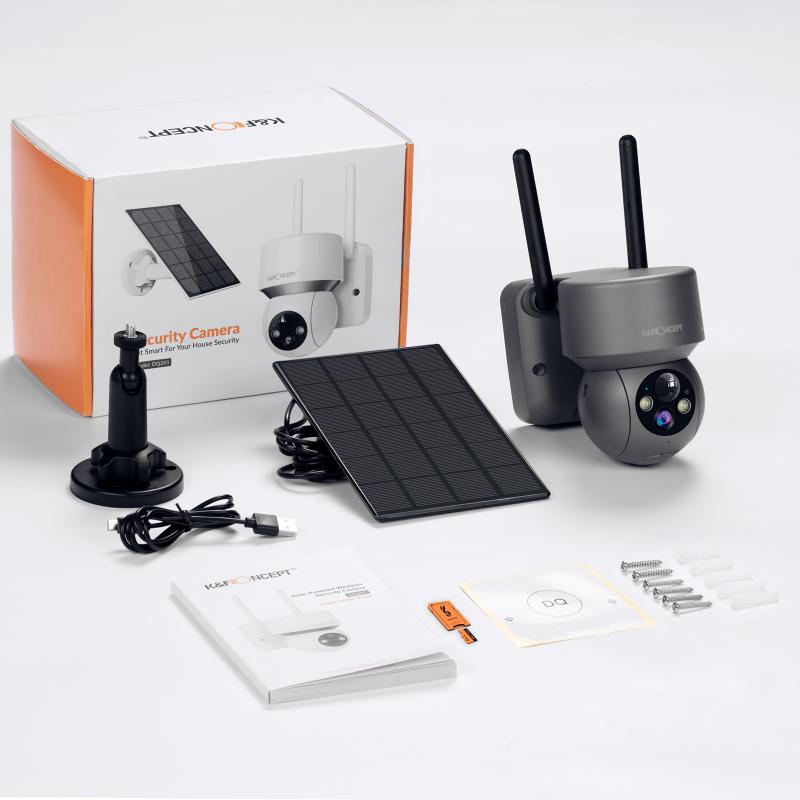
What Is Night Vision ?
Night vision refers to the ability to see in low-light or dark conditions. It is a technology that allows individuals to perceive their surroundings in environments where there is insufficient visible light. Night vision devices typically use image intensification technology or thermal imaging to enhance the available light or detect heat signatures, enabling users to see clearly in the dark. These devices are commonly used by military personnel, law enforcement agencies, and outdoor enthusiasts for various purposes such as surveillance, navigation, and wildlife observation. Night vision technology has evolved over the years, with advancements in image quality, range, and portability.
1、 Physiology of night vision in animals
Night vision refers to the ability of certain animals to see in low-light conditions, such as during the night or in dimly lit environments. It is a remarkable adaptation that allows these animals to navigate, hunt, and communicate effectively in darkness. The physiology of night vision in animals involves several key mechanisms that enhance their visual capabilities in low-light environments.
One of the primary adaptations for night vision is the presence of specialized cells called rod photoreceptors in the retina. Rods are highly sensitive to light and are responsible for detecting low levels of illumination. These cells contain a pigment called rhodopsin, which undergoes a chemical reaction when exposed to light, triggering a signal that is transmitted to the brain for visual processing.
Another crucial adaptation is the presence of a reflective layer behind the retina called the tapetum lucidum. This layer acts like a mirror, reflecting light back through the retina and increasing the amount of light available for photoreceptor cells to detect. This enhances the animal's ability to see in extremely low-light conditions.
Additionally, some animals possess a higher density of rods in their retinas, allowing for increased light sensitivity. They may also have larger pupils that can dilate more extensively, allowing more light to enter the eye. These adaptations collectively enable animals to gather and process available light more efficiently, enhancing their night vision capabilities.
Recent research has shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying night vision in animals. Scientists have discovered specific genes and proteins involved in the development and function of rod photoreceptors, providing insights into the genetic basis of night vision. Additionally, advancements in imaging techniques have allowed researchers to study the structure and organization of the tapetum lucidum, further unraveling the intricacies of night vision adaptations.
Understanding the physiology of night vision in animals not only provides valuable insights into the evolution of vision but also has practical applications. Researchers are exploring ways to mimic these adaptations in technology, such as developing improved night vision devices for human use. By studying the remarkable abilities of animals in low-light conditions, we can continue to expand our knowledge and potentially enhance our own visual capabilities in the future.

2、 Technology behind night vision devices
Night vision refers to the ability to see in low-light or dark conditions, where the human eye would typically struggle to perceive objects. It is a technology that enables enhanced visibility during nighttime or in environments with limited light sources. Night vision devices, such as goggles, scopes, or cameras, utilize various technologies to amplify the available light and make it visible to the human eye.
The technology behind night vision devices has evolved significantly over the years. The earliest night vision devices, developed during World War II, used image intensification technology. These devices worked by collecting the available light through an objective lens, which then passed through a photocathode that converted photons into electrons. These electrons were then accelerated and amplified before striking a phosphor screen, which produced a visible image.
Modern night vision devices have seen advancements in image intensification technology, resulting in improved image quality and clarity. Additionally, thermal imaging technology has become increasingly prevalent in night vision devices. Thermal imaging works by detecting the heat emitted by objects and converting it into a visible image. This technology allows users to see objects based on their heat signatures, rather than relying solely on available light.
In recent years, there have been advancements in digital night vision technology. Digital night vision devices use sensors to capture the available light and convert it into a digital image. These devices often offer features such as image and video recording, as well as the ability to view the image in real-time on a screen.
The latest point of view on night vision technology focuses on improving image resolution, reducing device size and weight, and enhancing the overall user experience. Additionally, there is ongoing research and development in areas such as augmented reality and artificial intelligence, which could potentially revolutionize night vision capabilities.
Overall, night vision technology continues to evolve, providing users with enhanced visibility in low-light conditions and contributing to various fields such as military operations, law enforcement, wildlife observation, and security.

