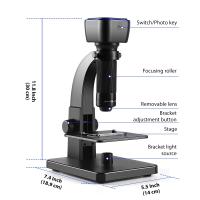
What Do The Parts Of The Microscope Do ?
The parts of a microscope have specific functions that contribute to its overall operation. The eyepiece, or ocular lens, is where the viewer looks through to observe the specimen. The objective lenses, located on a rotating nosepiece, provide different levels of magnification. The stage is where the specimen is placed for examination, and it often includes clips or a mechanical stage to hold the specimen in place. The condenser is responsible for focusing and directing light onto the specimen. The diaphragm controls the amount of light passing through the condenser. The coarse and fine focus knobs are used to adjust the focus of the microscope, bringing the specimen into clear view. Finally, the light source, typically located at the base of the microscope, provides illumination for the specimen.
1、 Objective lens: Magnifies the specimen.
The objective lens is an essential part of a microscope that plays a crucial role in magnifying the specimen. It is located near the bottom of the microscope and is responsible for gathering light from the specimen and forming a magnified image. The objective lens is typically made up of multiple lenses that work together to provide high-resolution and clear images.
When light passes through the specimen, the objective lens collects and focuses the light onto the intermediate image plane. This intermediate image is then further magnified by the eyepiece lens, allowing the viewer to see a highly magnified image of the specimen.
The objective lens is available in different magnification powers, typically ranging from 4x to 100x or higher. Each objective lens has a specific magnification power, and the user can switch between different objective lenses to achieve different levels of magnification.
In addition to magnification, the objective lens also determines the numerical aperture (NA) of the microscope. The NA is a measure of the lens's ability to gather light and resolve fine details. Higher NA objectives provide better resolution and allow for the visualization of smaller structures within the specimen.
Modern microscopes often come with a range of objective lenses, allowing users to select the appropriate lens for their specific needs. This flexibility in magnification and resolution enables scientists, researchers, and students to observe and study a wide range of specimens, from cells and tissues to microorganisms and nanoparticles.
In summary, the objective lens of a microscope is responsible for magnifying the specimen and gathering light to form a clear and detailed image. It is a critical component that allows for the visualization and study of microscopic structures and objects.

2、 Eyepiece lens: Further magnifies the image for the viewer.
The microscope is an essential tool used in various scientific fields to observe and study objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. It consists of several parts, each with a specific function that contributes to the overall magnification and clarity of the image.
The eyepiece lens, also known as the ocular lens, is located at the top of the microscope and is the part through which the viewer looks. Its primary function is to further magnify the image produced by the objective lens. The eyepiece lens typically has a magnification power of 10x, meaning it enlarges the image ten times for the viewer. This allows for a more detailed examination of the specimen.
In addition to magnification, the eyepiece lens also helps to focus the image and correct any aberrations or distortions that may occur. It is designed to provide a clear and sharp view of the specimen, ensuring accurate observations and analysis.
It is important to note that the latest advancements in microscope technology have led to the development of digital microscopes, which may have different features and capabilities. Some digital microscopes have built-in cameras that allow for direct viewing of the specimen on a computer screen, eliminating the need for an eyepiece lens. However, the basic principle of magnification and image clarity remains the same.
Overall, the eyepiece lens plays a crucial role in the functioning of a microscope by further magnifying the image and providing a clear view for the viewer. Its design and capabilities continue to evolve with advancements in technology, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of microscopic observations.

3、 Stage: Supports the specimen being observed.
The stage is an essential part of a microscope that supports the specimen being observed. It is a flat platform where the specimen is placed for examination. The stage typically has a hole or opening in the center to allow light to pass through and illuminate the specimen. It is usually equipped with clips or mechanical stage controls to secure the specimen in place and move it in different directions for better viewing.
The main function of the stage is to provide stability and support to the specimen, ensuring that it remains in focus during observation. It also allows for precise positioning and manipulation of the specimen, enabling the user to examine different areas of interest.
In addition to supporting the specimen, the stage may also have other features depending on the type of microscope. For example, in a compound microscope, the stage may have a condenser, which is a lens system that focuses and directs light onto the specimen. This helps to enhance the contrast and clarity of the image.
In more advanced microscopes, the stage may be motorized, allowing for automated scanning and imaging of multiple areas of the specimen. This can be particularly useful in research and diagnostic applications where large numbers of samples need to be analyzed.
Overall, the stage of a microscope plays a crucial role in providing a stable platform for specimen observation and manipulation. It ensures that the specimen remains in focus and allows for precise positioning, ultimately enabling detailed examination and analysis.

4、 Condenser: Focuses light onto the specimen.
The parts of a microscope play crucial roles in the functioning of the instrument. One of these important parts is the condenser. The condenser is responsible for focusing light onto the specimen being observed. It is located beneath the stage and consists of lenses that help concentrate and direct the light towards the specimen.
The main function of the condenser is to enhance the illumination of the specimen. By focusing the light, it increases the clarity and visibility of the object under observation. This is particularly important when studying small or transparent specimens that may be difficult to see without proper illumination.
The condenser also helps control the amount of light that reaches the specimen. By adjusting the position of the condenser, the user can regulate the intensity of the light, which is especially useful when dealing with specimens that require different levels of illumination.
In addition to focusing and controlling light, the condenser also plays a role in improving the resolution of the microscope. By concentrating the light onto the specimen, it increases the contrast and sharpness of the image, allowing for better observation and analysis.
It is worth noting that the role and design of the condenser may vary depending on the type of microscope being used. For example, in some microscopes, the condenser may have additional features such as an iris diaphragm, which further controls the amount of light passing through.
In conclusion, the condenser is an essential part of the microscope that focuses light onto the specimen, enhances illumination, controls light intensity, and improves resolution. Its proper use and adjustment are crucial for obtaining clear and detailed images during microscopic observations.