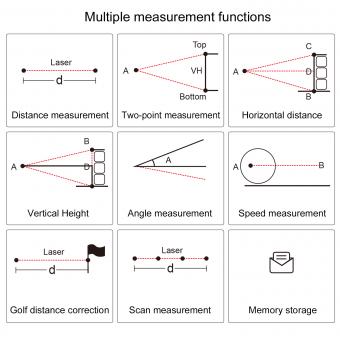
Laser Rangefinder How It Works ?
A laser rangefinder works by emitting a laser beam towards a target and measuring the time it takes for the beam to bounce back. The device uses the speed of light to calculate the distance between the rangefinder and the target. By precisely measuring the time it takes for the laser beam to travel to the target and back, the rangefinder can determine the distance with high accuracy. This technology is commonly used in various applications such as surveying, hunting, golfing, and military operations.
1、 Principle of Time-of-Flight Measurement in Laser Rangefinders
A laser rangefinder is a device that uses laser technology to measure the distance between the device and a target. The principle of time-of-flight measurement is commonly used in laser rangefinders to determine this distance accurately.
In a laser rangefinder, a laser beam is emitted towards the target. The beam reflects off the target and returns to the rangefinder. The time it takes for the laser beam to travel to the target and back is measured. By knowing the speed of light, the distance can be calculated using the formula: distance = (speed of light x time) / 2.
To measure the time-of-flight accurately, laser rangefinders use various techniques. One common method is called pulse or time-of-flight measurement. In this method, the laser emits short pulses of light towards the target. The rangefinder measures the time it takes for the pulse to travel to the target and back. By multiplying this time by the speed of light and dividing by 2, the distance can be determined.
Another technique used in laser rangefinders is called phase-shift measurement. In this method, the laser emits a continuous wave of light towards the target. The rangefinder measures the phase shift of the reflected light compared to the emitted light. By knowing the wavelength of the laser, the phase shift can be converted into distance.
The latest advancements in laser rangefinder technology have focused on improving accuracy, range, and speed. For example, some rangefinders now use multiple laser beams or advanced algorithms to enhance accuracy and reduce errors caused by environmental factors such as wind or rain. Additionally, the use of higher-powered lasers and improved detectors has increased the range of laser rangefinders, allowing them to measure longer distances accurately.
In conclusion, laser rangefinders work based on the principle of time-of-flight measurement. By emitting laser beams towards a target and measuring the time it takes for the beams to travel to the target and back, the distance can be calculated accurately. Ongoing advancements in technology continue to improve the accuracy, range, and speed of laser rangefinders.
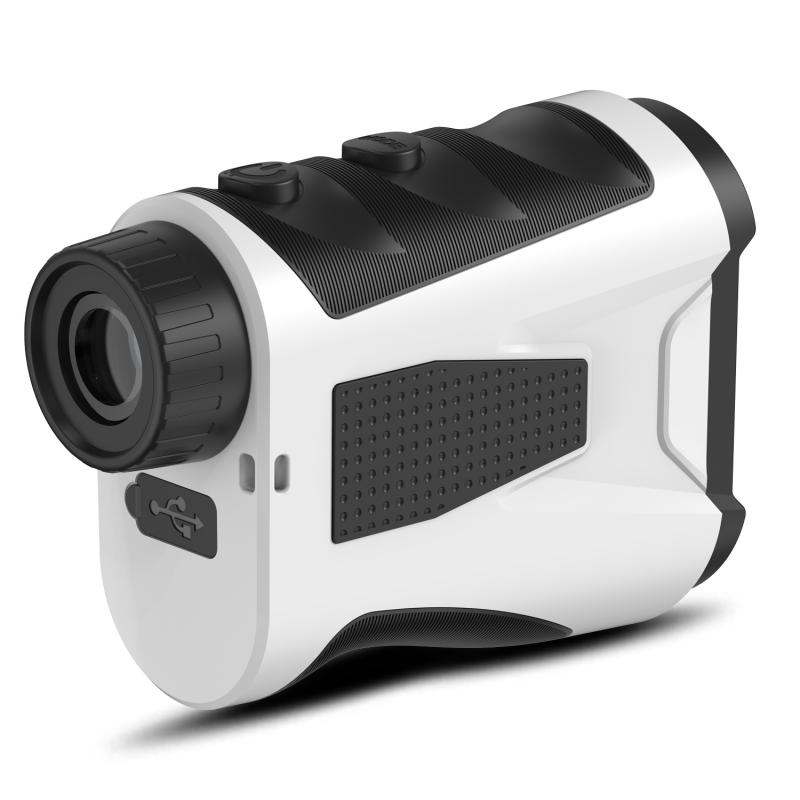

2、 Components and Functionality of Laser Rangefinders
A laser rangefinder is a device that uses laser technology to measure the distance between the device and a target. It works by emitting a laser beam towards the target and then measuring the time it takes for the beam to bounce back to the device. By knowing the speed of light, the rangefinder can calculate the distance based on the time it takes for the laser beam to return.
