What Lenses Are In A Microscope ?
A microscope typically contains two types of lenses: objective lenses and eyepiece lenses. The objective lenses are located near the specimen and are responsible for magnifying the image of the specimen. They come in different magnification powers, ranging from low to high. The eyepiece lens, also known as the ocular lens, is located at the top of the microscope and is responsible for further magnifying the image produced by the objective lens. The eyepiece lens typically has a magnification power of 10x. Together, the objective and eyepiece lenses work to produce a highly magnified image of the specimen being observed.
1、 Objective lens
What lenses are in a microscope? The most important lens in a microscope is the objective lens. This lens is responsible for magnifying the specimen and producing a clear image. The objective lens is located near the bottom of the microscope and is usually made up of several lenses that work together to produce a high-quality image.
In recent years, there has been a lot of interest in developing new types of objective lenses that can provide even higher levels of magnification and resolution. One of the most promising developments in this area is the use of super-resolution microscopy techniques, which allow scientists to see structures that were previously too small to be observed with traditional microscopes.
Another important lens in a microscope is the eyepiece lens, which is located near the top of the microscope and is used to view the magnified image produced by the objective lens. The eyepiece lens is usually a simple lens that provides additional magnification and helps to focus the image.
Overall, the lenses in a microscope are critical components that determine the quality and resolution of the images produced. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated lenses and imaging techniques that will allow us to explore the microscopic world in even greater detail.

2、 Eyepiece lens
What lenses are in a microscope? The two main lenses in a microscope are the objective lens and the eyepiece lens. The objective lens is located at the bottom of the microscope and is responsible for magnifying the specimen being viewed. The eyepiece lens is located at the top of the microscope and is responsible for further magnifying the image produced by the objective lens and projecting it into the viewer's eye.
In addition to these two main lenses, some microscopes may also have other lenses such as a condenser lens, which helps to focus the light onto the specimen, or a polarizing lens, which is used for examining polarized light.
It is worth noting that with the advancement of technology, there are now digital microscopes that use cameras and software to produce images instead of traditional lenses. These digital microscopes can offer higher magnification and resolution, as well as the ability to capture and store images for later analysis.
Overall, the lenses in a microscope are crucial components that allow us to see and study the microscopic world. Whether using traditional lenses or digital technology, microscopes continue to play a vital role in scientific research and discovery.
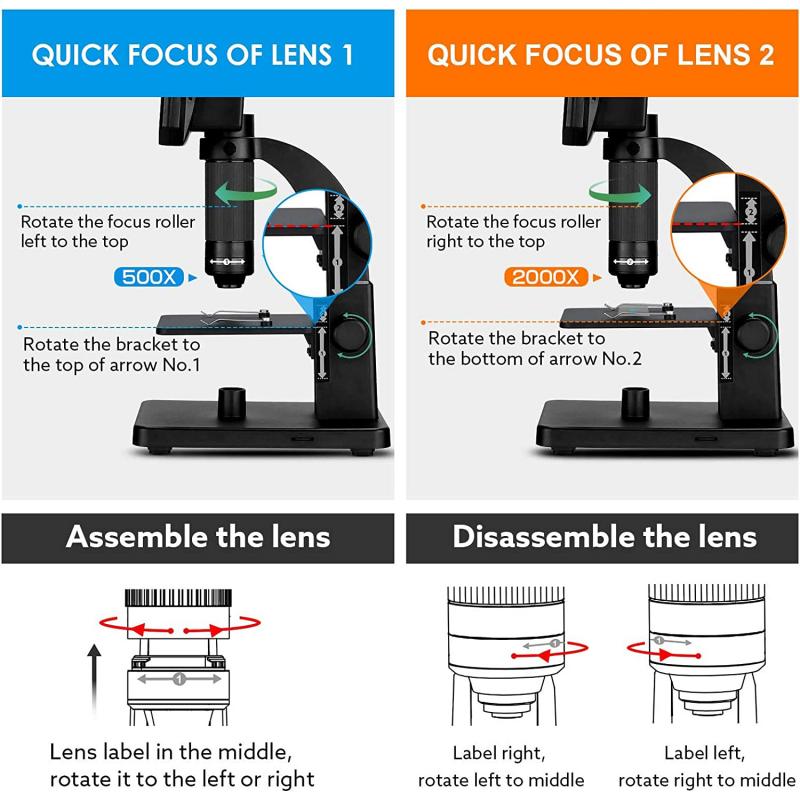
3、 Condenser lens
What lenses are in a microscope? One of the lenses in a microscope is the condenser lens. The condenser lens is located beneath the stage and is responsible for focusing the light onto the specimen. It works by collecting and concentrating the light from the light source, and then directing it onto the specimen. This helps to increase the amount of light that reaches the specimen, making it easier to see and study.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of advanced imaging techniques in microscopy. These techniques include super-resolution microscopy, which allows for the visualization of structures that are smaller than the diffraction limit of light. To achieve this, specialized lenses and techniques are required, such as the use of high numerical aperture objectives and the use of fluorescent dyes.
Another area of interest is the development of new types of lenses for microscopy. For example, researchers are exploring the use of metamaterials, which are materials that have properties not found in nature. These materials can be used to create lenses that are more efficient and have better resolution than traditional lenses.
Overall, the condenser lens remains an important component of the microscope, but there is ongoing research and development in the field of microscopy that is leading to new and exciting advances in imaging technology.

4、 Immersion lens
What lenses are in a microscope? A microscope typically contains several lenses, including the objective lens, eyepiece lens, and condenser lens. The objective lens is the primary lens responsible for magnifying the specimen, while the eyepiece lens further magnifies the image for the viewer's eye. The condenser lens helps to focus the light onto the specimen, improving the clarity of the image.
In addition to these standard lenses, some microscopes may also include an immersion lens. An immersion lens is a specialized lens that is designed to work with immersion oil, which is placed between the lens and the specimen. This oil helps to reduce the amount of light that is lost as it passes through the lens, resulting in a clearer and more detailed image.
The use of immersion lenses has become increasingly popular in recent years, particularly in high-resolution microscopy techniques such as confocal microscopy and super-resolution microscopy. These techniques require extremely high levels of magnification and resolution, and the use of immersion lenses can help to achieve these goals.
Overall, the lenses in a microscope play a critical role in determining the quality and clarity of the images that are produced. The addition of specialized lenses such as immersion lenses can help to further improve the performance of the microscope, allowing researchers to explore the microscopic world in even greater detail.





































There are no comments for this blog.