower depth of field and a blurred background. Conversely, a narrower aperture (larger f-stop) lets in less light, resulting in a larger depth of field and a sharper background.
Shutter Speed: Shutter speed determines the length of time the camera's shutter remains open, allowing light to reach the image sensor. It is measured in fractions of a second, such as 1/1000 or 1/30. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. Experimenting with different shutter speeds can capture dynamic action or create artistic effects.
ISO: ISO measures the sensitivity of the camera's image sensor to light. A lower ISO (e.g., 100) is ideal for bright conditions, while a higher ISO (e.g., 800 or above) is suitable for low-light situations. However, higher ISO settings can introduce digital noise, reducing image quality. Modern cameras often have improved ISO performance, allowing for higher settings with minimal noise.
To master exposure control, it is crucial to understand the relationship between these three settings. Adjusting one setting will require compensating with another to maintain proper exposure. For example, if you increase the aperture size to let in more light, you may need to increase the shutter speed or lower the ISO to avoid overexposure.
As technology advances, digital cameras offer various automatic modes that simplify exposure control for beginners. These modes, such as aperture priority, shutter priority, or program mode, allow users to focus on composition while the camera adjusts the other settings accordingly. However, learning to manually control aperture, shutter speed, and ISO will provide greater creative control and flexibility in capturing the desired image.
In conclusion, mastering exposure control is crucial for beginners using digital cameras. Understanding aperture, shutter speed, and ISO settings allows photographers to manipulate light and create visually appealing images. While automatic modes can be helpful, learning to manually control these settings will enhance your photography skills and enable you to capture stunning photographs in any situation.






























There are no comments for this blog.