What Is A Dissecting Microscope Used For ?
A dissecting microscope, also known as a stereo microscope, is used for observing and manipulating larger specimens that cannot be viewed under a regular compound microscope. It provides a three-dimensional view of the specimen, allowing for detailed examination of its surface and structure. This type of microscope is commonly used in fields such as biology, botany, entomology, and forensic science, where the examination of larger objects is necessary. It is particularly useful for tasks like dissection, sorting, and identification of specimens, as well as for conducting detailed inspections and measurements. The dissecting microscope typically has lower magnification power compared to a compound microscope, but it compensates for this with a wider field of view and greater depth of focus, enabling researchers to work with larger samples and maintain a clear view of the specimen at different angles.
1、 Magnifying small specimens for detailed examination and dissection.
A dissecting microscope, also known as a stereo microscope, is a specialized optical instrument used for magnifying small specimens for detailed examination and dissection. It provides a three-dimensional view of the specimen, allowing scientists and researchers to observe and manipulate the object with precision.
The primary purpose of a dissecting microscope is to study specimens that are too small to be seen clearly with the naked eye. It is commonly used in various scientific fields such as biology, botany, entomology, and forensic science. This type of microscope is particularly useful when working with larger specimens that require a greater working distance and a wider field of view.
One of the key features of a dissecting microscope is its ability to provide a stereoscopic image. This means that it presents a three-dimensional view of the specimen, allowing for better depth perception and spatial awareness. This feature is especially important when conducting delicate dissections or manipulations, as it enables researchers to accurately navigate and identify specific structures within the specimen.
In addition to magnification and stereoscopic imaging, dissecting microscopes often come equipped with adjustable lighting sources. This allows researchers to illuminate the specimen from different angles, enhancing visibility and highlighting specific details. Some advanced models also offer features like zoom capabilities, digital imaging, and video recording, enabling researchers to capture and document their observations.
In recent years, there have been advancements in imaging technology that have further enhanced the capabilities of dissecting microscopes. For example, the integration of digital cameras and software has made it easier to capture high-resolution images and share them with colleagues or analyze them using image processing techniques. Additionally, the development of fluorescence microscopy techniques has allowed for the visualization of specific structures or molecules within the specimen, opening up new avenues for research and discovery.
Overall, the dissecting microscope continues to be an essential tool in scientific research, enabling scientists to explore and understand the intricate details of small specimens. Its versatility, ease of use, and ability to provide a three-dimensional view make it an invaluable instrument in various fields of study.

2、 Enhancing visibility of intricate structures in biological samples.
A dissecting microscope, also known as a stereo microscope, is a specialized optical instrument used to enhance the visibility of intricate structures in biological samples. It is designed to provide a three-dimensional view of the specimen, allowing researchers to observe and manipulate small objects with precision.
One of the primary uses of a dissecting microscope is in the field of biology, particularly in the study of small organisms or tissues. It enables scientists to examine the external features of specimens in detail, such as the surface of an insect, the petals of a flower, or the structure of a small organ. By magnifying the sample, the microscope allows for a closer examination of these intricate structures, aiding in the identification and classification of organisms.
In addition to biological research, dissecting microscopes are also widely used in various other fields. For example, they are commonly employed in the field of forensic science to analyze evidence such as hair, fibers, or fingerprints. They are also utilized in the field of entomology to study insects, in the field of botany to examine plant structures, and in the field of geology to analyze rocks and minerals.
