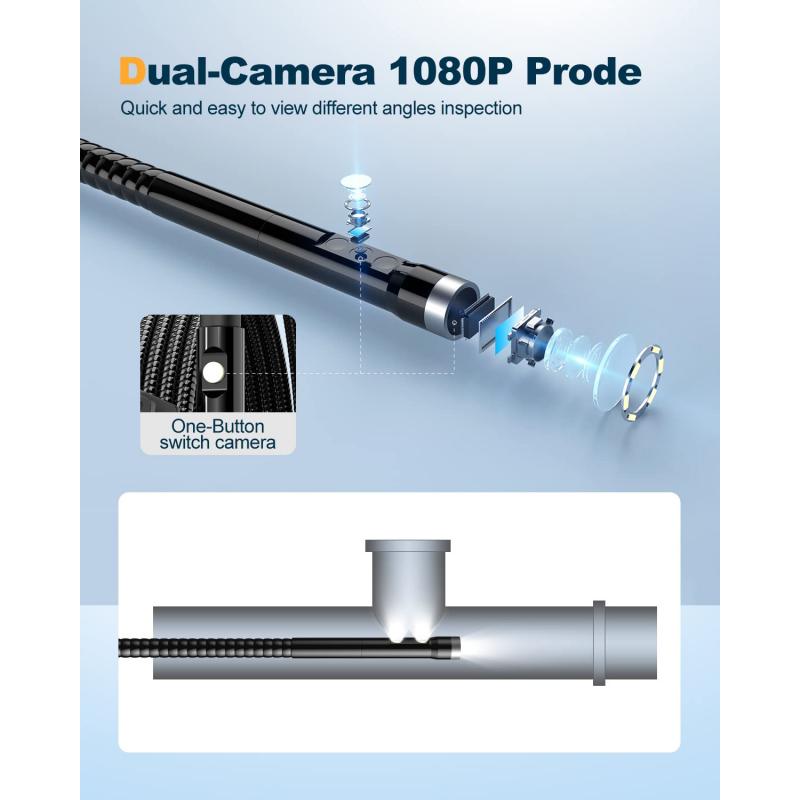
What Is Endoscopic Hemostasis ?
Endoscopic hemostasis refers to a medical procedure performed using an endoscope to control bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. It involves the use of specialized instruments and techniques to identify and treat the source of bleeding, such as ulcers, tumors, or blood vessels. The endoscope is a flexible tube with a light and camera at its tip, which allows the doctor to visualize the internal organs and guide the treatment. Endoscopic hemostasis techniques may include cauterization, injection of medications, clipping, or ligation, depending on the nature and location of the bleeding. This minimally invasive approach offers several advantages, including the ability to diagnose and treat bleeding in real-time, avoiding the need for open surgery, and reducing the risk of complications.
1、 Endoscopic hemostasis: Overview and techniques for gastrointestinal bleeding management.
Endoscopic hemostasis refers to a medical procedure used to stop bleeding in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It involves the use of an endoscope, a flexible tube with a light and camera attached to it, which is inserted through the mouth or anus to visualize the GI tract and identify the source of bleeding.
Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur due to various reasons, such as ulcers, tumors, vascular malformations, or trauma. Endoscopic hemostasis is a minimally invasive technique that allows for both diagnosis and treatment of the bleeding source. It offers several advantages over traditional surgical methods, including reduced patient discomfort, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
There are different techniques used in endoscopic hemostasis, depending on the location and severity of the bleeding. These techniques include injection therapy, thermal therapy, mechanical therapy, and combination therapy. Injection therapy involves the injection of medications, such as epinephrine or sclerosants, into the bleeding site to promote clot formation. Thermal therapy uses heat energy, either through electrocautery or argon plasma coagulation, to cauterize the bleeding vessel. Mechanical therapy involves the use of clips or bands to mechanically close off the bleeding vessel. Combination therapy may involve a combination of these techniques to achieve hemostasis.
The latest point of view in endoscopic hemostasis is the increasing use of advanced endoscopic techniques, such as endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), for the management of GI bleeding. EUS allows for better visualization of the bleeding source and can guide the placement of therapeutic devices more accurately. ESD enables the removal of larger lesions or tumors that may be causing bleeding, thus providing both diagnostic and therapeutic benefits.
In conclusion, endoscopic hemostasis is a valuable technique for managing gastrointestinal bleeding. It offers a minimally invasive approach to identify and treat the bleeding source, resulting in improved patient outcomes. The use of advanced endoscopic techniques further enhances the effectiveness of this procedure.

