What Is Borescope ?
A borescope is a flexible optical instrument used to visually inspect hard-to-reach areas. It typically consists of a long, thin tube with a light source and a camera at one end, and an eyepiece or a display screen at the other end. Borescopes are commonly used in various industries, such as automotive, aviation, plumbing, and manufacturing, to examine the internal components of machinery, pipes, engines, or other inaccessible areas. They allow for non-destructive inspection and can help identify defects, damage, or blockages without the need for disassembly. Borescopes come in different sizes and configurations, including rigid and flexible types, and may have additional features like articulation or video recording capabilities.
1、 Definition and Function of a Borescope
A borescope is a flexible optical instrument used to visually inspect hard-to-reach areas that are otherwise inaccessible to the human eye. It consists of a long, slender tube with a light source and a camera at one end, and an eyepiece or a display screen at the other end. The tube is typically made of a flexible material, allowing it to be maneuvered through narrow openings, tight corners, and curved paths.
Borescopes are commonly used in various industries such as aviation, automotive, manufacturing, and plumbing, among others. They are particularly useful for inspecting the internal components of engines, pipes, and machinery, where physical access is limited. By inserting the borescope into the area of interest, operators can visually examine the condition, cleanliness, and potential defects of the inspected object.
The latest advancements in borescope technology have led to the development of digital borescopes, which offer enhanced image quality and greater flexibility. These borescopes often come equipped with advanced features such as video recording, image capture, and wireless connectivity, allowing for easier documentation and sharing of inspection results.
In addition to visual inspection, borescopes can also be equipped with additional tools such as probes, hooks, and magnets, enabling operators to retrieve objects or perform minor repairs within the inspected area.
Overall, borescopes play a crucial role in non-destructive testing and maintenance procedures, helping to identify potential issues, prevent costly repairs, and ensure the safety and efficiency of various systems and equipment.
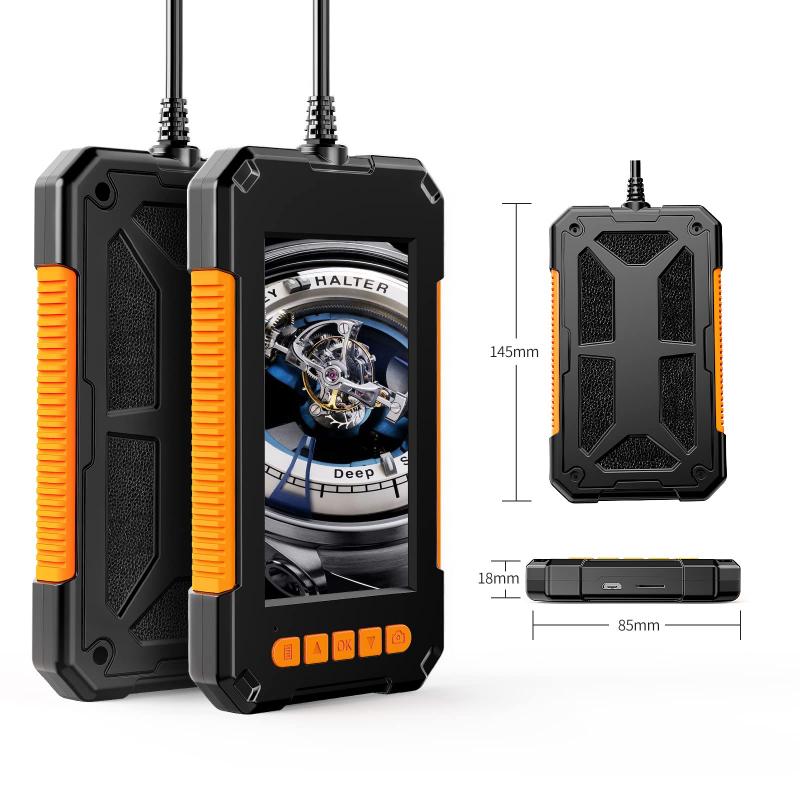

