What Has The Microscope Discovered ?
The microscope has discovered a vast array of microscopic organisms, such as bacteria and protozoa, that were previously unknown to humans. It has also revealed the intricate structures and functions of cells, allowing for a deeper understanding of biology and medicine. Additionally, the microscope has enabled scientists to observe and study the details of various tissues, organs, and organisms, leading to advancements in fields like anatomy, pathology, and genetics. Furthermore, the microscope has played a crucial role in the discovery and exploration of the microscopic world, uncovering phenomena like mitosis, meiosis, and the existence of subcellular structures like mitochondria and ribosomes. Overall, the microscope has revolutionized scientific research and has been instrumental in expanding our knowledge of the natural world.
1、 Microorganisms and their role in disease transmission.
Microorganisms and their role in disease transmission have been extensively studied and discovered through the use of microscopes. The microscope has revolutionized our understanding of the invisible world of microorganisms, revealing their intricate structures, behaviors, and their impact on human health.
One of the most significant discoveries made using microscopes is the identification of various disease-causing microorganisms. For instance, the microscope played a crucial role in the discovery of bacteria, such as the ones responsible for tuberculosis, cholera, and pneumonia. It allowed scientists to observe these microorganisms in detail, understand their morphology, and develop effective treatments and preventive measures.
Furthermore, the microscope has also revealed the existence of viruses, which are smaller than bacteria and cannot be seen with the naked eye. Viruses, such as the influenza virus and the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), have been identified and studied using electron microscopes. This knowledge has been instrumental in developing vaccines and antiviral medications to combat these diseases.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy techniques have allowed scientists to delve even deeper into the world of microorganisms. For example, the development of confocal microscopy and super-resolution microscopy has enabled researchers to visualize microorganisms at the molecular level. This has led to a better understanding of their mechanisms of action, interactions with host cells, and the development of drug resistance.
Moreover, the use of microscopes has also shed light on the role of microorganisms in the human microbiome. The human body is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiota, which play a crucial role in maintaining our health. Microscopy techniques have allowed scientists to study the composition and function of the microbiota, leading to insights into its role in digestion, immune function, and even mental health.
In conclusion, the microscope has been instrumental in discovering and understanding microorganisms and their role in disease transmission. From identifying disease-causing bacteria and viruses to exploring the human microbiome, microscopy has provided invaluable insights into the invisible world of microorganisms. With ongoing advancements in microscopy techniques, we can expect further discoveries and a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between microorganisms and human health.
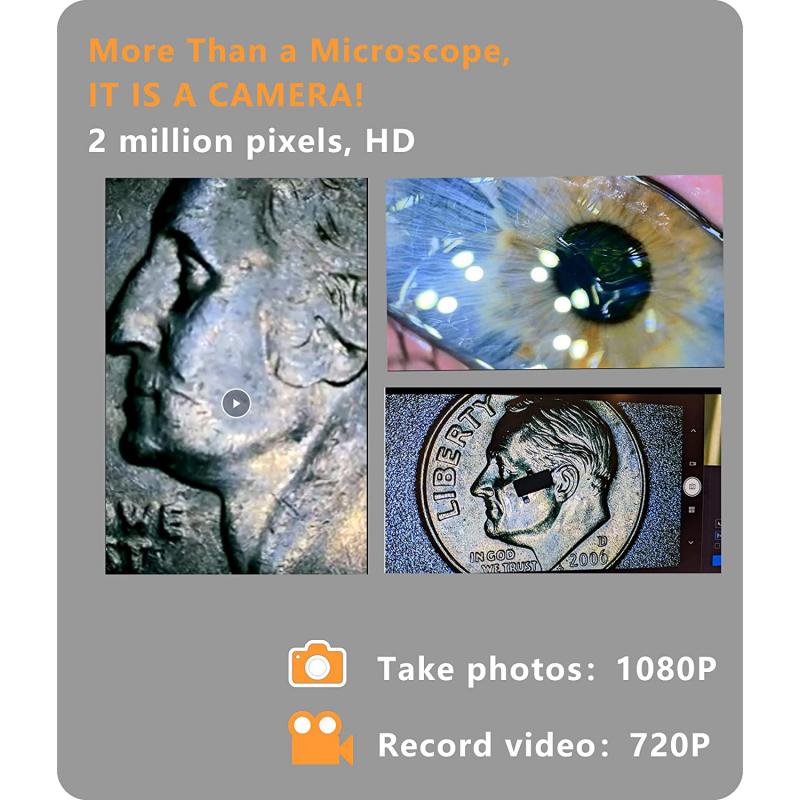
2、 Cellular structures and organelles.
The microscope has been an invaluable tool in the field of biology, allowing scientists to explore the intricate world of cellular structures and organelles. Through the use of various types of microscopes, researchers have made groundbreaking discoveries that have revolutionized our understanding of life at the microscopic level.
One of the most significant discoveries made using the microscope is the existence of cells. In the 17th century, Robert Hooke observed thin slices of cork under a microscope and described the structures he saw as "cells," which resembled the small rooms monks lived in. This discovery laid the foundation for the cell theory, which states that all living organisms are composed of cells.
