What Is An Endoscope ?
An endoscope is a medical device used to visualize and examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity within the body. It consists of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at one end. The tube is inserted into the body through a natural opening or a small incision, allowing doctors to view the internal structures on a monitor in real-time. Endoscopes are commonly used in various medical procedures, such as gastrointestinal endoscopy to examine the digestive tract, bronchoscopy to examine the airways, and arthroscopy to examine joints. They provide a minimally invasive way to diagnose and treat certain conditions, as well as to collect tissue samples for further analysis.
1、 Definition and Function of an Endoscope
An endoscope is a medical device used to visualize and examine the internal organs and structures of the body. It consists of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at one end, which allows doctors to see real-time images of the patient's internal organs on a monitor. The tube can be inserted into the body through natural openings such as the mouth, anus, or urethra, or through small incisions made during minimally invasive surgeries.
The primary function of an endoscope is to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions. It allows doctors to visually inspect the inside of the body without the need for invasive surgeries, reducing the risks and recovery time associated with traditional open surgeries. Endoscopes are commonly used in gastroenterology, urology, gynecology, and orthopedics, among other medical specialties.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in endoscopic technology. The development of high-definition cameras and improved lighting systems has greatly enhanced the quality of images produced by endoscopes, allowing for more accurate diagnoses. Additionally, the miniaturization of endoscopic instruments has enabled the exploration of previously inaccessible areas of the body, leading to improved detection and treatment of diseases.
Moreover, the integration of robotic systems with endoscopes has revolutionized surgical procedures. Robotic-assisted endoscopic surgeries offer increased precision, dexterity, and control, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy and minimal invasiveness.
In conclusion, an endoscope is a vital tool in modern medicine, allowing doctors to visualize and examine internal organs and structures with minimal invasiveness. With ongoing advancements in technology, endoscopes continue to play a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions, improving patient outcomes and quality of care.

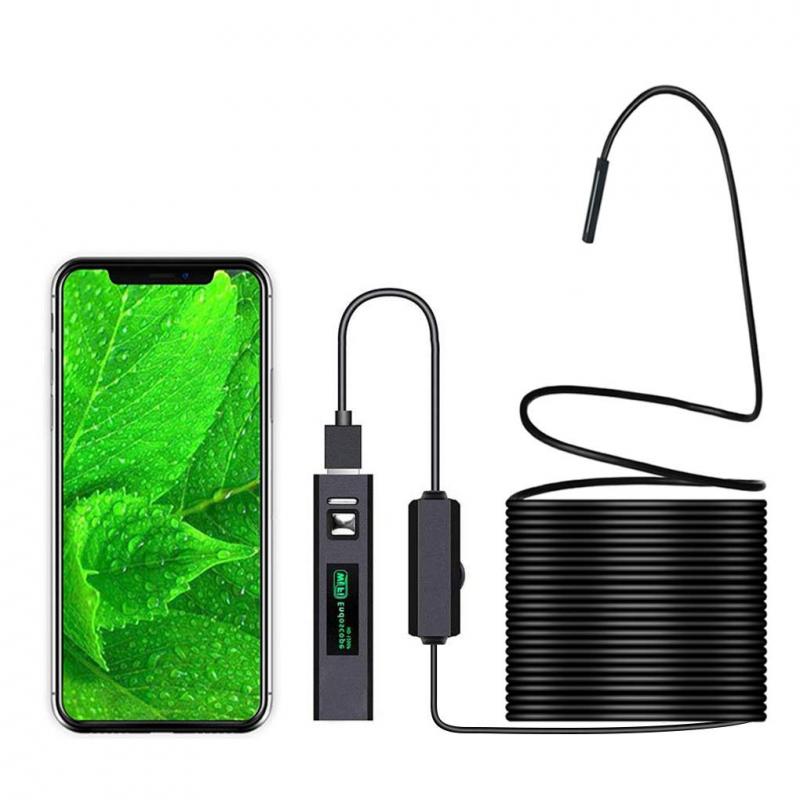
2、 Types of Endoscopes and Their Applications
An endoscope is a medical device used to visualize and examine the internal organs and structures of the body. It consists of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at one end, which allows doctors to see real-time images of the body's internal structures on a monitor.
There are several types of endoscopes, each designed for specific applications. The most common type is the flexible endoscope, which is used to examine the gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and colon. This type of endoscope can also be used for procedures such as biopsies and polyp removal.
Another type of endoscope is the bronchoscope, which is used to examine the airways and lungs. It is commonly used to diagnose and treat conditions such as lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia.
Other types of endoscopes include the cystoscope, which is used to examine the bladder and urinary tract, and the hysteroscope, which is used to examine the uterus and diagnose conditions such as fibroids and polyps.
In recent years, there have been advancements in endoscopic technology, leading to the development of new types of endoscopes. For example, capsule endoscopy involves swallowing a small, pill-sized camera that takes pictures as it passes through the digestive system. This allows for a non-invasive examination of the small intestine, which was previously difficult to access with traditional endoscopes.
Overall, endoscopes have revolutionized the field of medicine by providing doctors with a minimally invasive way to visualize and diagnose various conditions. They have significantly improved patient outcomes and reduced the need for more invasive procedures.

