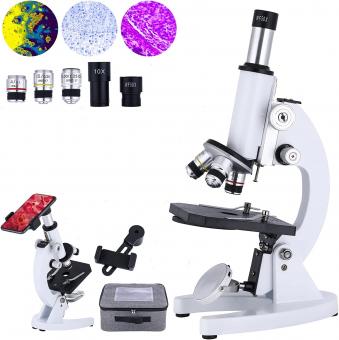
What Is A Microscope Used For ?
A microscope is an instrument used to magnify and observe small objects or organisms that are not visible to the naked eye. It works by using lenses to bend and focus light, allowing the user to see details that would otherwise be too small to see. Microscopes are commonly used in scientific research, medical diagnosis, and education to study cells, bacteria, viruses, and other microscopic organisms. They are also used in industries such as electronics, materials science, and quality control to examine small components and structures. There are several types of microscopes, including compound microscopes, electron microscopes, and scanning probe microscopes, each with their own unique capabilities and applications.
1、 Optical Microscopy
What is a microscope used for? A microscope is a scientific instrument that is used to magnify and observe small objects that are not visible to the naked eye. Optical microscopy is one of the most common types of microscopy, which uses visible light to magnify the sample. It is used in a wide range of fields, including biology, medicine, materials science, and nanotechnology.
In biology and medicine, microscopes are used to study cells, tissues, and microorganisms. They are used to observe the structure and function of cells, to diagnose diseases, and to develop new treatments. In materials science, microscopes are used to study the structure and properties of materials at the atomic and molecular level. This information is used to develop new materials with specific properties, such as strength, conductivity, and flexibility.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of microscopes for nanotechnology research. Nanotechnology involves the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale, which is the scale of atoms and molecules. Microscopes are used to observe and manipulate nanoscale materials, which has led to the development of new materials and devices with unique properties.
Overall, microscopes are essential tools in scientific research and have contributed to many important discoveries and advancements in various fields. With the development of new technologies, such as super-resolution microscopy, the capabilities of microscopes continue to expand, allowing scientists to observe and manipulate materials at an even smaller scale.

2、 Electron Microscopy
Electron microscopy is a powerful tool used to study the structure and properties of materials at the nanoscale level. It uses a beam of electrons to create high-resolution images of samples, allowing scientists to observe and analyze the smallest details of a material's structure.
Electron microscopy has a wide range of applications in various fields, including materials science, biology, chemistry, and physics. In materials science, it is used to study the microstructure of materials, such as metals, ceramics, and polymers, to understand their properties and behavior. In biology, it is used to study the structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs, providing insights into the mechanisms of disease and the development of new treatments.
The latest advancements in electron microscopy have enabled researchers to study materials and biological samples with unprecedented detail and accuracy. For example, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has revolutionized the field of structural biology by allowing scientists to visualize the three-dimensional structure of proteins and other biomolecules at near-atomic resolution. This has led to the development of new drugs and therapies for a range of diseases, including cancer and Alzheimer's.
In conclusion, electron microscopy is a vital tool for scientific research, providing insights into the structure and properties of materials and biological samples at the nanoscale level. The latest advancements in electron microscopy have opened up new avenues for research and discovery, and it is likely to continue to play a crucial role in scientific progress in the years to come.

3、 Scanning Probe Microscopy
"What is a microscope used for?" A microscope is a scientific instrument that is used to magnify and observe small objects that are not visible to the naked eye. It is commonly used in various fields such as biology, medicine, chemistry, and materials science to study the structure and properties of microscopic objects.
One type of microscope that has gained significant attention in recent years is Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM). SPM is a type of microscope that uses a physical probe to scan the surface of a sample to create an image with high resolution. It is used to study the surface properties of materials at the nanoscale level, which is important in the development of new materials and technologies.
SPM has several advantages over other types of microscopes. It can provide information about the surface topography, chemical composition, and electronic properties of a sample. It can also be used to manipulate and modify the surface of a sample at the nanoscale level, which is important in the development of nanotechnology.
In recent years, SPM has been used in various fields such as materials science, biology, and medicine. It has been used to study the properties of materials such as graphene, which has potential applications in electronics and energy storage. It has also been used to study the structure and properties of biological molecules such as proteins and DNA, which is important in the development of new drugs and therapies.
In conclusion, a microscope is a versatile scientific instrument that is used in various fields to study the structure and properties of microscopic objects. SPM is a type of microscope that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its ability to provide high-resolution images and information about the surface properties of materials at the nanoscale level.

4、 Confocal Microscopy
What is a microscope used for? A microscope is a scientific instrument that is used to magnify and observe small objects that are not visible to the naked eye. It is an essential tool in many fields of science, including biology, medicine, and materials science. Microscopes can be used to study the structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs, as well as to analyze the properties of materials at the microscopic level.
One type of microscope that has gained popularity in recent years is confocal microscopy. Confocal microscopy is a technique that uses a laser to scan a sample and create a three-dimensional image. This technique is particularly useful for studying biological samples, as it allows researchers to visualize the internal structures of cells and tissues in great detail.
Confocal microscopy has many applications in the field of biology. For example, it can be used to study the development of embryos, the behavior of cells in response to stimuli, and the interactions between different types of cells. It can also be used to study the structure and function of proteins and other biomolecules.
In addition to its applications in biology, confocal microscopy is also used in materials science to study the properties of materials at the microscopic level. For example, it can be used to study the structure of polymers, the behavior of nanoparticles, and the properties of thin films.
Overall, the microscope is an essential tool in many fields of science, and confocal microscopy is just one example of the many techniques that are used to study the microscopic world. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that new and more powerful microscopes will be developed, allowing us to see even smaller and more complex structures.






































There are no comments for this blog.