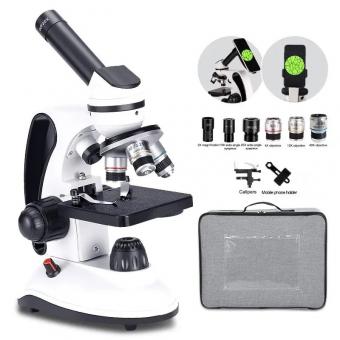
What Is A Compound Light Microscope ?
A compound light microscope is a type of microscope that uses multiple lenses to magnify the image of a specimen. It consists of two or more lenses, typically an objective lens and an eyepiece lens, which work together to produce a magnified image. The objective lens is positioned close to the specimen and collects light rays from it, while the eyepiece lens further magnifies the image for the viewer. The compound light microscope utilizes visible light as its source of illumination, which passes through the specimen and lenses to create a magnified and focused image. This type of microscope is commonly used in various scientific fields, such as biology and medicine, for observing small organisms, cells, tissues, and other microscopic structures.
1、 Optical system
A compound light microscope is an optical instrument that uses a series of lenses to magnify small objects or organisms that are not visible to the naked eye. It is called a compound microscope because it uses two sets of lenses - the objective lens and the eyepiece lens - to produce a magnified image.
The optical system of a compound light microscope consists of several key components. The objective lens is located near the specimen and is responsible for gathering light and forming a magnified image. The eyepiece lens, also known as the ocular lens, is positioned at the top of the microscope and further magnifies the image produced by the objective lens. The combination of these lenses allows for high magnification and resolution.
In addition to the lenses, the optical system of a compound light microscope also includes a light source, typically located at the base of the microscope. This light source illuminates the specimen, allowing it to be seen more clearly. Some microscopes also have adjustable diaphragms or filters to control the intensity and direction of the light.
The compound light microscope has been a fundamental tool in scientific research and education for centuries. It has enabled scientists to study the intricate details of cells, microorganisms, and other small structures. With advancements in technology, modern compound microscopes now often include features such as digital imaging capabilities, allowing for the capture and analysis of images on a computer.
In conclusion, a compound light microscope is an optical system that utilizes lenses to magnify small objects. It has played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the microscopic world and continues to be an essential tool in various scientific disciplines.
2、 Illumination system
A compound light microscope is a type of microscope that uses multiple lenses to magnify and observe small objects or organisms. It is called a compound microscope because it utilizes two sets of lenses - the objective lens and the eyepiece lens - to produce a magnified image.
The illumination system is an essential component of a compound light microscope. It consists of a light source, typically an incandescent bulb or LED, which provides the necessary illumination to view the specimen. The light passes through a condenser lens, which focuses and directs the light onto the specimen. This ensures that the specimen is evenly illuminated, allowing for clear and detailed observation.
The illumination system plays a crucial role in enhancing the visibility and contrast of the specimen. Different techniques can be employed to optimize the illumination, such as adjusting the intensity of the light source or using filters to control the wavelength of light. These techniques help to highlight specific features of the specimen and improve the overall image quality.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated illumination systems for compound light microscopes. For instance, some microscopes now incorporate LED light sources, which offer several advantages over traditional incandescent bulbs, including longer lifespan, lower energy consumption, and better control over the intensity and color of the light. Additionally, advanced imaging techniques, such as fluorescence microscopy, utilize specific wavelengths of light to visualize specific structures or molecules within the specimen.
Overall, the illumination system is a critical component of a compound light microscope, enabling scientists and researchers to observe and study microscopic objects with greater clarity and precision.

3、 Stage and specimen holder
A compound light microscope is a type of microscope that uses multiple lenses to magnify small objects or specimens. It is called a compound microscope because it uses two sets of lenses - the objective lens and the eyepiece lens - to produce a magnified image. The objective lens is located near the specimen and provides the initial magnification, while the eyepiece lens further magnifies the image for the viewer.
One of the key components of a compound light microscope is the stage and specimen holder. The stage is a flat platform where the specimen is placed for observation. It typically has a hole or opening in the center to allow light to pass through the specimen. The specimen holder, also known as a slide holder or stage clips, is used to secure the specimen in place on the stage. It ensures that the specimen remains in focus and does not move during observation.
The stage and specimen holder have evolved over time to accommodate different types of specimens and improve the overall functionality of the microscope. Modern microscopes often have adjustable stages that can move in multiple directions, allowing for precise positioning of the specimen. Some stages also come with mechanical controls that enable the user to move the specimen smoothly and accurately.
Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of specialized specimen holders. For example, there are holders designed specifically for holding slides, petri dishes, or even live specimens. These holders provide stability and ease of use, allowing researchers and scientists to study a wide range of specimens with greater convenience and accuracy.
In conclusion, the stage and specimen holder are essential components of a compound light microscope. They provide a stable platform for observing specimens and have evolved to meet the needs of modern microscopy techniques.

4、 Objective lenses
A compound light microscope is a type of microscope that uses multiple lenses to magnify small objects or organisms. It is called a compound microscope because it uses two sets of lenses - the objective lenses and the eyepiece lenses - to produce a magnified image.
The objective lenses are the primary lenses of the compound microscope. They are located on a rotating nosepiece and are available in different magnification powers, typically ranging from 4x to 100x. These lenses are responsible for gathering light from the specimen and forming a magnified image. The magnification power of the objective lenses is usually indicated on the side of each lens.
The eyepiece lenses, also known as the ocular lenses, are located at the top of the microscope and are the lenses that the viewer looks through. They further magnify the image produced by the objective lenses, typically by 10x. The combination of the magnification power of the objective lenses and the eyepiece lenses determines the total magnification of the microscope.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated compound light microscopes. These microscopes often include additional features such as digital imaging capabilities, allowing users to capture and analyze images on a computer. Some microscopes also incorporate fluorescent imaging techniques, enabling the visualization of specific molecules or structures within a specimen.
Overall, the compound light microscope remains a fundamental tool in various scientific fields, including biology, medicine, and materials science. Its ability to provide high-resolution images of microscopic objects has revolutionized our understanding of the natural world and continues to contribute to new discoveries and advancements in scientific research.