What Is The Slide On A Microscope ?
The slide on a microscope is a thin, flat piece of glass or plastic that holds the specimen being observed. It is typically rectangular in shape and has dimensions of approximately 25mm by 75mm. The slide is placed on the stage of the microscope and secured in place using clips or a mechanical stage. The specimen, such as a tissue sample or a microorganism, is mounted onto the slide using various techniques, such as staining or fixing. The slide allows the specimen to be easily manipulated and positioned under the microscope's objective lenses for magnification and examination.
1、 Microscope Slide: Definition and Purpose
A microscope slide is a thin, flat piece of glass or plastic that is used to hold and support a specimen for observation under a microscope. It is typically rectangular in shape, measuring about 75mm by 25mm, and has a thickness of around 1mm. The slide is usually transparent to allow light to pass through and illuminate the specimen.
The purpose of a microscope slide is to provide a stable platform for mounting the specimen and to protect it from damage during observation. The specimen is typically placed on the slide and covered with a thin glass cover slip to prevent it from drying out and to protect it from dust and other contaminants.
Microscope slides are an essential tool in microscopy as they allow scientists and researchers to examine and study a wide range of specimens, including cells, tissues, microorganisms, and other small objects. They are used in various fields such as biology, medicine, forensics, and materials science.
In recent years, there have been advancements in slide technology to improve the quality of observations. For example, there are now specialized slides available for specific applications, such as fluorescence microscopy, which allow for the visualization of specific molecules or structures within a specimen. Additionally, there are slides with built-in chambers or wells that enable the observation of live cells or the study of multiple specimens on a single slide.
Overall, microscope slides play a crucial role in microscopy by providing a platform for the examination and analysis of specimens. They continue to evolve to meet the needs of researchers and scientists, enabling them to gain a deeper understanding of the microscopic world.

2、 Types of Microscope Slides: Glass vs. Plastic
The slide on a microscope is a small rectangular piece of material that holds the specimen being observed under the microscope. It is an essential component of the microscope as it allows the user to view the specimen at high magnification.
There are two main types of microscope slides: glass slides and plastic slides. Glass slides have been the traditional choice for many years due to their clarity and ability to withstand high temperatures. They are made from high-quality glass that is resistant to scratching and chemical damage. Glass slides provide excellent optical clarity, allowing for clear and detailed observation of the specimen. They are also reusable, making them a cost-effective option in the long run.
On the other hand, plastic slides have gained popularity in recent years due to their convenience and ease of use. They are made from transparent plastic materials such as polystyrene or polypropylene. Plastic slides are lightweight, disposable, and less prone to breakage compared to glass slides. They are particularly useful in educational settings or high-throughput laboratories where a large number of slides need to be prepared and analyzed.
Both glass and plastic slides have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the user. Glass slides are still widely used in research laboratories and clinical settings where high-quality imaging is crucial. Plastic slides, on the other hand, are more commonly used in educational institutions and routine laboratory work.
In conclusion, the choice between glass and plastic slides for microscopes depends on factors such as the intended use, budget, and personal preference. Glass slides offer superior optical clarity and reusability, while plastic slides provide convenience and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, the decision should be based on the specific needs of the user and the nature of the microscopy work being performed.

