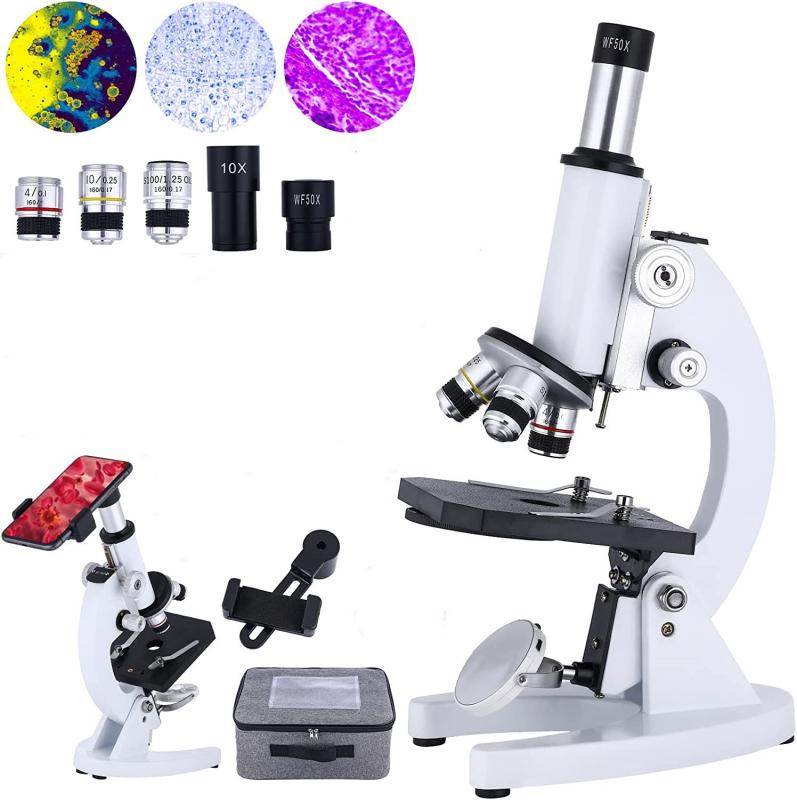
What Is A Microscope Made Of ?
A microscope is typically made of several components, including a base or stand, an eyepiece or ocular lens, an objective lens, a stage, and a light source. The base or stand provides stability and support for the microscope. The eyepiece or ocular lens is the lens through which the viewer looks to observe the specimen. The objective lens is responsible for magnifying the specimen and is located near the stage. The stage is a platform where the specimen is placed for observation. It often includes clips or other mechanisms to hold the specimen in place. Lastly, the light source, which can be a built-in lamp or an external source, provides illumination to enhance visibility of the specimen. Additionally, microscopes may have other features such as focus knobs, condensers, and diaphragms to adjust and control the focus and lighting conditions.
1、 Optical components (lenses, mirrors) for magnification and focusing.
A microscope is an essential scientific tool used to observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. It is composed of various components that work together to magnify and focus the image of the specimen being observed. The main components of a microscope are the optical components, which include lenses and mirrors.
Lenses are crucial in a microscope as they help in magnifying the image of the specimen. There are typically two types of lenses used in a microscope: the objective lens and the eyepiece lens. The objective lens is located near the specimen and provides the initial magnification, while the eyepiece lens is positioned near the viewer's eye and further magnifies the image produced by the objective lens.
Mirrors are another important component of a microscope, particularly in older models. They are used to reflect light onto the specimen, allowing for proper illumination. However, in modern microscopes, mirrors have been largely replaced by built-in light sources such as LED or halogen bulbs.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated microscopes. For instance, electron microscopes use a beam of electrons instead of light to magnify the specimen, resulting in much higher magnification and resolution. These microscopes are composed of complex components such as electron lenses and detectors.
Furthermore, with the advent of digital imaging, many microscopes now incorporate cameras and computer software to capture and analyze images. This allows for easier documentation, sharing, and analysis of microscopic observations.
In conclusion, a microscope is primarily made up of optical components such as lenses and mirrors, which enable magnification and focusing of the specimen. However, with advancements in technology, microscopes have evolved to incorporate more sophisticated components like electron lenses and digital imaging systems, enhancing their capabilities and expanding their applications in various scientific fields.

