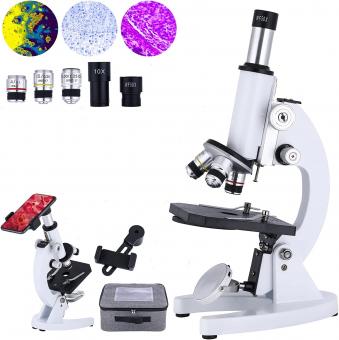
What Lens Is Used In A Microscope ?
A microscope uses a combination of lenses to magnify an object. The two main types of lenses used in a microscope are the objective lens and the eyepiece lens. The objective lens is located near the specimen and is responsible for producing a magnified image of the object. The eyepiece lens is located near the viewer's eye and further magnifies the image produced by the objective lens. The combination of these lenses allows for high magnification and resolution of the specimen being observed.
1、 Objective lens
The objective lens is the primary lens used in a microscope. It is responsible for magnifying the specimen and producing a clear and detailed image. The objective lens is located at the bottom of the microscope and is typically made up of several lenses that work together to produce a high-quality image.
In recent years, there have been advancements in objective lens technology that have improved the resolution and clarity of microscope images. One such advancement is the development of super-resolution microscopy, which uses specialized objective lenses to achieve resolutions beyond the diffraction limit of light. This has allowed researchers to study biological structures and processes at a level of detail that was previously impossible.
Another recent development in objective lens technology is the use of adaptive optics. This technology uses deformable mirrors to correct for aberrations in the objective lens, resulting in sharper and clearer images. Adaptive optics has been particularly useful in studying living cells and tissues, where aberrations caused by movement and changes in refractive index can be a significant challenge.
Overall, the objective lens remains a critical component of the microscope, and advancements in technology continue to improve its performance and capabilities.

2、 Eyepiece lens
The eyepiece lens, also known as the ocular lens, is one of the two lenses used in a microscope. It is located at the top of the microscope and is the lens that the viewer looks through to observe the specimen. The eyepiece lens typically has a magnification power of 10x, although some microscopes may have eyepieces with higher magnification powers.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using digital microscopes, which use a camera instead of an eyepiece lens to observe the specimen. These microscopes have a built-in camera that captures images of the specimen and displays them on a computer screen or other digital device. This allows for easier sharing and analysis of the images, as well as the ability to store and manipulate the images digitally.
However, traditional microscopes with eyepiece lenses are still widely used in many fields, including biology, medicine, and materials science. The eyepiece lens provides a clear and detailed view of the specimen, and allows for precise observation and analysis. Additionally, some microscopes may have multiple eyepiece lenses, allowing for different magnification powers and the ability to view the specimen from different angles.
Overall, while digital microscopes are becoming more popular, the eyepiece lens remains an important component of traditional microscopes and continues to be used in many scientific applications.

3、 Condenser lens
The condenser lens is an essential component of a microscope that is used to focus and direct light onto the specimen being observed. It is located beneath the stage and is responsible for illuminating the specimen with a concentrated beam of light. The condenser lens is typically a small, convex lens that is positioned close to the specimen, and it works by collecting and focusing light from the microscope's light source onto the specimen.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing new types of condenser lenses that can improve the performance of microscopes. For example, researchers have been exploring the use of metasurfaces, which are ultra-thin layers of material that can manipulate light in unique ways. By incorporating metasurfaces into the design of condenser lenses, it may be possible to achieve higher resolution and better contrast in microscope images.
Another area of research is the development of adaptive optics for microscopes. Adaptive optics systems use deformable mirrors or other components to correct for aberrations in the microscope's optical system, which can improve image quality. By incorporating adaptive optics into the design of condenser lenses, it may be possible to achieve even higher levels of resolution and clarity in microscope images.
Overall, the condenser lens remains a critical component of the microscope, and ongoing research is focused on developing new and innovative ways to improve its performance.
4、 Immersion lens
The lens used in a microscope is called an objective lens. This lens is responsible for magnifying the specimen being observed. The objective lens is typically made up of several lenses that work together to produce a clear and magnified image. The quality of the objective lens is crucial to the overall performance of the microscope.
One type of objective lens that has gained popularity in recent years is the immersion lens. This lens is designed to work with a special immersion oil that is placed between the lens and the specimen. The oil has the same refractive index as glass, which helps to reduce the amount of light that is lost as it passes through the lens. This results in a clearer and more detailed image.
Immersion lenses are commonly used in high-resolution microscopy techniques such as confocal microscopy and two-photon microscopy. These techniques require a high level of precision and clarity, which can be achieved with the use of an immersion lens.
In addition to immersion lenses, there are also other types of objective lenses that are used in microscopy. These include achromatic lenses, apochromatic lenses, and plan-apochromatic lenses. Each of these lenses has its own unique properties and is used for specific applications.
Overall, the lens used in a microscope is a critical component that determines the quality and clarity of the images produced. The use of immersion lenses has revolutionized high-resolution microscopy and has allowed researchers to observe and study biological structures in greater detail than ever before.