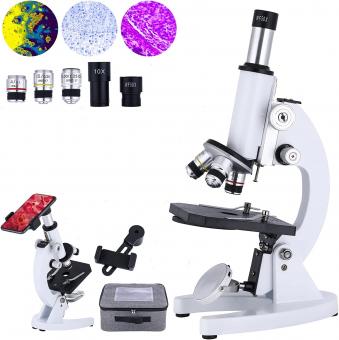
What Are The Steps To Focus A Microscope ?
To focus a microscope, follow these steps:
1. Start by placing a slide on the stage of the microscope.
2. Use the coarse adjustment knob to lower the stage until the slide is close to the objective lens.
3. Look through the eyepiece and adjust the interpupillary distance if needed.
4. Turn on the light source and adjust the intensity if necessary.
5. Begin focusing using the coarse adjustment knob, moving the stage upward until the image comes into view.
6. Once the image is visible, switch to the fine adjustment knob for precise focusing.
7. Adjust the diaphragm to control the amount of light passing through the slide.
8. If using a compound microscope, switch to a higher magnification objective lens and repeat the focusing process.
9. Fine-tune the focus as needed to obtain a clear and sharp image.
10. Once finished, turn off the light source and remove the slide from the stage.
Remember to handle the microscope with care and avoid touching the lenses with your fingers.
1、 Adjust the condenser
To focus a microscope, there are several steps that need to be followed. One of the important steps is to adjust the condenser. The condenser is a lens system located beneath the stage of the microscope, and it helps to focus the light onto the specimen.
To adjust the condenser, start by lowering it as close to the stage as possible. This will allow maximum light to pass through the specimen. Next, adjust the iris diaphragm, which is located within the condenser. Opening or closing the iris diaphragm will control the amount of light passing through the condenser. It is important to find the right balance of light, as too much or too little can affect the clarity of the image.
Once the condenser is properly adjusted, move on to adjusting the objective lenses. Start with the lowest power objective lens and gradually increase the magnification as needed. Use the coarse focus knob to bring the specimen into rough focus, and then use the fine focus knob to bring it into sharp focus. It is important to make small adjustments and take your time to ensure a clear image.
Lastly, it is important to consider the latest point of view when focusing a microscope. With advancements in technology, some microscopes now have autofocus capabilities. These microscopes use sensors to automatically adjust the focus, making the process easier and more efficient. Additionally, some microscopes now have digital imaging capabilities, allowing for real-time viewing and capturing of images. These advancements have greatly improved the accuracy and convenience of focusing a microscope.
In conclusion, adjusting the condenser is an important step in focusing a microscope. By properly adjusting the condenser, along with the objective lenses, one can achieve a clear and detailed image of the specimen. With the latest advancements in microscope technology, focusing has become even more precise and convenient.

2、 Set the lowest magnification objective lens
To focus a microscope, follow these steps:
1. Start by placing the microscope on a stable surface and ensure it is properly plugged in or has fresh batteries.
2. Turn on the microscope's light source, which is usually located at the base or near the stage. Adjust the intensity of the light as needed.
3. Set the lowest magnification objective lens (usually 4x or 10x) into position. This is the lens closest to the specimen and provides the widest field of view.
4. Place the specimen on the stage of the microscope. Use the stage clips or slide holder to secure it in place.
5. Adjust the stage height using the coarse focus knob until the specimen is approximately in focus. This knob is usually located on the side or underneath the stage.
6. Look through the eyepiece and use the fine focus knob to bring the specimen into sharp focus. This knob is usually located on the side of the microscope and allows for precise adjustments.
7. Once the specimen is in focus, you can increase the magnification by rotating the nosepiece to switch to a higher power objective lens. Repeat the fine focus adjustment to bring the specimen back into sharp focus.
8. If available, use the condenser adjustment knob to control the amount of light passing through the specimen. This can enhance the contrast and clarity of the image.
9. Finally, adjust the interpupillary distance by moving the eyepieces closer or further apart to match the distance between your eyes.
It is important to note that the specific steps may vary slightly depending on the type and model of microscope being used. Always refer to the manufacturer's instructions for the most accurate guidance. Additionally, newer microscopes may have digital features or automated focusing capabilities, which can simplify the process.

3、 Place the slide on the stage
To focus a microscope, there are several steps that need to be followed. The first step is to ensure that the microscope is properly set up on a stable surface. Once this is done, the next step is to place the slide on the stage of the microscope. The slide should be positioned in such a way that the area of interest is directly under the objective lens.
After placing the slide on the stage, the next step is to adjust the condenser. The condenser is responsible for focusing the light onto the specimen. By adjusting the condenser, the amount of light that passes through the specimen can be controlled, which in turn affects the clarity of the image.
Once the condenser is adjusted, the next step is to select the appropriate objective lens. Microscopes typically have multiple objective lenses with different magnification powers. The lowest magnification lens should be selected first, and then the focus can be adjusted using the coarse focus knob. The coarse focus knob moves the stage up and down, allowing for rough focusing of the image.
Once the image is roughly focused, the fine focus knob can be used to make finer adjustments. The fine focus knob moves the stage in smaller increments, allowing for precise focusing of the image. It is important to make small adjustments and check the focus frequently to ensure that the image is clear and sharp.
In addition to these steps, it is also important to consider other factors that can affect the focus of the microscope. These include adjusting the diaphragm to control the amount of light, using immersion oil for high magnification lenses, and ensuring that the microscope is properly cleaned and maintained.
Overall, focusing a microscope requires careful attention to detail and a systematic approach. By following these steps and considering other factors, one can achieve clear and sharp images through the microscope.

4、 Use coarse focus knob to bring the specimen into view
To focus a microscope, there are several steps that need to be followed. The process typically begins with placing the specimen on the stage and securing it in place using the stage clips. Once the specimen is in position, the following steps can be taken:
1. Start by using the lowest magnification objective lens. This will provide a wider field of view and make it easier to locate the specimen.
2. Adjust the light source to ensure proper illumination. This can be done by adjusting the diaphragm or iris control to control the amount of light passing through the specimen.
3. Look through the eyepiece and use the coarse focus knob to bring the specimen into view. This knob moves the stage up and down, allowing you to focus on the specimen. Begin by turning the knob in one direction until the specimen comes into view.
4. Once the specimen is in focus, use the fine focus knob to sharpen the image. This knob provides more precise control and allows for fine adjustments to the focus.
5. If needed, switch to a higher magnification objective lens to examine the specimen in more detail. Repeat the focusing process using the coarse and fine focus knobs as necessary.
It is important to note that different microscopes may have slightly different mechanisms for focusing. Some microscopes may have separate knobs for coarse and fine focus, while others may have a single knob that combines both functions. Additionally, some microscopes may have additional features such as a stage height adjustment or a focus lock to help maintain focus while changing magnification.