The components of a laser rangefinder typically include a laser diode, a receiver, a clock, and a microprocessor. The laser diode emits a short pulse of laser light towards the target. The receiver then detects the reflected laser light and converts it into an electrical signal. The clock measures the time it takes for the laser pulse to travel to the target and back, and the microprocessor calculates the distance based on this time measurement.
The functionality of a laser rangefinder is based on the principle of time-of-flight measurement. The rangefinder measures the time it takes for the laser pulse to travel to the target and back, and then uses this time to calculate the distance. This method is highly accurate and can provide precise distance measurements.
In recent years, there have been advancements in laser rangefinder technology. Some rangefinders now incorporate additional features such as angle compensation, which takes into account the angle between the device and the target to provide more accurate distance measurements. Additionally, there are rangefinders that can measure not only distance but also speed, making them useful for activities such as hunting or golfing.
Overall, laser rangefinders are reliable and efficient devices that provide accurate distance measurements. They are widely used in various fields such as surveying, construction, sports, and military applications. With ongoing advancements in technology, laser rangefinders continue to improve in terms of accuracy and functionality.
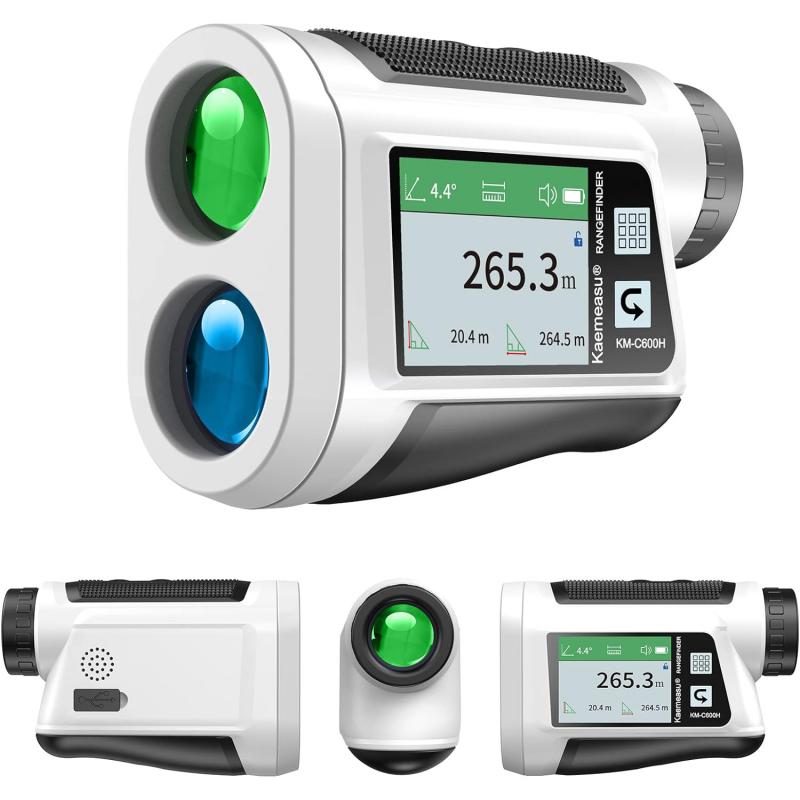

3、 Calculation of Distance using Laser Rangefinders
A laser rangefinder is a device that uses laser technology to measure the distance between the device and a target. It works by emitting a laser beam towards the target and then measuring the time it takes for the beam to bounce back to the device. By knowing the speed of light, the device can calculate the distance based on the time it takes for the laser beam to return.
The laser rangefinder consists of several components that work together to accurately measure distance. These include a laser diode, a receiver, and a microprocessor. The laser diode emits a short pulse of laser light towards the target. The receiver then detects the reflected light and measures the time it takes for the light to return.
To calculate the distance, the microprocessor uses the time-of-flight principle. It multiplies the time it takes for the laser beam to travel to the target and back by the speed of light to determine the total distance. This calculation is done in a matter of milliseconds, allowing for quick and accurate distance measurements.