2、 Types of Borescopes and their Applications
A borescope is a flexible optical instrument used to visually inspect hard-to-reach areas that are inaccessible to the naked eye. It consists of a long, thin tube with a light source and a camera at one end, and an eyepiece or a display screen at the other end. The camera captures images or videos of the internal components or surfaces of objects, allowing for detailed inspection and analysis.
There are several types of borescopes available, each designed for specific applications. The most common types include rigid borescopes, flexible borescopes, and video borescopes. Rigid borescopes are straight and inflexible, making them suitable for inspecting straight and narrow spaces. Flexible borescopes, on the other hand, have a flexible insertion tube that can be maneuvered around bends and curves, making them ideal for inspecting complex and curved structures. Video borescopes have a built-in camera and display screen, enabling real-time viewing and recording of inspections.
Borescopes find applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and healthcare. They are used for inspecting engines, turbines, pipes, welds, aircraft components, and even human body cavities during medical procedures. Borescopes are invaluable tools for detecting defects, cracks, corrosion, blockages, and other anomalies that may affect the performance or safety of the inspected object.
In recent years, advancements in borescope technology have led to the development of more compact and portable devices with higher image quality and enhanced features. Some borescopes now offer wireless connectivity, allowing for remote viewing and control through smartphones or tablets. Additionally, there has been a rise in the use of borescopes with advanced imaging capabilities, such as high-definition cameras and 3D imaging, providing even greater detail and accuracy in inspections.
Overall, borescopes play a crucial role in non-destructive testing and inspection processes, enabling professionals to access and assess hard-to-reach areas with ease and precision.
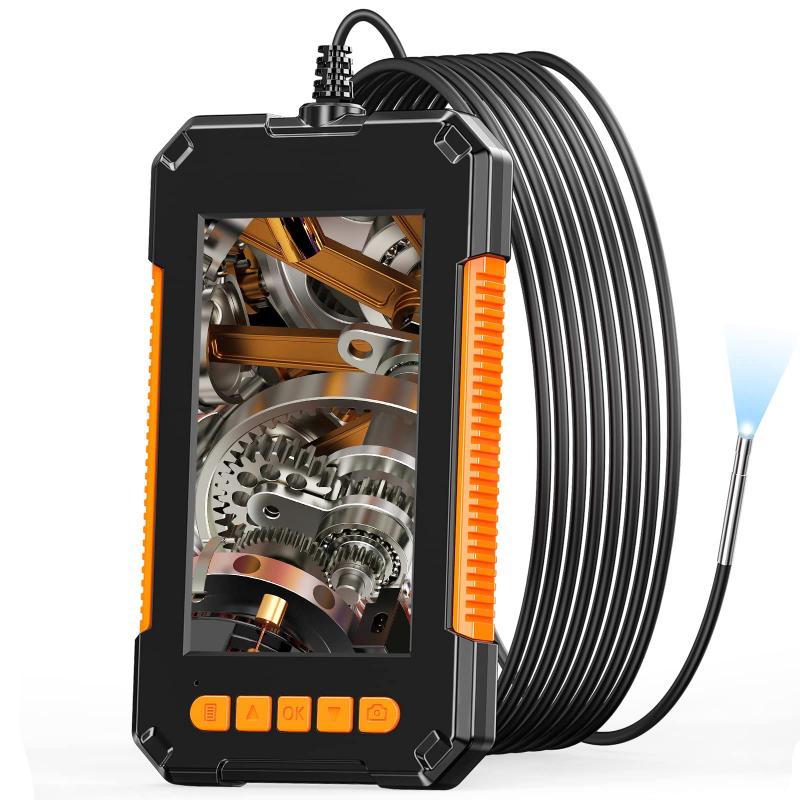

3、 Components and Features of a Borescope
A borescope is a versatile inspection tool used to visually examine hard-to-reach areas that are inaccessible to the naked eye. It consists of a flexible tube with a camera at one end and an eyepiece or display screen at the other end. The camera captures high-resolution images or videos of the internal components or surfaces of objects, allowing for detailed inspection and analysis.
The main components of a borescope include the insertion tube, which is flexible and can be maneuvered into tight spaces, and the camera head, which is equipped with a light source to illuminate the area being inspected. The camera head may also have additional features such as adjustable focus, zoom capabilities, and articulation, allowing for better visibility and control during inspections.
Borescopes can be either rigid or flexible, depending on the application. Rigid borescopes are typically used for straight-line inspections, while flexible borescopes are more suitable for navigating through curved or complex pathways. The eyepiece or display screen provides real-time viewing of the captured images or videos, enabling the operator to assess the condition of the inspected area.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of digital borescopes, which offer enhanced image quality, wireless connectivity, and the ability to record and store inspection data. These digital borescopes often come with software that allows for image and video analysis, measurement, and documentation.
Overall, borescopes have become indispensable tools in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and plumbing, enabling professionals to conduct thorough inspections, identify issues, and make informed decisions regarding maintenance or repairs.

4、 Advantages and Limitations of Borescopes
A borescope is a flexible optical instrument used to visually inspect hard-to-reach areas such as pipes, engines, and other confined spaces. It consists of a long, thin tube with a light source and a camera at one end, which allows the user to see and record images or videos of the area being inspected. Borescopes are commonly used in various industries, including automotive, aviation, manufacturing, and plumbing.
The advantages of using borescopes are numerous. Firstly, they eliminate the need for disassembling equipment or structures, saving time and effort. This non-destructive inspection method also reduces the risk of causing further damage during the inspection process. Borescopes provide high-resolution images and videos, allowing for accurate and detailed visual inspection. They can also be equipped with additional features such as zoom, measurement tools, and image/video recording capabilities, enhancing their functionality.
However, borescopes also have limitations. The image quality may be affected by factors such as poor lighting conditions or the presence of debris or fluids in the inspected area. The flexibility of the borescope tube may be limited, making it difficult to navigate through complex or narrow spaces. Additionally, the cost of borescopes can be relatively high, especially for advanced models with additional features.
From a latest point of view, advancements in technology have led to the development of more advanced borescopes. These include wireless borescopes that can transmit images and videos to a smartphone or tablet, making inspections even more convenient. Furthermore, some borescopes now offer enhanced image processing capabilities, such as image stabilization and noise reduction, improving the overall image quality.
In conclusion, borescopes are valuable tools for visual inspection in hard-to-reach areas. While they have advantages such as time and cost savings, as well as high-resolution imaging, they also have limitations related to image quality and flexibility. However, with the latest advancements in technology, borescopes continue to evolve and offer improved functionality and convenience.