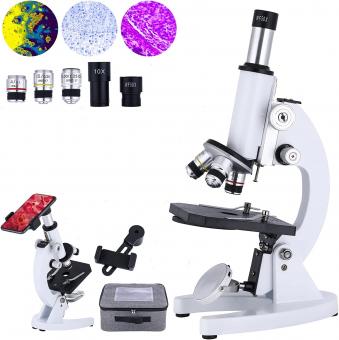
What Is Microscope Used For ?
A microscope is a scientific instrument used to magnify and observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. It is commonly used in various fields such as biology, medicine, chemistry, and materials science. Microscopes allow scientists to study the structure, composition, and behavior of microscopic organisms, cells, tissues, and materials. They can reveal intricate details and provide valuable insights into the world of the very small. Microscopes come in different types, including light microscopes, electron microscopes, and scanning probe microscopes, each with its own specific applications and capabilities. Overall, microscopes play a crucial role in advancing scientific knowledge and understanding in a wide range of disciplines.
1、 Magnification and Observation of Small Objects
A microscope is a scientific instrument that is used for magnification and observation of small objects. It allows scientists and researchers to study objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. By using a combination of lenses and light, microscopes can greatly enhance the size and clarity of the object being observed.
One of the primary uses of a microscope is in the field of biology. Biologists use microscopes to study cells, tissues, and organisms at a microscopic level. This allows them to understand the structure and function of living organisms in greater detail. Microscopes are also used in medical research and diagnosis, as they can help identify and study diseases and abnormalities at a cellular level.
Microscopes are also used in various other scientific fields, such as chemistry and materials science. Chemists use microscopes to analyze the composition and structure of substances at a molecular level. Materials scientists use microscopes to study the properties and behavior of different materials, which is crucial for developing new materials with specific properties.
In recent years, there have been advancements in microscopy techniques that have further expanded the capabilities of microscopes. For example, electron microscopes use a beam of electrons instead of light, allowing for even higher magnification and resolution. This has enabled scientists to study objects at an atomic level, providing valuable insights into the structure and behavior of matter.
In conclusion, microscopes are used for magnification and observation of small objects, allowing scientists to study and understand the world at a microscopic level. With advancements in technology, microscopes continue to play a crucial role in various scientific fields, providing valuable insights and pushing the boundaries of our knowledge.
2、 Scientific Research and Analysis
A microscope is a scientific instrument used for scientific research and analysis. It is a tool that allows scientists to observe and study objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Microscopes have been used for centuries to explore the microscopic world and have played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of various scientific disciplines.
Microscopes are used in a wide range of scientific fields, including biology, chemistry, physics, and materials science. In biology, microscopes are used to study cells, tissues, and microorganisms, enabling scientists to investigate the intricate structures and functions of living organisms. In chemistry, microscopes are used to analyze the composition and structure of materials at the atomic and molecular level. In physics, microscopes are used to study the behavior of particles and to investigate the fundamental properties of matter.
The latest point of view regarding the use of microscopes in scientific research and analysis is the development of advanced imaging techniques. Scientists are constantly pushing the boundaries of microscopy by developing new methods that enhance resolution, increase imaging speed, and enable the visualization of dynamic processes in real-time. For example, super-resolution microscopy techniques, such as stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy and single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM), have revolutionized the field by allowing scientists to observe structures and processes at the nanoscale.
Furthermore, advancements in microscopy have also led to the integration of other technologies, such as fluorescence imaging, confocal microscopy, and electron microscopy, which provide additional insights into the properties and behavior of microscopic objects. These techniques have become indispensable tools in scientific research, enabling scientists to make groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in various fields.
In conclusion, microscopes are essential instruments in scientific research and analysis. They allow scientists to explore the microscopic world, study the intricate structures and functions of living organisms, analyze the composition and behavior of materials, and push the boundaries of our understanding. The latest advancements in microscopy techniques have further enhanced our ability to visualize and study the microscopic world, leading to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge.

3、 Medical Diagnosis and Examination
A microscope is a powerful tool used in various fields, including medical diagnosis and examination. It allows healthcare professionals to observe and analyze samples at a microscopic level, providing valuable insights into the structure and function of cells, tissues, and microorganisms.
In medical diagnosis, microscopes are used to examine blood, urine, and other bodily fluids for the presence of abnormal cells or microorganisms. This helps in the identification and diagnosis of diseases such as cancer, infections, and autoimmune disorders. Microscopic examination of tissue samples, known as histopathology, is also crucial in determining the nature and extent of diseases, aiding in treatment planning and prognosis.
Microscopes are also used in medical research to study the mechanisms of diseases and develop new treatments. For example, researchers use advanced microscopy techniques to visualize cellular processes, study the effects of drugs on cells, and investigate the interactions between pathogens and host cells. This knowledge contributes to the development of targeted therapies and the understanding of disease progression.
In recent years, technological advancements have further enhanced the capabilities of microscopes in medical diagnosis and examination. For instance, digital microscopy allows for the capture and storage of high-resolution images, enabling remote consultation and collaboration among healthcare professionals. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms with microscopy has shown promising results in automating the analysis of medical images, improving efficiency and accuracy in diagnosis.
Overall, microscopes play a vital role in medical diagnosis and examination by providing detailed visualization and analysis of biological samples. With ongoing advancements, they continue to contribute to the understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of various diseases, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.

4、 Quality Control and Inspection in Manufacturing
A microscope is a powerful tool used for quality control and inspection in manufacturing. It allows for detailed examination and analysis of various materials and products, ensuring that they meet the required standards and specifications.
One of the primary uses of a microscope in quality control is to inspect the surface of materials and products for defects or imperfections. By magnifying the surface, even the tiniest flaws can be detected, such as scratches, cracks, or uneven surfaces. This helps manufacturers identify and rectify any issues before the product reaches the market, ensuring customer satisfaction and preventing potential recalls or returns.
Microscopes are also used to examine the internal structure of materials and products. This is particularly important in industries such as electronics or automotive, where the integrity of internal components is crucial. By using techniques like cross-sectioning or microscopy, manufacturers can assess the quality of solder joints, circuit boards, or other internal parts, ensuring they are properly assembled and functioning correctly.
Furthermore, microscopes are essential for analyzing the composition and characteristics of materials. They can be used to identify the presence of impurities, measure the size and distribution of particles, or assess the quality of coatings or surface treatments. This information is vital for ensuring that materials and products meet the required specifications and perform as intended.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have further enhanced its capabilities in quality control and inspection. For example, digital microscopes now allow for real-time imaging and analysis, enabling faster and more accurate assessments. Additionally, automated microscopy systems can be integrated into production lines, providing continuous monitoring and analysis of products, further improving efficiency and quality control.
In conclusion, microscopes play a crucial role in quality control and inspection in manufacturing. They enable detailed examination of materials and products, helping to identify defects, assess internal structures, and analyze composition. With the latest advancements in microscopy technology, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.