2、 Illumination system (light source, condenser) for sample visibility.
A microscope is an essential scientific tool used to magnify and observe small objects or organisms that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. It is composed of several components that work together to provide a clear and detailed image of the specimen being examined.
One of the key components of a microscope is the illumination system, which consists of a light source and a condenser. The light source provides the necessary illumination to illuminate the specimen, allowing it to be visible under the microscope. In most modern microscopes, the light source is typically an LED (light-emitting diode) or a halogen lamp. These light sources provide a bright and consistent light that is essential for obtaining a clear image.
The condenser is responsible for focusing and directing the light onto the specimen. It is located beneath the stage and contains lenses that help to concentrate the light onto the specimen. The condenser also plays a crucial role in controlling the amount and angle of light that reaches the specimen, ensuring optimal visibility and contrast.
In recent years, advancements in microscope technology have led to the development of more sophisticated illumination systems. For example, some microscopes now incorporate fluorescence illumination, which uses specific wavelengths of light to excite fluorescent molecules in the specimen. This allows for the visualization of specific structures or molecules within the specimen, providing valuable insights into cellular processes and functions.
Overall, the illumination system of a microscope is a critical component that enables the observation and analysis of microscopic samples. Its continuous improvement and innovation contribute to the advancement of scientific research and our understanding of the microscopic world.
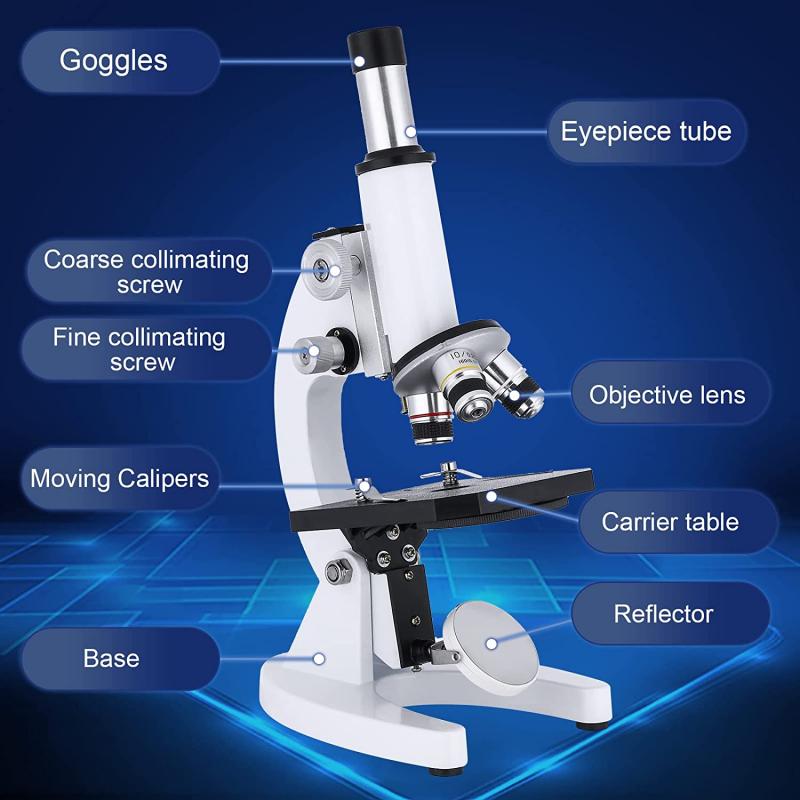
3、 Mechanical frame (base, arm, stage) for stability and positioning.
A microscope is an essential scientific instrument used to observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. It is composed of several components that work together to magnify and illuminate the specimen being observed. One of the main components of a microscope is the mechanical frame, which provides stability and positioning for the other parts.
The mechanical frame of a microscope typically consists of a base, an arm, and a stage. The base serves as the foundation of the microscope, providing stability and support. The arm connects the base to the rest of the microscope and allows for easy handling and movement. The stage is a flat platform where the specimen is placed for observation. It is usually equipped with clips or slides to hold the specimen in place.
