What Does The Head Do On A Microscope ?
The head on a microscope is the part that holds the eyepiece and the objective lenses. It allows the user to adjust the position of the lenses and the focus of the microscope. The head can also be rotated to change the orientation of the image being viewed.
1、 Magnification
The head of a microscope is an essential component that houses the eyepiece and objective lenses. The primary function of the head is to provide a platform for the user to view the magnified image of the specimen. The head of a microscope is designed to allow the user to adjust the focus and magnification of the image. The head can be rotated to change the angle of the eyepiece, which makes it easier for the user to view the specimen from different angles.
Magnification is the process of enlarging the size of an object. In microscopy, magnification is achieved by using a combination of lenses that increase the size of the image of the specimen. The head of a microscope plays a crucial role in magnification by housing the objective lenses. The objective lenses are responsible for magnifying the image of the specimen, and the head allows the user to switch between different objective lenses to achieve different levels of magnification.
In recent years, there has been a significant advancement in microscope technology, which has led to the development of high-resolution microscopes. These microscopes use advanced imaging techniques such as confocal microscopy and super-resolution microscopy to achieve higher magnification and resolution. The head of these microscopes is designed to accommodate these advanced imaging techniques, allowing the user to achieve higher magnification and resolution than ever before.
In conclusion, the head of a microscope is an essential component that plays a crucial role in magnification. It houses the objective lenses and allows the user to adjust the focus and magnification of the image. With the latest advancements in microscope technology, the head of a microscope has become even more critical in achieving higher magnification and resolution.

2、 Resolution
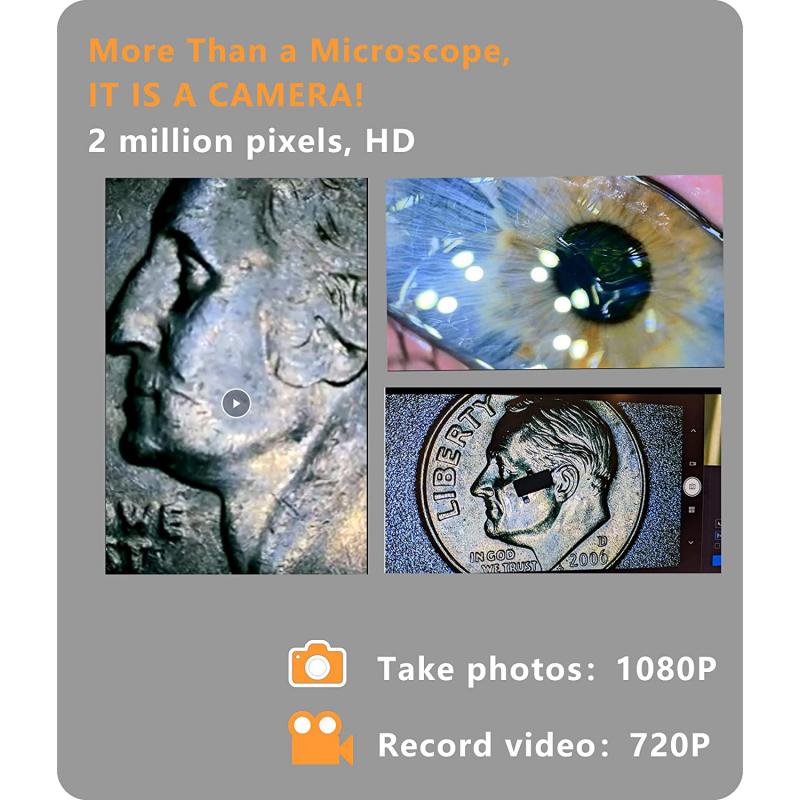
What does the head do on a microscope? The head of a microscope is an essential component that holds the eyepiece and objective lenses. It allows the user to adjust the focus and magnification of the specimen being observed. The head can be rotated to change the angle of the eyepiece, making it more comfortable for the user to view the specimen. Additionally, some microscope heads have a built-in camera that allows for digital imaging and recording of the specimen.
One of the most critical aspects of the head of a microscope is its impact on resolution. Resolution refers to the ability of a microscope to distinguish between two closely spaced objects. The head of a microscope plays a crucial role in determining the resolution of the microscope. The quality of the lenses, the distance between the lenses, and the angle of the lenses all affect the resolution of the microscope.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in improving the resolution of microscopes beyond the traditional limits of light microscopy. This has led to the development of new techniques such as super-resolution microscopy, which uses advanced imaging methods to achieve resolutions beyond the diffraction limit of light. These techniques require specialized microscope heads that can accommodate the complex imaging systems needed to achieve super-resolution.
