What Is Endoscope In Physics ?
In physics, an endoscope is not a commonly used term. However, in the field of medicine, an endoscope is a medical device used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. It typically consists of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at the end, allowing doctors to visualize and diagnose various medical conditions. Endoscopes are commonly used in procedures such as colonoscopy, gastroscopy, and bronchoscopy.
1、 Optical Endoscope: A device for visualizing internal structures using light.
An endoscope is a device used in the field of physics to visualize internal structures using light. It is commonly used in medical procedures to examine the inside of the human body, but it also has applications in other fields such as industrial inspection and scientific research.
The optical endoscope, in particular, utilizes light to capture images of the internal structures. It consists of a flexible or rigid tube with a light source and a camera at one end. The light source illuminates the area of interest, and the camera captures the images which are then transmitted to a monitor for viewing.
The use of light in endoscopy allows for non-invasive examination of internal structures, reducing the need for more invasive procedures. It provides real-time visualization, enabling doctors and researchers to observe and diagnose various conditions. The images obtained through an optical endoscope can provide valuable information about the health and functioning of organs, tissues, and other internal structures.
In recent years, there have been advancements in endoscopic technology, such as the development of miniaturized cameras and improved image resolution. These advancements have further enhanced the capabilities of endoscopes, allowing for more detailed and accurate visualization of internal structures.
Furthermore, there has been a growing interest in the development of advanced imaging techniques, such as fluorescence and confocal microscopy, which can be integrated into endoscopic systems. These techniques enable the visualization of specific molecules or cellular structures, providing even more detailed information about the internal environment.
Overall, the optical endoscope is a crucial tool in physics, enabling researchers and medical professionals to explore and understand the internal structures of the human body and other objects of interest. Its continued development and integration with advanced imaging techniques hold great promise for future advancements in the field.
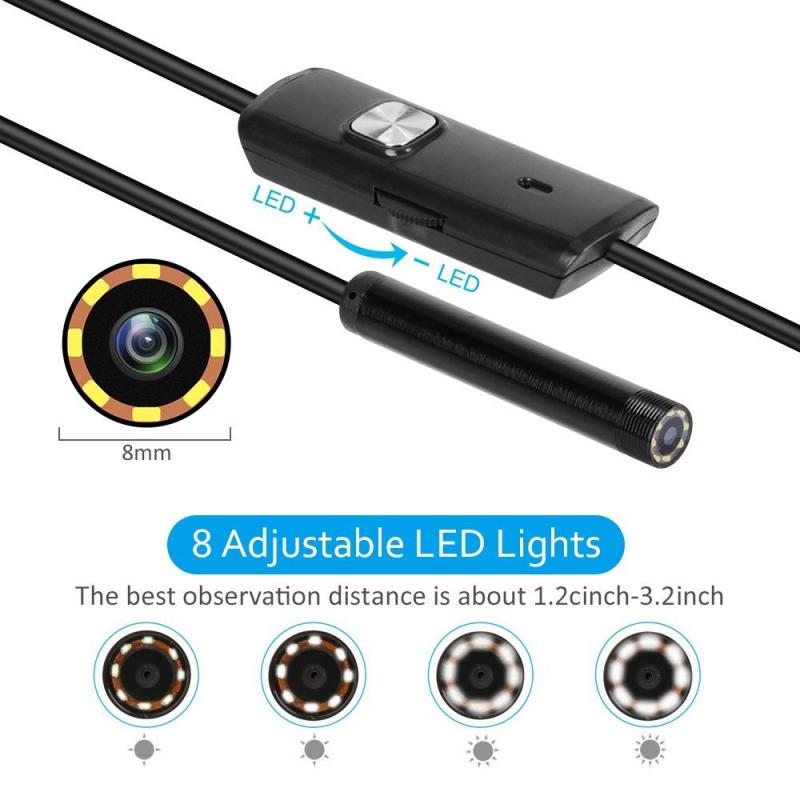

