What Are Filters In Photography ?
In photography, filters are accessories that are placed in front of the camera lens to alter or enhance the image being captured. They can be made of glass or plastic and come in various shapes and sizes. Filters serve different purposes and can be used for creative or technical reasons. Some common types of filters include:
1. UV filters: These filters are primarily used to protect the camera lens from scratches, dust, and moisture. They also help reduce the bluish cast that can occur in outdoor photography.
2. Polarizing filters: These filters are used to reduce glare and reflections from non-metallic surfaces such as water or glass. They also enhance color saturation and contrast in the image.
3. Neutral density (ND) filters: ND filters are designed to reduce the amount of light entering the camera without affecting the color or contrast. They are useful in situations where a slower shutter speed or wider aperture is desired, such as capturing motion blur or achieving a shallow depth of field in bright conditions.
4. Graduated neutral density (GND) filters: GND filters have a gradient effect, with one half being clear and the other half being neutral density. They are commonly used in landscape photography to balance the exposure between the bright sky and darker foreground.
These are just a few examples of the many filters available in photography, each serving a specific purpose to enhance or modify the captured image.
1、 Optical Filters: Enhance or alter light entering the camera lens.
Filters in photography are optical devices that are placed in front of the camera lens to enhance or alter the light entering the lens. They are used to manipulate the colors, contrast, and overall mood of a photograph, allowing photographers to achieve specific artistic effects or correct certain lighting conditions.
There are various types of filters available, each serving a different purpose. Some common types include color filters, neutral density filters, polarizing filters, and graduated filters. Color filters are used to modify the color balance of the image, either by intensifying or reducing certain colors. Neutral density filters reduce the amount of light entering the lens without affecting the color balance, allowing photographers to use slower shutter speeds or wider apertures in bright conditions. Polarizing filters reduce glare and reflections, enhance color saturation, and improve overall image clarity. Graduated filters are used to balance the exposure between the sky and the foreground in landscape photography.
In recent years, with the advancement of digital photography and post-processing software, the use of physical filters has somewhat declined. Many photographers now prefer to achieve similar effects through digital manipulation. However, there are still certain effects that are best achieved using physical filters, such as long exposure photography or reducing reflections in water or glass.
Overall, filters in photography provide photographers with a creative tool to enhance their images and achieve specific artistic effects. Whether it is to add drama to a landscape, correct lighting conditions, or create a unique color palette, filters continue to play a significant role in the world of photography.

2、 Color Filters: Modify color balance or create artistic effects.
Filters in photography are accessories that are placed in front of the camera lens to modify the way light enters the camera and interacts with the image sensor. These filters can have various effects on the final photograph, including altering color balance, creating artistic effects, or enhancing specific elements of the scene.
Color filters are one of the most commonly used types of filters in photography. They are designed to modify the color balance of the image by selectively allowing certain colors to pass through while blocking others. For example, a red filter will absorb most colors except for red, resulting in a photograph with enhanced red tones. Similarly, a blue filter will enhance blue tones, and so on. These filters can be used to create a specific mood or to correct color imbalances in a scene.
In addition to color correction, filters can also be used to create artistic effects. For instance, a polarizing filter can reduce glare and reflections, making colors appear more saturated and the sky bluer. Neutral density filters can be used to reduce the amount of light entering the camera, allowing for longer exposures or wider apertures in bright conditions. This can be particularly useful in landscape photography, where longer exposures can create a sense of motion in water or clouds.
With the advancements in digital photography, some photographers argue that the need for physical filters has diminished. Many of the effects that filters provide can now be achieved through post-processing techniques using software like Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom. However, there are still certain effects that are best achieved in-camera, such as long exposure photography or using graduated neutral density filters to balance exposure in high contrast scenes.
In conclusion, filters in photography, particularly color filters, play a crucial role in modifying the color balance and creating artistic effects in photographs. While some effects can now be replicated in post-processing, there are still certain effects that are best achieved using physical filters. Ultimately, the use of filters depends on the photographer's creative vision and the desired outcome for the photograph.

