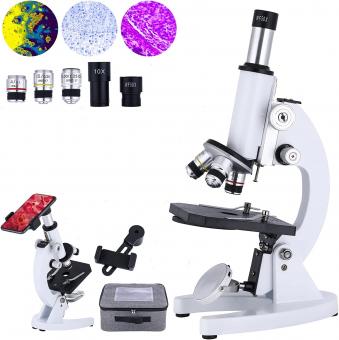
What Is The Arm On A Microscope ?
The arm on a microscope is a structural component that connects the base of the microscope to the head or body. It provides support and stability to the microscope, allowing for easy maneuverability and positioning. The arm is typically made of metal or plastic and is designed to be sturdy yet lightweight. It may also have a curved shape to provide a comfortable grip for the user when carrying or adjusting the microscope. The arm plays a crucial role in maintaining the alignment and balance of the microscope, ensuring accurate and steady observations.
1、 Microscope Arm: Structure and Function
The arm on a microscope is a crucial component that provides stability and support to the entire microscope system. It is typically a curved or L-shaped metal rod that connects the base of the microscope to the head or body tube. The arm is designed to hold and balance the weight of the microscope, allowing for easy maneuverability and precise focusing.
The primary function of the microscope arm is to provide structural integrity to the microscope. It ensures that the microscope remains stable and steady during use, preventing any unwanted vibrations or movements that could affect the quality of the image being observed. The arm also acts as a handle, allowing users to comfortably hold and carry the microscope from one location to another.
In addition to its structural role, the arm may also house various components of the microscope, such as the coarse and fine focus knobs or the illumination system. These components are often integrated into the arm to provide easy access and control for the user.
The design and construction of microscope arms have evolved over time to meet the changing needs of users. Modern microscope arms are often made from durable materials such as aluminum or stainless steel, which provide strength and stability while minimizing weight. Some microscope models even feature ergonomic designs, with contoured arms that offer enhanced comfort during prolonged use.
Overall, the arm on a microscope plays a vital role in maintaining stability, supporting the various components, and allowing for smooth and precise movements. It is an essential part of the microscope system that contributes to the overall functionality and usability of the instrument.
2、 Types of Microscope Arms: Fixed vs. Articulating
The arm on a microscope refers to the part of the microscope that connects the head or body tube to the base. It provides support and stability to the microscope, allowing for easy maneuverability and positioning. There are two main types of microscope arms: fixed and articulating.
A fixed arm is rigid and does not allow for any movement or adjustment. It is typically found in basic, entry-level microscopes where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. While a fixed arm provides stability, it limits the flexibility and versatility of the microscope.
On the other hand, an articulating arm is designed to provide a greater range of movement and adjustability. It allows the microscope head to be tilted, rotated, or moved in various directions, providing more ergonomic positioning options for the user. This type of arm is commonly found in advanced microscopes used in research laboratories, medical facilities, and other professional settings.
The latest point of view regarding microscope arms emphasizes the importance of ergonomics in microscopy. Ergonomics is the science of designing equipment and systems to optimize human well-being and performance. With prolonged microscope use, improper positioning and repetitive movements can lead to discomfort, fatigue, and even musculoskeletal disorders.
Articulating microscope arms are considered more ergonomic as they allow users to adjust the microscope to their preferred working position, reducing strain on the neck, back, and shoulders. This can improve user comfort, productivity, and overall well-being. Therefore, many modern microscopes are equipped with articulating arms to promote ergonomic practices and enhance user experience.
In conclusion, the arm on a microscope plays a crucial role in providing stability and maneuverability. While fixed arms are simple and cost-effective, articulating arms offer greater flexibility and ergonomic benefits. The latest perspective emphasizes the importance of ergonomics in microscopy, leading to the widespread use of articulating arms in modern microscopes.

3、 Materials Used in Microscope Arm Construction
The arm on a microscope is a crucial component that provides stability and support to the entire microscope system. It is typically located between the base and the head of the microscope and is responsible for holding the head and the stage together. The arm is designed to allow for easy movement and adjustment of the microscope head, enabling users to position the microscope for optimal viewing.
The materials used in microscope arm construction have evolved over time to ensure durability, stability, and ease of use. In the past, microscope arms were commonly made of cast iron or steel, which provided strength but added significant weight to the microscope. However, advancements in materials science have led to the use of lighter and more durable materials such as aluminum alloys and high-strength plastics.
Aluminum alloys are now widely used in microscope arm construction due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio. These alloys offer the necessary rigidity and stability while keeping the microscope lightweight and easy to handle. Additionally, aluminum alloys are resistant to corrosion, ensuring the longevity of the microscope.
High-strength plastics, such as reinforced nylon or polycarbonate, are also utilized in some microscope arm designs. These materials offer advantages such as reduced weight, improved shock absorption, and increased resistance to chemicals and temperature variations. Furthermore, plastics allow for more intricate and ergonomic designs, enhancing user comfort and ease of operation.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of carbon fiber composites for microscope arm construction. Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength and stiffness while being significantly lighter than traditional materials. This allows for even greater portability and maneuverability of microscopes, particularly in field applications.
Overall, the choice of materials for microscope arm construction depends on factors such as the intended use, budget, and desired features. Manufacturers strive to strike a balance between strength, weight, durability, and cost to provide users with the best possible microscope experience.

4、 Ergonomics of Microscope Arm Design
The arm on a microscope refers to the part of the microscope that connects the base to the head or body tube. It provides support and stability to the microscope, allowing for easy maneuverability and positioning. The design of the microscope arm plays a crucial role in the ergonomics of microscope usage.
Ergonomics is the science of designing equipment and systems to fit the human body, maximizing efficiency and minimizing discomfort or injury. In the context of microscope arm design, ergonomics focuses on creating a comfortable and user-friendly experience for microscope users.
The latest point of view in ergonomics of microscope arm design emphasizes the importance of adjustability and flexibility. Microscope users come in different shapes and sizes, and their comfort levels may vary. Therefore, the arm should be adjustable in height and angle to accommodate different users and allow for proper posture during microscope use.
Additionally, the arm should be designed to minimize strain on the user's neck, shoulders, and back. This can be achieved by ensuring that the microscope head is positioned at a comfortable viewing angle and that the arm provides adequate support and stability.
Furthermore, the arm should be designed to allow for easy and smooth movement of the microscope. This includes features such as smooth rotation and locking mechanisms to secure the microscope in place when needed.
Overall, the ergonomics of microscope arm design aim to enhance user comfort, reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders, and improve overall productivity and efficiency. By considering the latest point of view in ergonomics, microscope manufacturers can create products that prioritize user well-being and satisfaction.