2、 Flexible Endoscope: A type of endoscope with a flexible insertion tube.
An endoscope is a medical device used to visualize and examine the internal organs and cavities of the human body. It consists of a long, thin tube with a light source and a camera at one end, which allows doctors to see inside the body without the need for invasive surgery. In physics, an endoscope is a tool that utilizes the principles of optics to transmit light and images through a flexible insertion tube.
A flexible endoscope is a type of endoscope that has a flexible insertion tube, allowing it to navigate through the body's natural curves and bends. This flexibility enables doctors to access hard-to-reach areas and perform procedures with minimal discomfort for the patient. The insertion tube is typically made of a series of flexible fibers or a combination of fibers and lenses, which transmit light and images from the camera to the viewing screen.
The latest advancements in endoscope technology have led to the development of high-definition cameras and improved image quality. These advancements have greatly enhanced the diagnostic capabilities of endoscopes, allowing doctors to detect and diagnose diseases and conditions with greater accuracy. Additionally, the use of miniaturized cameras and wireless transmission systems has made endoscopes more compact and portable, enabling their use in a wider range of medical settings.
In recent years, there has also been a growing interest in the development of robotic endoscopes. These robotic systems aim to enhance the precision and control of endoscopic procedures by incorporating robotic arms and advanced imaging technologies. Robotic endoscopes have the potential to revolutionize minimally invasive surgery and improve patient outcomes.
Overall, endoscopes, particularly flexible endoscopes, have become indispensable tools in modern medicine. They have revolutionized the way doctors diagnose and treat various medical conditions, offering a less invasive and more accurate alternative to traditional surgical procedures. With ongoing advancements in technology, the future of endoscopy holds great promise for further improving patient care and outcomes.
3、 Rigid Endoscope: A type of endoscope with a rigid insertion tube.
In physics, an endoscope is a device used for visualizing and examining the internal structures of an object or organism. It consists of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at one end, which allows for the capture and transmission of images or videos. The other end of the tube is inserted into the object or organism being examined.
One type of endoscope commonly used is the rigid endoscope. As the name suggests, it has a rigid insertion tube, which provides stability and control during the examination process. The rigid endoscope is typically used for procedures that require precise maneuverability and access to hard-to-reach areas.
The rigid endoscope is widely used in various fields, including medicine, engineering, and research. In medicine, it is commonly used for minimally invasive surgeries, allowing surgeons to visualize and operate on internal organs without the need for large incisions. In engineering, it is used for inspecting and maintaining complex machinery or structures. In research, it enables scientists to study microscopic structures and phenomena in a non-destructive manner.
The latest advancements in endoscope technology have led to the development of high-definition cameras and improved lighting systems, allowing for clearer and more detailed images. Additionally, miniaturization of endoscope components has made it possible to create smaller and more flexible devices, further expanding their applications.
In conclusion, a rigid endoscope is a type of endoscope with a rigid insertion tube. It is a valuable tool in various fields, enabling visualization and examination of internal structures with precision and control. Ongoing advancements in endoscope technology continue to enhance its capabilities and broaden its applications.

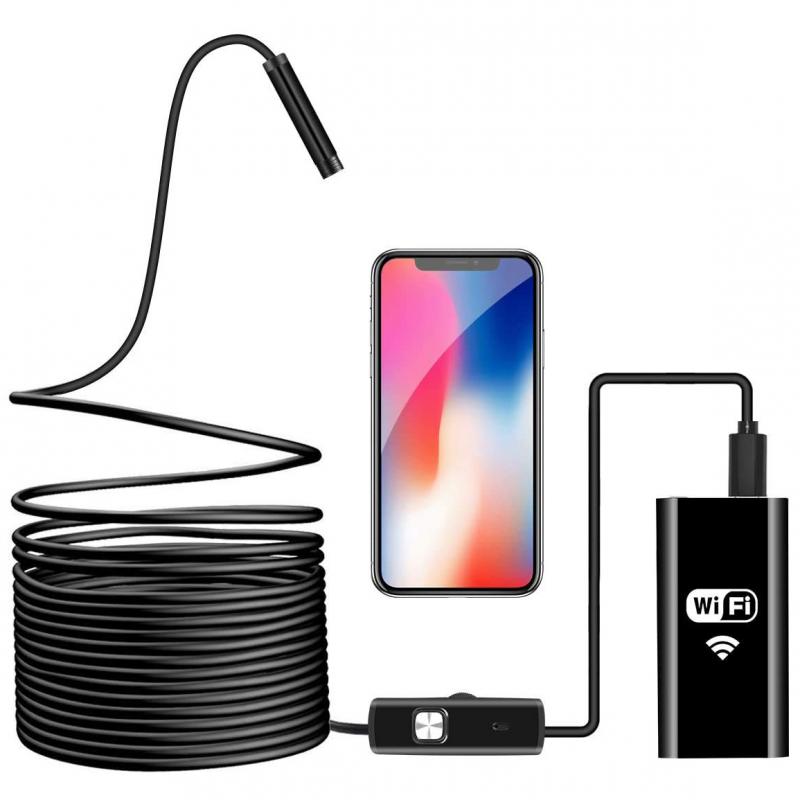
4、 Video Endoscope: An endoscope that captures and displays real-time video images.
An endoscope is a device used in various fields, including medicine, engineering, and physics, to visualize and examine internal structures or inaccessible areas. In physics, an endoscope is typically referred to as a video endoscope, which captures and displays real-time video images.
Video endoscopes consist of a flexible or rigid tube with a light source and a camera at one end. The tube is inserted into the area of interest, allowing the camera to capture high-resolution images or videos. These images are then transmitted to a monitor, enabling real-time visualization and analysis.
In physics research, video endoscopes have proven to be invaluable tools for exploring and studying inaccessible or hazardous environments. They allow scientists to observe and document phenomena in real-time, providing valuable insights into various physical processes.
The latest advancements in video endoscope technology have led to the development of more compact and versatile devices. Miniaturized video endoscopes can now be used in nanoscale research, enabling scientists to explore microscopic structures and phenomena. Additionally, advancements in imaging technology have improved the resolution and clarity of video endoscope images, enhancing the accuracy and detail of observations.
In conclusion, a video endoscope in physics is a device that captures and displays real-time video images of internal structures or inaccessible areas. It is a valuable tool for researchers, enabling them to explore and study various physical phenomena in real-time. The latest advancements in video endoscope technology have expanded its applications, allowing for exploration at both macro and nanoscales.































There are no comments for this blog.