In recent years, there have been advancements in laser rangefinder technology. Some devices now use multiple laser beams to improve accuracy and reduce errors caused by factors such as wind or movement. Additionally, some laser rangefinders can now measure not only distance but also other parameters like angle, speed, and even temperature.
Overall, laser rangefinders have become an essential tool in various fields such as surveying, hunting, and golfing. Their ability to quickly and accurately measure distances has made them invaluable for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
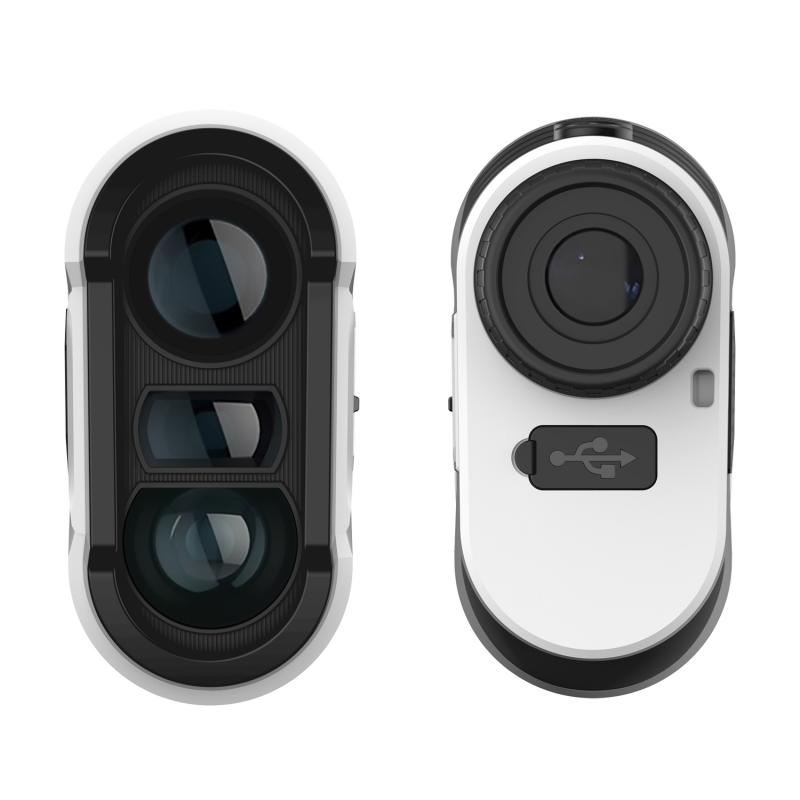

4、 Factors Affecting Accuracy in Laser Rangefinders
A laser rangefinder is a device that uses laser technology to measure the distance between the device and a target. It works by emitting a laser beam towards the target and measuring the time it takes for the beam to bounce back to the device. By knowing the speed of light, the device can calculate the distance accurately.
The laser rangefinder consists of several components, including a laser diode, a receiver, and a microprocessor. The laser diode emits a short pulse of laser light towards the target. The receiver detects the reflected light and measures the time it takes for the light to return. The microprocessor then calculates the distance based on the time measurement.
Factors affecting accuracy in laser rangefinders include:
1. Target Reflectivity: The accuracy of a laser rangefinder can be affected by the reflectivity of the target. Highly reflective surfaces, such as mirrors or glass, can cause the laser beam to bounce off at different angles, leading to inaccurate distance measurements.
2. Atmospheric Conditions: Atmospheric conditions, such as fog, rain, or dust, can scatter the laser beam and reduce its intensity. This scattering can affect the accuracy of the rangefinder, especially over long distances.
3. Target Size and Shape: The size and shape of the target can also affect the accuracy of the rangefinder. Small or irregularly shaped targets may not reflect the laser beam back to the device effectively, leading to inaccurate measurements.
4. User Error: User error, such as improper alignment or shaky hands, can also impact the accuracy of the rangefinder. It is important for the user to hold the device steady and aim it accurately at the target for precise measurements.
The latest point of view regarding accuracy in laser rangefinders involves advancements in technology. Manufacturers are continuously improving the design and performance of laser rangefinders to enhance accuracy. This includes the use of advanced algorithms and signal processing techniques to minimize errors caused by factors such as target reflectivity and atmospheric conditions. Additionally, some rangefinders now incorporate image stabilization technology to compensate for user movement and ensure more accurate measurements. These advancements aim to provide users with more reliable and precise distance measurements in various conditions.