3、 Infrared light and its role in night vision
Night vision refers to the ability to see in low-light or dark conditions. It allows individuals to perceive their surroundings when natural sources of light, such as the sun or moon, are not present or insufficient. Night vision technology has been developed to enhance this ability, and one crucial component of this technology is infrared light.
Infrared light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is not visible to the human eye. It has longer wavelengths than visible light, and it is emitted by objects as heat. In night vision technology, infrared light plays a vital role in illuminating the environment. Infrared light sources, such as infrared LEDs or lasers, emit light that is invisible to humans but can be detected by specialized sensors or cameras.
Night vision devices, such as goggles or cameras, capture the infrared light reflected or emitted by objects in the environment. These devices then amplify the captured light and convert it into a visible image, allowing the user to see in the dark. The amplified image is typically displayed in shades of green, as the human eye is more sensitive to green light.
The latest advancements in night vision technology have focused on improving the sensitivity and resolution of infrared sensors, as well as reducing the size and weight of the devices. This has led to the development of more compact and portable night vision goggles and cameras, making them more accessible to a wider range of users.
Additionally, some recent developments have explored the integration of infrared sensors with other technologies, such as augmented reality or artificial intelligence. These advancements aim to enhance the user's situational awareness and provide real-time information about their surroundings, further improving the effectiveness of night vision capabilities.
In conclusion, night vision relies on the use of infrared light to enable vision in low-light or dark conditions. The latest advancements in technology have led to more compact and portable devices, as well as the integration of infrared sensors with other technologies, opening up new possibilities for enhanced night vision capabilities.
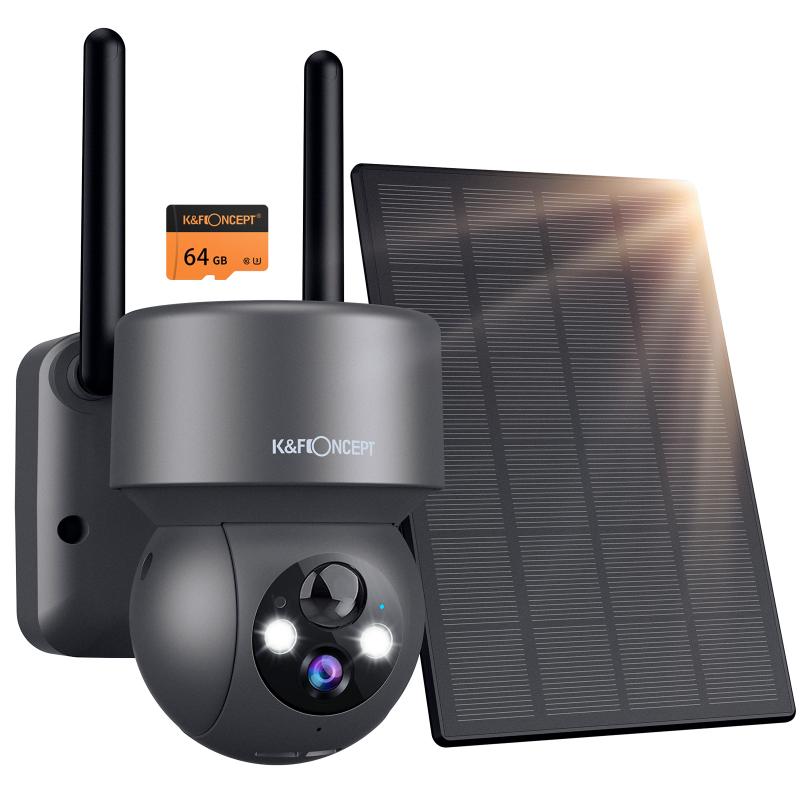

4、 Night vision in military and law enforcement applications
Night vision refers to the ability to see in low-light or dark conditions using specialized technology. In military and law enforcement applications, night vision plays a crucial role in enhancing situational awareness and providing a tactical advantage during nighttime operations.
Night vision technology works by amplifying the available light, such as moonlight or ambient light, and converting it into a visible image. This is achieved through the use of image intensifier tubes or thermal imaging sensors. Image intensifier tubes amplify the existing light, while thermal imaging sensors detect the heat emitted by objects and create an image based on the temperature differences.
The use of night vision in military and law enforcement allows personnel to navigate through dark environments, detect potential threats, and conduct covert operations. It provides a significant advantage by enabling operators to see clearly in conditions where the naked eye would struggle.
In recent years, there have been advancements in night vision technology, leading to improved performance and capabilities. These advancements include higher resolution imagery, extended detection ranges, reduced size and weight of equipment, and integration with other technologies such as augmented reality displays.
Furthermore, there has been a shift towards the development of more affordable and accessible night vision solutions. This has allowed smaller law enforcement agencies and even civilian users to benefit from night vision technology, expanding its applications beyond traditional military use.
Overall, night vision technology continues to evolve, providing military and law enforcement personnel with enhanced capabilities for nighttime operations. As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in image quality, range, and integration with other systems, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness and safety of those who rely on night vision in their line of work.