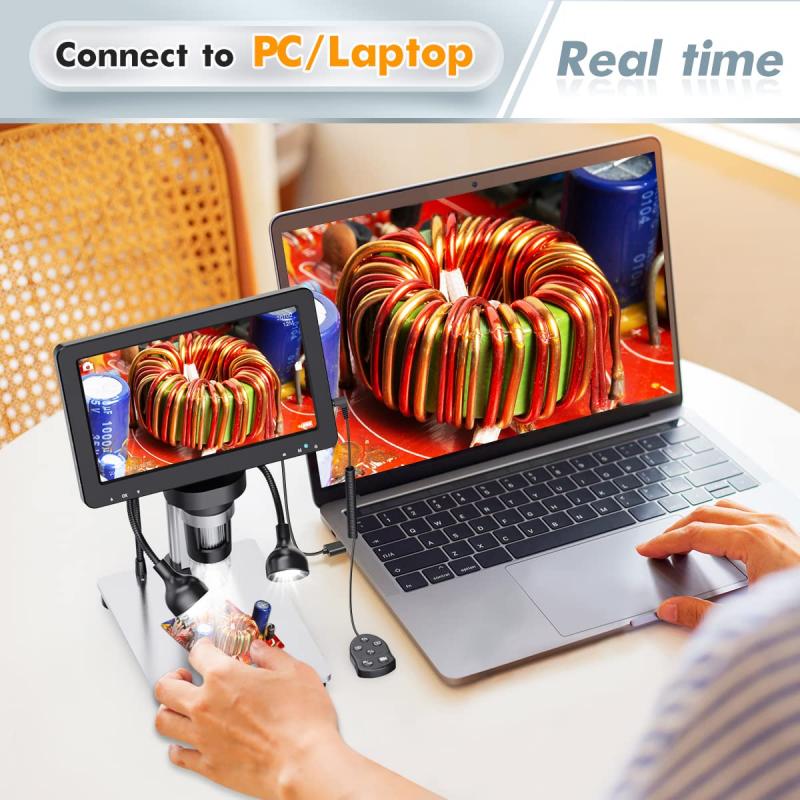
With advancements in technology, modern dissecting microscopes often come equipped with additional features such as built-in cameras or digital imaging capabilities. This allows researchers to capture high-resolution images or videos of the specimens, facilitating documentation and analysis. Furthermore, some microscopes offer the ability to perform fluorescence imaging, enabling the visualization of specific structures or molecules within the sample.
In conclusion, a dissecting microscope is primarily used to enhance the visibility of intricate structures in biological samples. Its applications extend beyond biology and are utilized in various scientific fields for detailed examination and analysis. The latest advancements in technology have further improved the capabilities of dissecting microscopes, enabling researchers to capture and analyze specimens with greater precision and efficiency.

3、 Enabling precise dissection and manipulation of tiny organisms or tissues.
A dissecting microscope, also known as a stereo microscope, is a specialized tool used in various scientific fields to enable precise dissection and manipulation of tiny organisms or tissues. It provides a three-dimensional view of the specimen, allowing researchers to observe and work on it with enhanced depth perception.
One of the primary uses of a dissecting microscope is in biological research, particularly in the field of anatomy and histology. It allows scientists to examine small organisms or tissues in detail, making it easier to identify and study their structures and functions. This is particularly useful when studying delicate or complex structures that cannot be easily observed with a regular microscope.
In addition to biological research, dissecting microscopes are also widely used in fields such as entomology, botany, and forensic science. Entomologists use these microscopes to study insects, their anatomy, and behavior. Botanists use them to examine plant structures, such as flowers, leaves, and seeds. Forensic scientists use dissecting microscopes to analyze evidence, such as hair, fibers, or small fragments, in criminal investigations.
Moreover, dissecting microscopes have found applications in the field of electronics and engineering. They are used to inspect and manipulate small components, such as circuit boards or microchips, with precision. This is crucial in industries like electronics manufacturing or quality control, where tiny defects or irregularities can have significant consequences.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of digital dissecting microscopes. These microscopes are equipped with cameras and software that allow researchers to capture high-resolution images and videos of the specimens. This enables easier documentation, sharing, and analysis of the observed structures, enhancing collaboration and research efficiency.
Overall, a dissecting microscope is an essential tool in various scientific disciplines, enabling researchers to explore and understand the intricate details of tiny organisms or tissues. Its versatility and precision make it a valuable asset in scientific research, education, and industrial applications.
