What Can You See With 2000x Magnification ?
With a 2000x magnification, you can see very fine details of objects that are not visible to the naked eye. This level of magnification allows you to observe the intricate structures of cells, bacteria, and other microorganisms. You can also examine the fine details of materials such as fibers, crystals, and minerals. Additionally, with this level of magnification, you can explore the surface features of small insects, plant structures, and even some small geological formations.
1、 Cellular Structures and Organelles
With a magnification of 2000x, one can observe a plethora of cellular structures and organelles that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. This level of magnification allows for a detailed examination of the intricate components that make up a cell, providing valuable insights into its structure and function.
At this magnification, one can clearly observe the nucleus, which houses the cell's genetic material, the DNA. The nucleus appears as a distinct, round structure within the cell, often surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. Within the nucleus, one may also observe the nucleolus, a dense region responsible for the production of ribosomes.
Moving beyond the nucleus, the cytoplasm becomes visible, revealing a network of membranous structures known as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The ER plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. It can appear as a series of interconnected tubes or flattened sacs, depending on the type of ER being observed.
Additionally, one can observe the Golgi apparatus, a stack of flattened membranous sacs responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins for transport within or outside the cell. The Golgi apparatus often appears as a series of closely packed, curved structures near the nucleus.
Mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, are also visible at this magnification. These bean-shaped organelles are responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration. They possess a double membrane, with the inner membrane forming folds called cristae, which increase the surface area for energy production.
Other cellular structures that can be observed include lysosomes, which contain enzymes for intracellular digestion, and peroxisomes, involved in detoxification processes. Additionally, one may observe various types of vesicles, vacuoles, and cytoskeletal elements such as microtubules and microfilaments.
It is important to note that advancements in microscopy techniques and technologies continue to enhance our understanding of cellular structures. Newer imaging methods, such as super-resolution microscopy, allow for even higher magnifications and improved resolution, enabling scientists to delve deeper into the intricate world of cellular structures and organelles.

2、 Microorganisms and Bacteria
With a magnification of 2000x, one can observe a wide range of microorganisms and bacteria that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. This level of magnification allows for detailed examination of their structures, behaviors, and interactions, providing valuable insights into the microscopic world.
At this magnification, one can observe various types of bacteria, such as cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), and spirilla (spiral-shaped). These bacteria can be found in diverse environments, including soil, water, and the human body. By studying their morphology, scientists can identify different species and understand their roles in ecosystems or their potential impact on human health.
Additionally, 2000x magnification enables the observation of microorganisms like protozoa, algae, and fungi. Protozoa are single-celled organisms that exhibit complex behaviors, such as movement and feeding. Algae, on the other hand, are photosynthetic microorganisms that play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems and are responsible for a significant portion of Earth's oxygen production. Fungi, including molds and yeasts, can also be observed at this magnification, allowing for the study of their structures and reproductive mechanisms.
It is important to note that advancements in microscopy techniques and technology have allowed for even higher magnifications and improved resolution. For instance, electron microscopy can achieve magnifications up to several million times, revealing even finer details of microorganisms and bacteria. This has led to groundbreaking discoveries in various fields, including medicine, environmental science, and biotechnology.
In conclusion, with a magnification of 2000x, one can observe a diverse array of microorganisms and bacteria, providing valuable insights into their structures and behaviors. However, it is worth noting that further advancements in microscopy techniques have allowed for even higher magnifications and more detailed observations.

