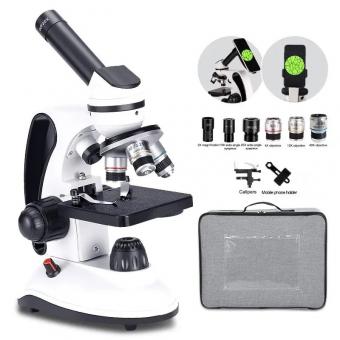
What Magnification Does A Light Microscope Have ?
A light microscope typically has a magnification range of 40x to 1000x. However, with the use of oil immersion lenses, the magnification can be increased up to 2000x.
1、 Optical magnification
What magnification does a light microscope have? The answer is optical magnification, which refers to the increase in apparent size of an object when viewed through a microscope. Light microscopes use visible light to magnify specimens, and they typically have a maximum magnification of around 1000x. However, the actual magnification depends on the quality of the lenses and the resolution of the microscope.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in improving the magnification capabilities of light microscopes. One approach is to use advanced imaging techniques such as super-resolution microscopy, which can achieve resolutions beyond the diffraction limit of light. This allows researchers to visualize structures and processes at the nanoscale level, which was previously impossible with conventional light microscopy.
Another approach is to combine light microscopy with other imaging modalities such as electron microscopy or X-ray microscopy. This enables researchers to obtain complementary information about the same specimen, which can provide a more complete understanding of its structure and function.
Overall, while the maximum magnification of light microscopes has not changed significantly in recent years, advances in imaging techniques and multimodal imaging have greatly expanded their capabilities. As a result, light microscopy remains a powerful tool for biological and biomedical research.

2、 Numerical aperture
The magnification of a light microscope depends on the lenses used and can range from 40x to 1000x. However, the numerical aperture (NA) of the lenses is a more important factor in determining the resolution and clarity of the image produced by the microscope. NA is a measure of the ability of the lens to gather light and resolve fine details in the specimen. The higher the NA, the better the resolution of the microscope.
In recent years, there has been a trend towards using high NA lenses in light microscopy to achieve super-resolution imaging. Super-resolution microscopy techniques such as structured illumination microscopy (SIM), stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy, and single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) have revolutionized the field of microscopy by allowing researchers to visualize structures and processes at the nanoscale level.
The use of high NA lenses in combination with these super-resolution techniques has enabled researchers to study biological processes in unprecedented detail. For example, SMLM has been used to visualize the distribution of proteins and other molecules in cells with a resolution of a few nanometers. This has led to new insights into the organization and function of cellular structures such as the cytoskeleton and the synapse.
In conclusion, while the magnification of a light microscope is important, the numerical aperture of the lenses is a more critical factor in determining the resolution and clarity of the image produced. The use of high NA lenses in combination with super-resolution techniques has opened up new avenues for research in the field of microscopy.

3、 Resolution
"What magnification does a light microscope have?" is a common question asked by students and researchers alike. The answer to this question is not straightforward, as the magnification of a light microscope can vary depending on the lens used and the quality of the microscope itself. However, in general, a light microscope can magnify objects up to 1000 times their original size.
It is important to note that while magnification is an important aspect of microscopy, it is not the only factor that determines the quality of the image produced. Resolution, or the ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects, is also crucial. The resolution of a light microscope is limited by the wavelength of light used to illuminate the sample. This means that there is a limit to how small of a detail can be resolved using a light microscope.
However, recent advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for improved resolution beyond the traditional limits of light microscopy. Techniques such as super-resolution microscopy and structured illumination microscopy have pushed the boundaries of what is possible with light microscopy, allowing for the visualization of structures as small as individual molecules.
In conclusion, while the magnification of a light microscope can vary, it is important to consider resolution as well when evaluating the quality of the image produced. Recent advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for improved resolution beyond the traditional limits of light microscopy, opening up new possibilities for scientific research and discovery.
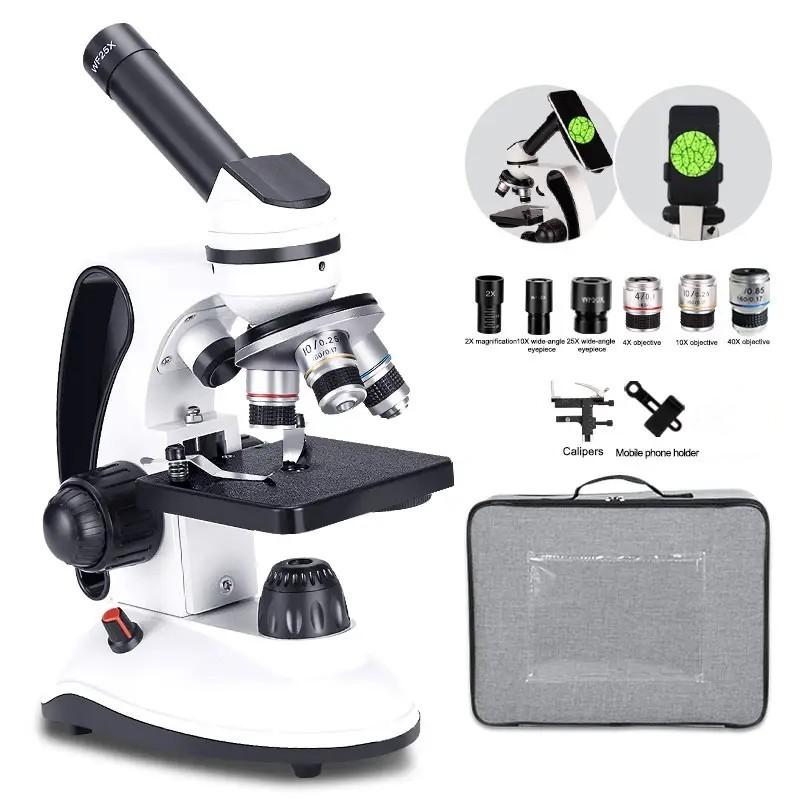
4、 Field of view
The magnification of a light microscope refers to the degree to which an object is enlarged when viewed through the microscope. The magnification of a light microscope can vary depending on the type of lens used and the quality of the microscope itself. Generally, light microscopes have a magnification range of 40x to 1000x, with some high-end models capable of magnifying up to 2000x.
The field of view of a light microscope refers to the area of the specimen that can be seen through the microscope at any given time. The field of view is determined by the size of the objective lens and the magnification of the microscope. As the magnification of the microscope increases, the field of view decreases, meaning that less of the specimen can be seen at any given time.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of digital microscopes, which use digital cameras to capture images of specimens and display them on a computer screen. Digital microscopes offer a number of advantages over traditional light microscopes, including the ability to capture high-resolution images and the ability to share images with others over the internet.
Overall, the magnification and field of view of a light microscope are important factors to consider when choosing a microscope for scientific research or educational purposes. While the magnification of a microscope is important for seeing fine details, the field of view is important for getting a broader view of the specimen as a whole.