3、 Preparing a Microscope Slide: Step-by-Step Guide
The slide on a microscope is a thin, flat piece of glass or plastic that holds the specimen being observed under the microscope. It is an essential component of the microscope as it allows the user to view the specimen at high magnification and resolution.
Preparing a microscope slide involves several steps to ensure that the specimen is properly mounted and ready for observation. The first step is to collect the specimen and place it on the slide. This can be done by using a dropper or a needle to transfer a small amount of the specimen onto the slide. The specimen should be evenly distributed and not too thick to allow light to pass through.
Once the specimen is on the slide, a cover slip is placed on top to protect the specimen and prevent it from drying out. The cover slip is a small, thin piece of glass or plastic that is carefully placed over the specimen. It is important to avoid trapping air bubbles between the slide and the cover slip, as this can interfere with the clarity of the image.
After the slide is prepared, it is ready to be placed on the microscope stage. The slide is typically held in place by clips or a mechanical stage, ensuring that the specimen is in the field of view of the microscope's objective lens.
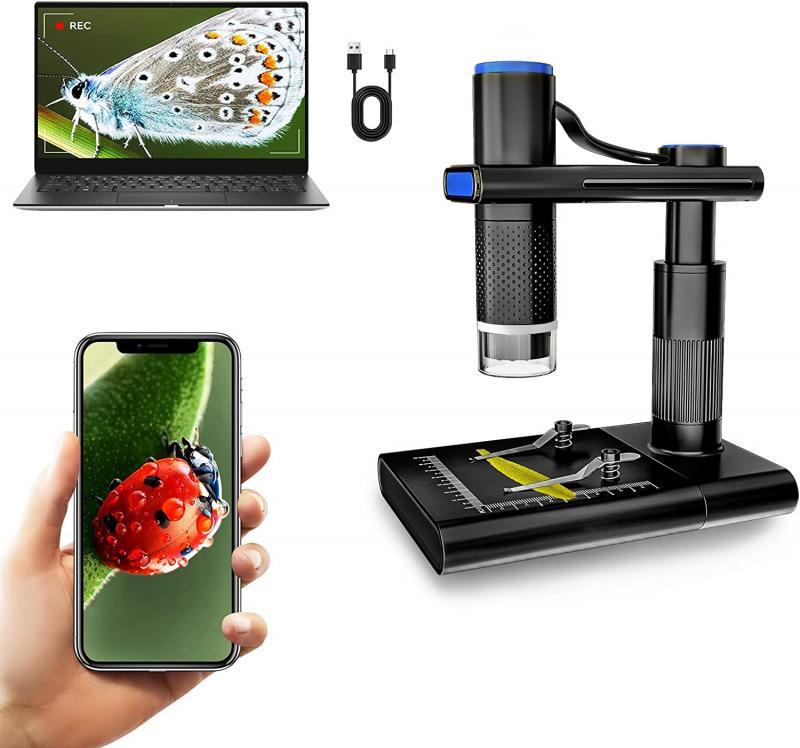
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of digital microscopes, which eliminate the need for physical slides. These microscopes allow for direct observation of specimens on a computer screen, eliminating the need for slide preparation. However, traditional microscope slides continue to be widely used in laboratories and educational settings.
In conclusion, the slide on a microscope is a crucial component that holds the specimen and allows for observation under high magnification. Proper preparation of the slide ensures that the specimen is mounted correctly and ready for examination.

4、 Proper Handling and Storage of Microscope Slides
The slide on a microscope is a small rectangular piece of glass or plastic that holds the specimen being observed under the microscope. It is an essential component of the microscope as it allows the user to view the specimen at high magnification.
Proper handling and storage of microscope slides are crucial to ensure accurate and reliable results. Firstly, it is important to handle slides with clean hands or wear gloves to prevent contamination. Any dirt, oil, or fingerprints on the slide can interfere with the clarity of the image. Additionally, slides should be held by their edges to avoid touching the area where the specimen is placed.
When it comes to storage, slides should be kept in a clean and dry environment to prevent damage or deterioration. They should be stored in slide boxes or racks specifically designed for this purpose. These storage containers should be labeled and organized to facilitate easy retrieval of slides when needed.
It is also recommended to store slides in a vertical position to prevent any potential damage or smudging of the specimen. Slides should be stored away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures, as these can cause fading or distortion of the specimen.
In recent years, there have been advancements in slide technology, such as the development of digital slides. These digital slides allow for the scanning and storage of high-resolution images of specimens, eliminating the need for physical slides. However, traditional glass slides are still widely used in many laboratories and educational institutions.
In conclusion, proper handling and storage of microscope slides are essential for obtaining accurate and reliable results. By following the recommended guidelines, users can ensure the longevity and quality of their slides, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of microscopic observations.




























There are no comments for this blog.