3、 Tissue and Cell Morphology
With a magnification of 2000x, one can observe intricate details of tissue and cell morphology that are not visible to the naked eye or even at lower magnifications. This level of magnification allows for a closer examination of cellular structures, providing valuable insights into their composition and organization.
At 2000x magnification, one can observe the fine structures of cells, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and various cytoskeletal elements. The nucleus, often referred to as the control center of the cell, can be seen with greater clarity, revealing its distinct components like the nucleolus and chromatin. Mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, can be observed in greater detail, showcasing their inner membrane folds called cristae.
Furthermore, 2000x magnification allows for the visualization of cellular processes and interactions. For example, one can observe the movement of vesicles within the cell, the formation of cellular extensions like filopodia or lamellipodia, and the intricate network of microtubules and microfilaments that contribute to cell shape and movement.
In addition to cellular structures, 2000x magnification enables the examination of tissue morphology. Tissues are composed of specialized cells that work together to perform specific functions. With this level of magnification, one can observe the arrangement and organization of cells within a tissue, such as the layers of epithelial cells in the skin or the elongated muscle fibers in skeletal muscle tissue.
It is important to note that the latest advancements in microscopy techniques, such as confocal microscopy and super-resolution microscopy, have pushed the boundaries of magnification and resolution even further. These techniques allow for the visualization of cellular and tissue structures at an unprecedented level of detail, providing researchers with a deeper understanding of biological processes and disease mechanisms.
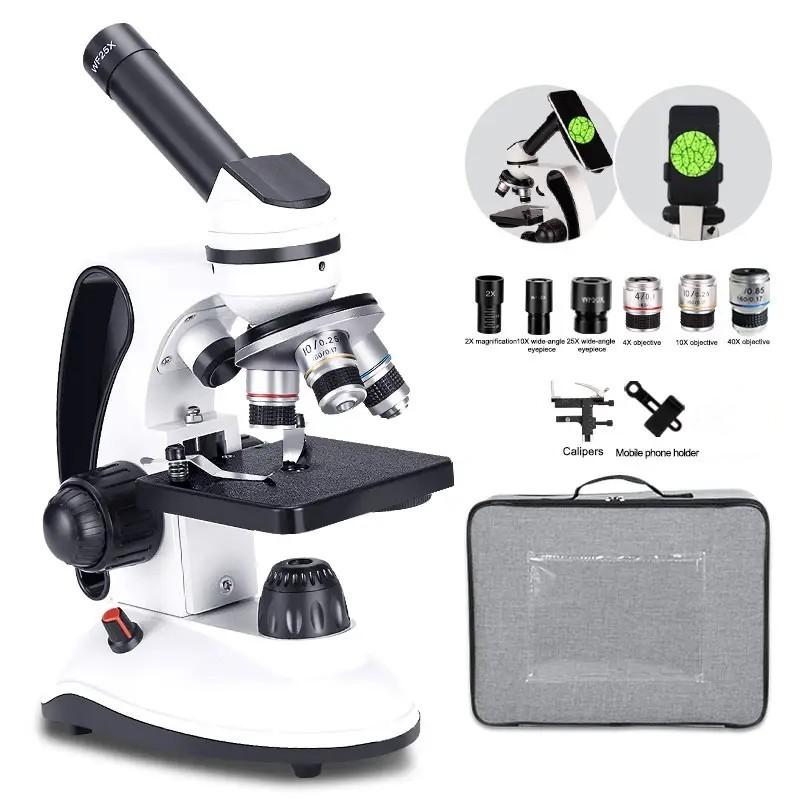
4、 Fine Details of Inorganic Materials
With a magnification of 2000x, one can observe the fine details of inorganic materials with exceptional clarity and precision. This level of magnification allows for a closer examination of the intricate structures and features of various substances, providing valuable insights into their composition and properties.
At this magnification, one can observe the intricate lattice structures of crystals, revealing the arrangement of atoms within the material. This level of detail is crucial in fields such as materials science and mineralogy, where understanding the crystal structure is essential for determining the properties and potential applications of a substance.
Additionally, 2000x magnification enables the observation of surface imperfections, such as cracks, scratches, or defects in materials. This level of scrutiny is particularly important in quality control and failure analysis, as it allows for the identification of potential weaknesses or manufacturing flaws that may affect the performance or durability of a product.
Furthermore, this level of magnification can reveal the presence of contaminants or impurities within a material. By examining the fine details, researchers can identify foreign particles or substances that may have unintentionally been introduced during the manufacturing process. This information is crucial for ensuring the purity and reliability of materials used in various industries, including electronics, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace.
It is important to note that the capabilities of microscopy techniques are continually advancing. With the latest advancements in technology, such as high-resolution electron microscopy, researchers can now achieve even higher magnifications and resolutions, allowing for an even more detailed examination of inorganic materials. These advancements have opened up new possibilities for studying nanoscale structures and phenomena, providing valuable insights into the world of materials science and nanotechnology.
In conclusion, with a magnification of 2000x, one can observe the fine details of inorganic materials, including crystal structures, surface imperfections, and the presence of contaminants. This level of magnification provides valuable information for various fields, from materials science to quality control, and continues to evolve with the latest advancements in microscopy technology.





























There are no comments for this blog.