3、 Components and Working Mechanism of an Endoscope
An endoscope is a medical device used to visualize and examine the internal organs and structures of the body. It consists of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at one end, and various attachments and controls at the other end. The tube is inserted into the body through a natural opening or a small incision, allowing the physician to view the internal organs in real-time on a monitor.
The components of an endoscope include the insertion tube, which is flexible and can be maneuvered through the body, and the light source, which illuminates the area being examined. The camera captures high-resolution images and transmits them to the monitor for the physician to analyze. Additionally, there are channels within the endoscope that allow for the insertion of surgical instruments or the delivery of medications or fluids.
The working mechanism of an endoscope involves the careful insertion of the tube into the body, guided by the physician's expertise. The light source illuminates the area of interest, while the camera captures images that are transmitted to the monitor. The physician can then navigate the endoscope through the body, examining the organs and structures in detail. If necessary, surgical instruments can be inserted through the channels to perform procedures such as biopsies or removal of abnormal tissue.
In recent years, there have been advancements in endoscope technology, such as the development of miniaturized cameras and improved image quality. These advancements have allowed for more precise and accurate diagnoses and treatments. Additionally, there has been a shift towards the use of disposable endoscopes, reducing the risk of infection transmission.
Overall, endoscopes have revolutionized the field of medicine by providing a minimally invasive way to visualize and treat internal conditions. They have become an essential tool in various medical specialties, including gastroenterology, urology, and gynecology, among others.

4、 Advancements in Endoscopic Technology
An endoscope is a medical device used to visualize and examine the internal organs and structures of the body. It consists of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at one end, which allows doctors to see real-time images of the patient's internal organs on a monitor. The tube can be inserted into the body through natural openings such as the mouth, anus, or small incisions made during minimally invasive surgeries.
Advancements in endoscopic technology have revolutionized the field of medicine, enabling doctors to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions with greater precision and minimal invasiveness. One of the latest advancements in endoscopic technology is the development of high-definition (HD) and ultra-high-definition (UHD) cameras, which provide clearer and more detailed images. This allows doctors to detect abnormalities and perform procedures with greater accuracy.
Another significant advancement is the incorporation of robotic systems into endoscopic procedures. Robotic-assisted endoscopy allows for enhanced dexterity and precision, as well as improved ergonomics for the surgeon. This technology enables complex procedures to be performed with greater ease and reduces the risk of complications.
Furthermore, there have been advancements in the miniaturization of endoscopic instruments, allowing for access to smaller and more delicate areas of the body. This has expanded the applications of endoscopy to various specialties, including cardiology, gastroenterology, urology, and gynecology.
Additionally, there have been developments in the field of wireless endoscopy, eliminating the need for cumbersome cables and improving patient comfort. Wireless endoscopes transmit images and data wirelessly to a monitor, providing flexibility and ease of use.
Overall, advancements in endoscopic technology have significantly improved patient outcomes by enabling earlier and more accurate diagnoses, reducing the need for invasive surgeries, and shortening recovery times. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations in endoscopic technology, leading to even more precise and minimally invasive procedures.




























There are no comments for this blog.