In addition to the mechanical frame, a microscope also includes other important components such as the eyepiece, objective lenses, and illumination system. The eyepiece, or ocular lens, is the part that the viewer looks through to observe the magnified image. The objective lenses, on the other hand, are responsible for magnifying the specimen. They are usually mounted on a rotating nosepiece, allowing the viewer to switch between different magnifications.
The illumination system of a microscope provides light to illuminate the specimen. This can be achieved through various methods, including a built-in light source or an external light source such as a lamp. The light is directed through the specimen and into the objective lenses, allowing for clear and detailed observation.
In recent years, there have been advancements in microscope technology, particularly in the field of digital microscopy. Digital microscopes incorporate digital cameras and computer software, allowing for real-time imaging and analysis of specimens. This has revolutionized the way scientists and researchers study microscopic objects, providing more accurate and efficient results.
In conclusion, a microscope is made up of various components, with the mechanical frame being a crucial part for stability and positioning. The advancements in technology have further enhanced the capabilities of microscopes, enabling scientists to explore the microscopic world with greater precision and convenience.

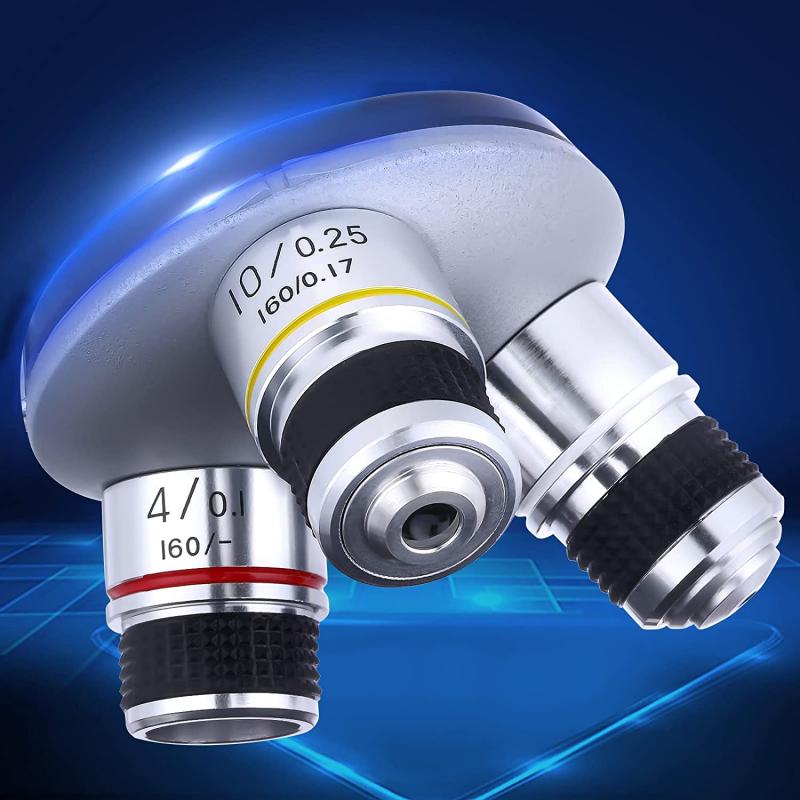
4、 Objective lenses for different levels of magnification.
A microscope is an essential scientific tool used to observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. It is made up of several components that work together to magnify and illuminate the specimen being observed.
The main parts of a microscope include the eyepiece, objective lenses, stage, condenser, and light source. The eyepiece, or ocular lens, is the lens through which the viewer looks to observe the specimen. It typically provides a magnification of 10x.
The objective lenses are the most important part of a microscope as they determine the level of magnification. Microscopes usually come with multiple objective lenses, each with a different level of magnification. These lenses are typically labeled with their magnification power, such as 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. The objective lenses are mounted on a rotating nosepiece, allowing the viewer to easily switch between different levels of magnification.
In recent years, there have been advancements in objective lens technology. High-resolution objective lenses with improved optical quality have been developed, allowing for clearer and more detailed observations. Additionally, some microscopes now come with specialized objective lenses for specific applications, such as oil immersion lenses for high-resolution imaging.
Overall, the objective lenses play a crucial role in the functioning of a microscope by providing different levels of magnification. They are constantly evolving to meet the demands of scientific research and provide better imaging capabilities.