3、 Neutral Density Filters: Reduce the amount of light entering the lens.
Neutral density filters are essential tools in photography that help control the amount of light entering the camera lens. They are designed to evenly reduce the intensity of all wavelengths of light, without affecting the color or hue of the image. By doing so, neutral density filters allow photographers to achieve various creative effects and overcome challenging lighting conditions.
The primary purpose of neutral density filters is to reduce the amount of light reaching the camera's sensor. This is particularly useful in situations where there is too much light, such as when shooting in bright sunlight or capturing long exposures during the day. By using a neutral density filter, photographers can achieve slower shutter speeds, which can create motion blur effects or capture smooth, flowing water. Additionally, these filters enable wider apertures to be used in bright conditions, allowing for shallower depth of field and selective focus.
Neutral density filters come in different strengths, measured in stops, which determine the amount of light reduction they provide. Common strengths include 1-stop, 2-stop, and 3-stop filters, but stronger filters are also available for extreme light reduction. Some filters are adjustable, allowing photographers to vary the amount of light reduction by rotating the filter.
In recent years, neutral density filters have become increasingly popular among photographers due to the rise of long exposure photography and the desire to capture creative effects in-camera. They are widely used in landscape photography to capture the movement of clouds, waterfalls, or waves, creating a sense of motion and tranquility in the final image. Additionally, neutral density filters are also used in architectural photography to remove people or moving objects from crowded scenes, resulting in clean and uncluttered compositions.
In conclusion, neutral density filters are essential tools for photographers, allowing them to control the amount of light entering the lens and achieve creative effects. Whether it's capturing long exposures, controlling depth of field, or removing unwanted elements from a scene, these filters provide photographers with greater control over their images and enhance their creative possibilities.
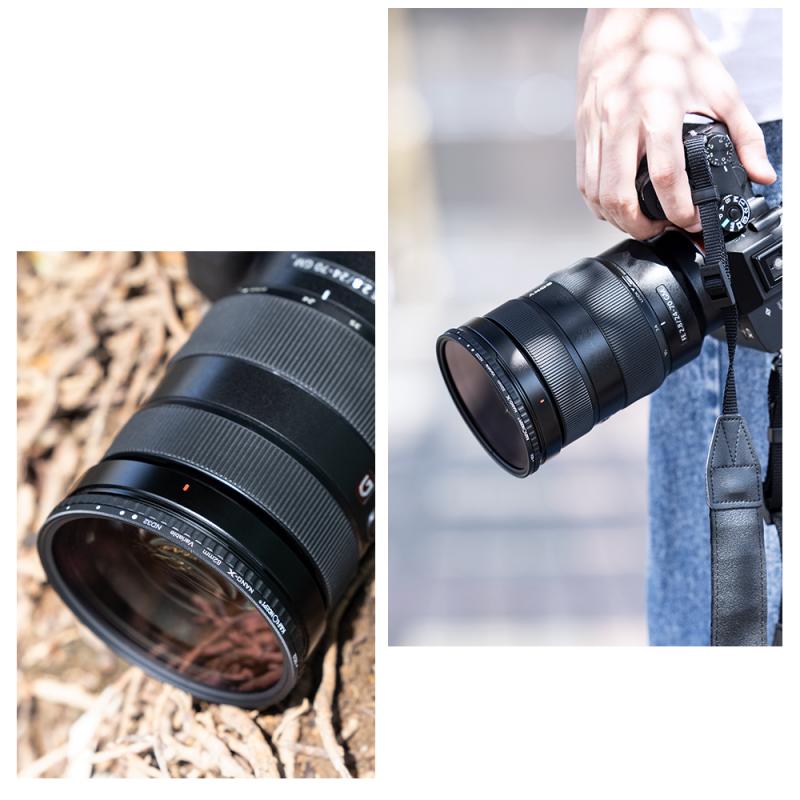

4、 Polarizing Filters: Minimize reflections and enhance color saturation.
Filters in photography are accessories that are placed in front of the camera lens to modify or enhance the image being captured. They can be made of glass or plastic and come in various shapes and sizes to fit different lenses.
One type of filter commonly used in photography is the polarizing filter. This filter is designed to minimize reflections and enhance color saturation in the image. It works by selectively blocking certain light waves that are responsible for causing reflections, resulting in a clearer and more vibrant image.
Polarizing filters are particularly useful when photographing scenes with water, glass, or other reflective surfaces. They can reduce glare and unwanted reflections, allowing the photographer to capture the true colors and details of the subject. For example, when photographing a landscape with a polarizing filter, the blue of the sky can be deepened, the clouds can be made more prominent, and the colors of foliage can be intensified.
In addition to reducing reflections, polarizing filters can also enhance the overall contrast of the image. They can darken the sky, making clouds stand out more, and increase the saturation of colors, making them appear more vibrant and rich.
It is worth noting that the effectiveness of a polarizing filter depends on the angle at which it is used. To achieve the desired effect, the photographer needs to rotate the filter until the reflections are minimized and the colors are enhanced. This adjustability allows for creative control and experimentation with different angles and lighting conditions.
In conclusion, polarizing filters are valuable tools in photography that can minimize reflections and enhance color saturation. They provide photographers with the ability to capture more vibrant and detailed images, particularly in scenes with reflective surfaces.