As technology advanced, more detailed observations of cellular structures and organelles became possible. The development of electron microscopy in the mid-20th century allowed scientists to visualize organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and nucleus in greater detail. This led to a deeper understanding of their functions within the cell.
Furthermore, the microscope has played a crucial role in unraveling the complexities of cellular processes. For example, the discovery of mitosis and meiosis, the processes by which cells divide, was made possible through microscopic observations. These findings have been instrumental in understanding how organisms grow, develop, and reproduce.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy techniques, such as super-resolution microscopy, have pushed the boundaries of what can be observed. This has allowed scientists to visualize cellular structures and organelles with unprecedented clarity and detail. For instance, super-resolution microscopy has revealed the intricate architecture of the cytoskeleton, a network of protein filaments that provides structural support to cells.
Moreover, the microscope has been instrumental in studying diseases at the cellular level. By examining diseased tissues and cells under the microscope, researchers have gained insights into the mechanisms underlying various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and infectious diseases. This knowledge has paved the way for the development of targeted therapies and interventions.
In conclusion, the microscope has been a powerful tool in uncovering the hidden world of cellular structures and organelles. From the initial discovery of cells to the latest advancements in microscopy techniques, it has provided scientists with a window into the intricate workings of life at the microscopic level. The continuous exploration and understanding of cellular structures and organelles will undoubtedly lead to further breakthroughs in biology and medicine.

3、 The complexity of biological systems at the microscopic level.
The microscope has been an invaluable tool in the field of biology, allowing scientists to explore and understand the intricate details of living organisms at the microscopic level. Over the years, it has made numerous discoveries that have revolutionized our understanding of the complexity of biological systems.
One of the most significant discoveries made using the microscope is the existence of cells. In the 17th century, Robert Hooke observed and coined the term "cell" while examining a thin slice of cork under a microscope. This discovery laid the foundation for the cell theory, which states that all living organisms are composed of cells. Since then, the microscope has enabled scientists to delve deeper into the structure and function of cells, revealing their various organelles and their roles in maintaining life.
Furthermore, the microscope has allowed scientists to study microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses, which were previously invisible to the naked eye. This has led to groundbreaking discoveries in the field of microbiology, including the identification of disease-causing pathogens and the development of antibiotics and vaccines.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy techniques have further expanded our understanding of biological systems. For instance, the development of electron microscopy has allowed scientists to visualize structures at an even higher resolution, revealing intricate details of cellular components and their interactions. Additionally, the advent of fluorescence microscopy has enabled the visualization of specific molecules within cells, providing insights into their localization and dynamics.
Moreover, the microscope has played a crucial role in the field of genetics. It has allowed scientists to observe and study chromosomes, DNA, and genes, unraveling the mechanisms of inheritance and genetic disorders. The ability to visualize and manipulate genetic material under the microscope has paved the way for advancements in genetic engineering and gene therapy.
In conclusion, the microscope has been instrumental in uncovering the complexity of biological systems at the microscopic level. From the discovery of cells to the visualization of cellular structures and genetic material, it has revolutionized our understanding of life itself. With ongoing advancements in microscopy techniques, we can expect further discoveries that will continue to shape our knowledge of the intricate workings of living organisms.

4、 The existence of previously unknown microscopic organisms.
The microscope has been an invaluable tool in the field of biology, allowing scientists to explore the intricate world of the microscopic. Over the years, it has made numerous groundbreaking discoveries, shedding light on the hidden wonders of the microscopic realm. One of the most significant findings facilitated by the microscope is the existence of previously unknown microscopic organisms.
Before the invention of the microscope, the existence of microscopic life was largely unknown. However, with the advent of this powerful instrument, scientists were able to observe and study organisms that were too small to be seen with the naked eye. This discovery revolutionized our understanding of life on Earth, revealing a vast array of microscopic organisms that play crucial roles in various ecosystems.
Microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, archaea, and protists, were found to be abundant in almost every environment, from the depths of the ocean to the soil beneath our feet. These organisms are involved in essential ecological processes, such as nutrient cycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships. Moreover, they have been found to have significant impacts on human health, both positive and negative.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy techniques have further expanded our knowledge of microscopic organisms. High-resolution microscopy, such as electron microscopy and super-resolution microscopy, has allowed scientists to visualize these organisms in unprecedented detail. This has led to the discovery of new species and the exploration of their intricate structures and behaviors.
Furthermore, the microscope has also revealed the existence of previously unknown interactions between microscopic organisms and their environment. For example, scientists have discovered intricate microbial communities, known as biofilms, which play a crucial role in various processes, including disease formation and water purification.
In conclusion, the microscope has been instrumental in uncovering the existence of previously unknown microscopic organisms. Its invention has revolutionized our understanding of life on Earth, revealing the immense diversity and importance of these tiny organisms. With ongoing advancements in microscopy techniques, we can expect further discoveries that will continue to expand our knowledge of the microscopic world and its significance in various fields, from ecology to medicine.