In conclusion, the head of a microscope is a critical component that plays a vital role in determining the resolution and overall performance of the microscope. As technology advances, the design and capabilities of microscope heads will continue to evolve to meet the demands of modern microscopy techniques.
3、 Illumination
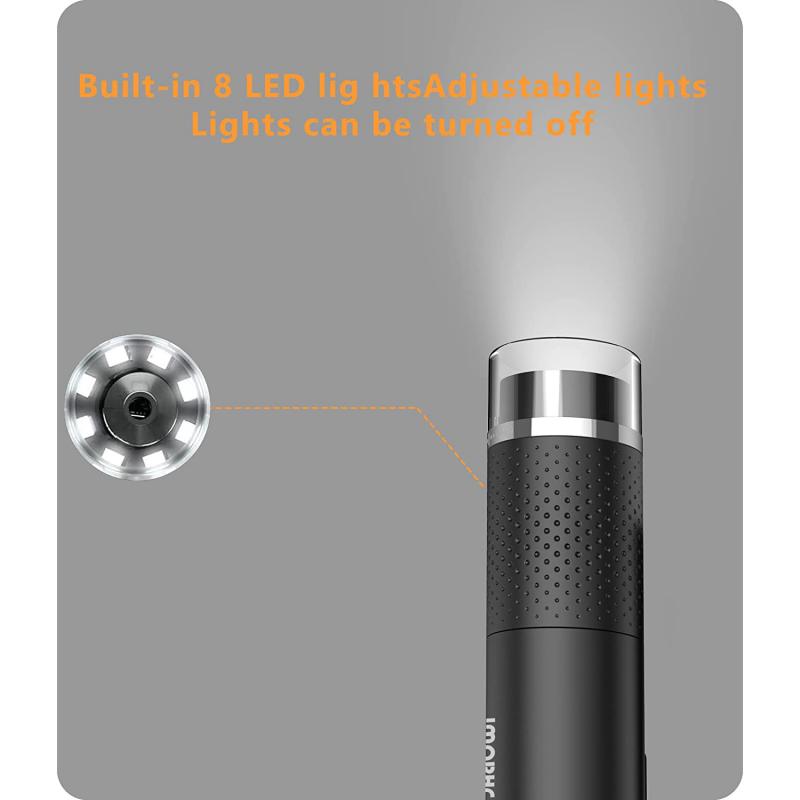
The head of a microscope is an essential component that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the microscope. The head of a microscope is responsible for providing illumination to the specimen being observed. The illumination is necessary to enhance the contrast and visibility of the specimen, making it easier to observe and study.
The head of a microscope typically contains a light source, which can be either a bulb or an LED. The light source is directed towards the specimen through a series of lenses and mirrors, which help to focus and direct the light onto the specimen. The head of the microscope also contains a condenser lens, which helps to focus the light onto the specimen, further enhancing the visibility and contrast.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of digital microscopes, which use advanced imaging technologies to provide high-resolution images of specimens. These microscopes often incorporate advanced illumination systems, such as LED lighting and fluorescence microscopy, which allow for more detailed and accurate observations of specimens.
Overall, the head of a microscope is a critical component that plays a vital role in the functioning of the microscope. It provides the necessary illumination to enhance the visibility and contrast of the specimen, making it easier to observe and study. With the advent of digital microscopes and advanced imaging technologies, the role of the head of the microscope has become even more critical in providing accurate and detailed observations of specimens.

4、 Focusing
The head of a microscope is an essential component that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the instrument. The head is the uppermost part of the microscope that houses the eyepiece and the objective lenses. The primary function of the head is to provide a means of focusing the image of the specimen being viewed.
Focusing is the process of adjusting the microscope's lenses to obtain a clear and sharp image of the specimen. The head of the microscope contains the eyepiece, which is responsible for magnifying the image produced by the objective lens. The objective lens, on the other hand, is responsible for producing the initial image of the specimen.
To focus the microscope, the user adjusts the position of the objective lens by turning the focusing knob. This movement changes the distance between the objective lens and the specimen, allowing the user to obtain a clear and sharp image. The head of the microscope also contains the diopter adjustment, which allows the user to adjust the focus of the eyepiece to match their individual eyesight.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of digital microscopes that use cameras to capture images of the specimen. These microscopes have eliminated the need for the user to adjust the focus manually, as the camera can automatically adjust the focus to obtain a clear image. However, the head of the microscope remains an essential component in both traditional and digital microscopes, as it houses the eyepiece and objective lenses that are necessary for viewing the specimen.







