2、 Endoscopic hemostasis: Role of thermal methods in stopping bleeding.
Endoscopic hemostasis refers to the use of endoscopic techniques to stop bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. It is a minimally invasive procedure that allows for the identification and treatment of the source of bleeding, thereby preventing further blood loss and potential complications.
One of the main methods used in endoscopic hemostasis is thermal therapy. This involves the application of heat to the bleeding site to achieve hemostasis. The two main thermal methods used are thermal coagulation and argon plasma coagulation.
Thermal coagulation involves the use of a heated probe or forceps to directly apply heat to the bleeding vessel, causing coagulation and sealing of the vessel. Argon plasma coagulation, on the other hand, uses a jet of ionized argon gas to deliver heat to the bleeding site, achieving similar results.
These thermal methods have proven to be effective in achieving hemostasis in various gastrointestinal bleeding scenarios, including peptic ulcers, arteriovenous malformations, and post-polypectomy bleeding. They are relatively safe and can be performed during an endoscopic procedure without the need for surgery.
The latest point of view on endoscopic hemostasis suggests that thermal methods continue to play a crucial role in stopping bleeding. However, there have been advancements in other techniques, such as the use of hemostatic powders and clips, which can be used in combination with thermal therapy to enhance efficacy.
Additionally, the development of advanced endoscopic imaging technologies, such as narrow-band imaging and chromoendoscopy, has improved the detection and localization of bleeding sources, allowing for more targeted and precise application of thermal therapy.
Overall, endoscopic hemostasis with thermal methods remains an important and effective approach in the management of gastrointestinal bleeding. It offers a less invasive alternative to surgery and can be performed promptly during endoscopic procedures, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.

3、 Endoscopic hemostasis: Application of mechanical methods for hemostasis.
Endoscopic hemostasis refers to the application of mechanical methods to achieve hemostasis (the stopping of bleeding) during endoscopic procedures. It involves the use of various techniques and devices to control bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
One common method of endoscopic hemostasis is through the use of clips or sutures. These devices are placed over the bleeding site to compress the blood vessels and stop the bleeding. Clips are typically made of metal or polymer and can be easily applied using endoscopic instruments. Sutures, on the other hand, involve the use of a needle and thread to stitch the bleeding vessel closed.
Another technique used in endoscopic hemostasis is through the application of thermal energy. This can be achieved using methods such as electrocautery or argon plasma coagulation. Electrocautery involves the use of an electric current to heat and coagulate the bleeding vessel, while argon plasma coagulation uses ionized argon gas to deliver thermal energy to the bleeding site.
In recent years, there have been advancements in endoscopic hemostasis techniques. One such advancement is the development of hemostatic powders. These powders, made of substances like cellulose or gelatin, can be sprayed onto the bleeding site to promote clot formation and stop bleeding. They provide a quick and effective method of achieving hemostasis, especially in cases where other techniques may be challenging or not feasible.
Overall, endoscopic hemostasis plays a crucial role in managing gastrointestinal bleeding during endoscopic procedures. It offers a minimally invasive approach to control bleeding and can help prevent the need for more invasive surgical interventions. The latest point of view emphasizes the importance of individualized treatment plans and the use of advanced endoscopic techniques to achieve optimal outcomes for patients.

4、 Endoscopic hemostasis: Use of injection therapy for controlling bleeding.
Endoscopic hemostasis refers to the use of injection therapy to control bleeding during endoscopic procedures. Endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows doctors to examine the inside of the body using a flexible tube with a light and camera attached to it. It is commonly used to diagnose and treat various gastrointestinal conditions.
During endoscopy, bleeding can occur due to various reasons such as ulcers, tumors, or vascular abnormalities. Endoscopic hemostasis techniques aim to stop the bleeding and prevent further complications. One of the commonly used methods is injection therapy, where a medication or solution is injected directly into the bleeding site to promote clotting and stop the bleeding.
The injected substances can include epinephrine, saline, or sclerosing agents. Epinephrine constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the bleeding site. Saline solution helps to wash away blood and provide a clear view for the endoscopist. Sclerosing agents, such as ethanol or polidocanol, can be used to induce blood vessel thrombosis and promote clot formation.
Endoscopic hemostasis has proven to be an effective and safe method for controlling bleeding during endoscopy. It allows for immediate intervention, avoiding the need for more invasive surgical procedures. The success rate of endoscopic hemostasis varies depending on the cause and severity of the bleeding, but it is generally high.
In recent years, there have been advancements in endoscopic hemostasis techniques. For example, the use of hemostatic powders has gained popularity. These powders, made of substances like cellulose or gelatin, are sprayed onto the bleeding site to form a mechanical barrier and promote clotting. Additionally, the development of advanced endoscopic devices, such as hemostatic clips or band ligation systems, has expanded the options for endoscopic hemostasis.
Overall, endoscopic hemostasis plays a crucial role in managing bleeding during endoscopic procedures. It offers a minimally invasive and effective approach to control bleeding, reducing the need for more invasive interventions and improving patient outcomes.