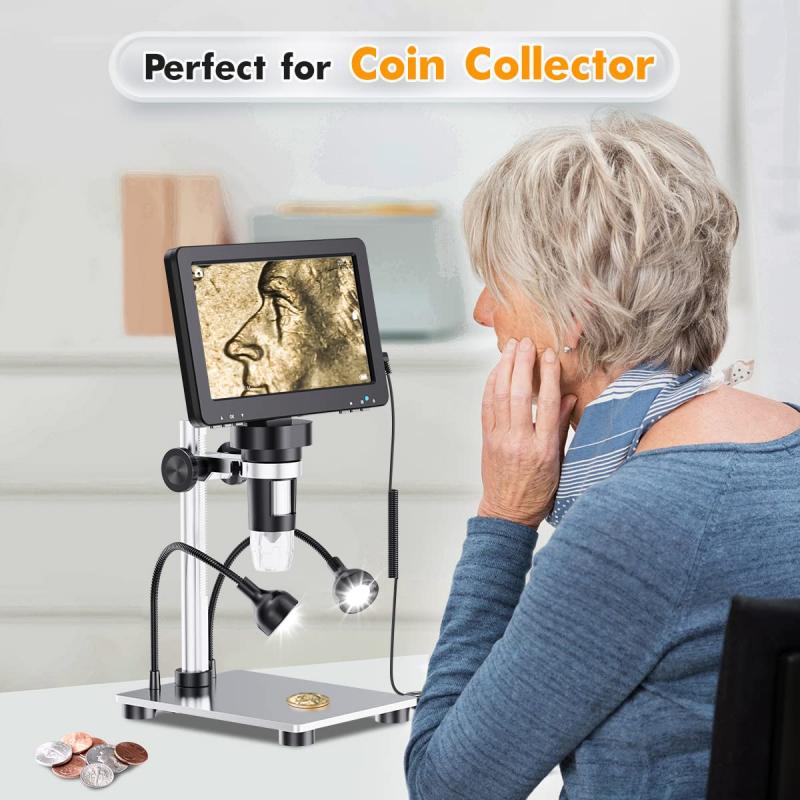

4、 Facilitating research in fields like biology, entomology, and botany.
A dissecting microscope, also known as a stereo microscope, is a valuable tool used in various scientific fields, primarily biology, entomology, and botany. This specialized microscope is designed to provide a three-dimensional view of the specimen being observed, allowing researchers to examine and manipulate objects with precision.
In the field of biology, a dissecting microscope is commonly used to study small organisms, such as insects, worms, and small plants. It enables researchers to observe the external structures of these organisms in detail, aiding in the identification of species, studying their behavior, and understanding their anatomy. Additionally, it allows for the dissection and examination of small tissues or organs, facilitating research on developmental biology and physiology.
Entomologists heavily rely on dissecting microscopes to study insects. They use this tool to examine the intricate details of insect morphology, such as the structure of wings, legs, mouthparts, and sensory organs. This information is crucial for species identification, understanding insect behavior, and studying their ecological roles.
Similarly, botanists utilize dissecting microscopes to investigate the structure and characteristics of plants. They can examine plant parts like leaves, flowers, and seeds, enabling them to identify different plant species, study plant anatomy, and investigate plant diseases.
In recent years, the use of dissecting microscopes has expanded beyond traditional fields. It has found applications in fields like forensic science, where it aids in the examination of evidence such as hair, fibers, and small biological samples. Additionally, it is used in the field of paleontology to study fossils and in the jewelry industry for the examination of gemstones.
Overall, the dissecting microscope plays a crucial role in facilitating research in various scientific disciplines. Its ability to provide a detailed, three-dimensional view of specimens allows researchers to explore and understand the intricate structures and functions of organisms, contributing to advancements in biology, entomology, botany, and beyond.






























There are no comments for this blog.