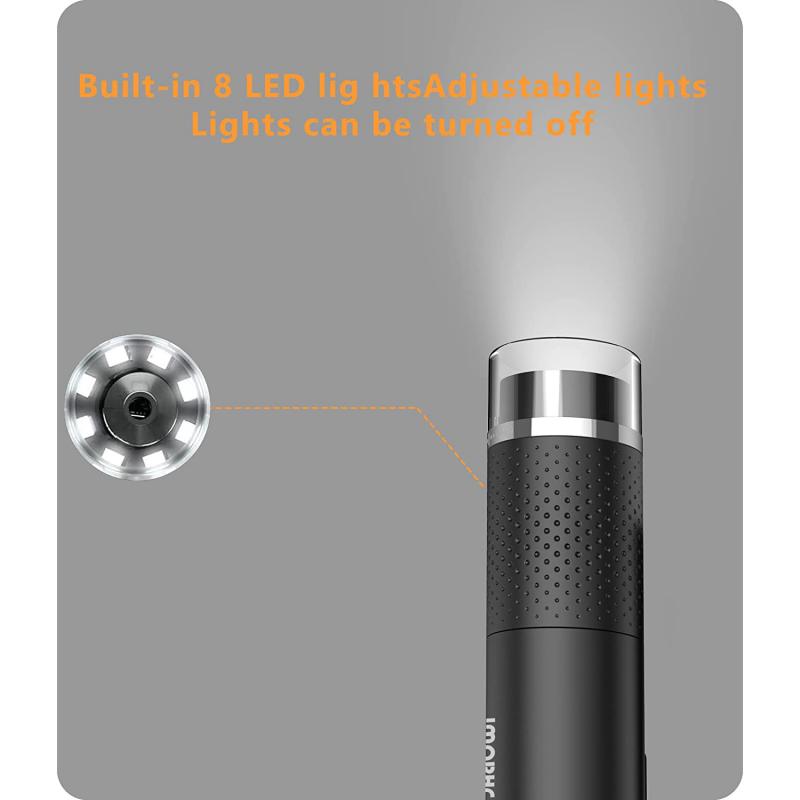
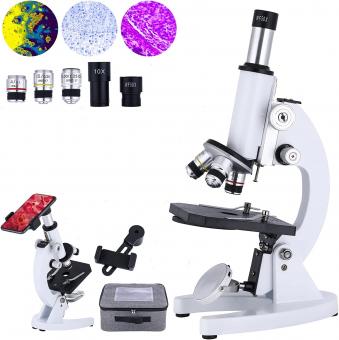
What Microscope Is Used To See Sperm ?
A microscope that is commonly used to see sperm is a compound light microscope. This type of microscope uses visible light and a series of lenses to magnify the sample. The sample is typically prepared on a slide and covered with a coverslip to protect it and keep it in place. The magnification of the microscope allows for the visualization of the sperm cells, which are typically very small and difficult to see with the naked eye. In addition to compound light microscopes, other types of microscopes such as electron microscopes can also be used to visualize sperm cells, but these are typically more specialized and require more advanced training to operate.
1、 Bright-field microscope
The bright-field microscope is commonly used to see sperm. This type of microscope uses a simple lens system to produce an image of a specimen by passing light through it. The specimen is placed on a glass slide and covered with a cover slip to protect it from damage and to keep it in place. The bright-field microscope is ideal for viewing live or stained specimens that have a high contrast with their surroundings.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using other types of microscopes to study sperm. For example, confocal microscopy is a powerful tool that allows researchers to view sperm in three dimensions. This technique uses a laser to scan the specimen and create a series of images that can be reconstructed into a 3D model. This approach has been used to study the structure and function of sperm in a variety of species.
Another emerging technique is super-resolution microscopy, which allows researchers to see structures that are smaller than the diffraction limit of light. This technique has been used to study the structure of the sperm tail, which is critical for motility and fertilization. By using super-resolution microscopy, researchers have been able to see the molecular structure of the proteins that make up the tail and how they interact with each other.
In conclusion, while the bright-field microscope is commonly used to see sperm, there are other emerging techniques that offer new insights into the structure and function of these important cells. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will continue to develop new ways to study sperm and other biological specimens.
2、 Phase-contrast microscope
The phase-contrast microscope is the most commonly used microscope to see sperm. This type of microscope is designed to enhance the contrast of transparent and colorless specimens, such as sperm cells, by converting the differences in refractive index into variations in brightness. This allows for clear visualization of the sperm cells and their movements.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using other types of microscopes, such as the fluorescence microscope, to study sperm. Fluorescence microscopy uses fluorescent dyes to label specific structures within the sperm cells, allowing for more detailed analysis of their morphology and function. This technique has been particularly useful in studying the acrosome reaction, which is a critical step in fertilization.
Another emerging technology in the field of sperm analysis is digital holographic microscopy. This technique uses laser light to create a holographic image of the sperm cells, which can then be reconstructed in three dimensions. This allows for more accurate measurements of sperm motility and morphology, which are important factors in male fertility.
Overall, while the phase-contrast microscope remains the most commonly used tool for visualizing sperm, new technologies are constantly being developed and refined to provide more detailed and accurate analysis of these important cells.

3、 Differential interference contrast microscope
The differential interference contrast microscope (DIC) is a type of light microscope that is commonly used to observe living cells and tissues. It is particularly useful for studying transparent or unstained specimens, such as sperm cells. DIC microscopy uses polarized light to create a three-dimensional image of the specimen, which enhances contrast and provides greater detail than traditional brightfield microscopy.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using advanced imaging techniques to study sperm cells. For example, researchers have used high-speed video microscopy to capture the movement of sperm in real-time, providing new insights into the mechanics of fertilization. Other studies have used fluorescence microscopy to label specific proteins or structures within the sperm cell, allowing researchers to track their movements and interactions.
Despite these advances, DIC microscopy remains a valuable tool for studying sperm cells. It is relatively simple and inexpensive compared to other imaging techniques, and it can provide detailed information about the morphology and behavior of sperm cells in real-time. Moreover, DIC microscopy can be used to study sperm cells in a variety of contexts, including in vitro fertilization, reproductive toxicology, and basic research on sperm function and development.
In conclusion, while there are many imaging techniques available for studying sperm cells, the differential interference contrast microscope remains a reliable and versatile tool for researchers in this field. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that new imaging techniques will emerge that will complement and enhance the capabilities of DIC microscopy.

4、 Fluorescence microscope
What microscope is used to see sperm? The answer is a fluorescence microscope. This type of microscope uses a high-intensity light source to excite fluorescent molecules in the sample, causing them to emit light of a different color. This allows for the visualization of specific structures or molecules within the sample, such as sperm.
In recent years, fluorescence microscopy has become increasingly popular in the field of reproductive biology. It has been used to study the behavior and function of sperm, as well as to diagnose infertility and other reproductive disorders. For example, researchers have used fluorescence microscopy to track the movement of sperm in real-time, allowing them to better understand how sperm navigate through the female reproductive tract.
Fluorescence microscopy has also been used to study the structure and function of sperm cells. By labeling specific proteins or structures within the sperm with fluorescent dyes, researchers can visualize these structures and study their role in sperm function. This has led to new insights into the mechanisms of sperm motility, fertilization, and embryonic development.
Overall, fluorescence microscopy is a powerful tool for studying sperm and other reproductive cells. Its ability to visualize specific structures and molecules within the sample has led to new discoveries and insights into the complex processes of reproduction.