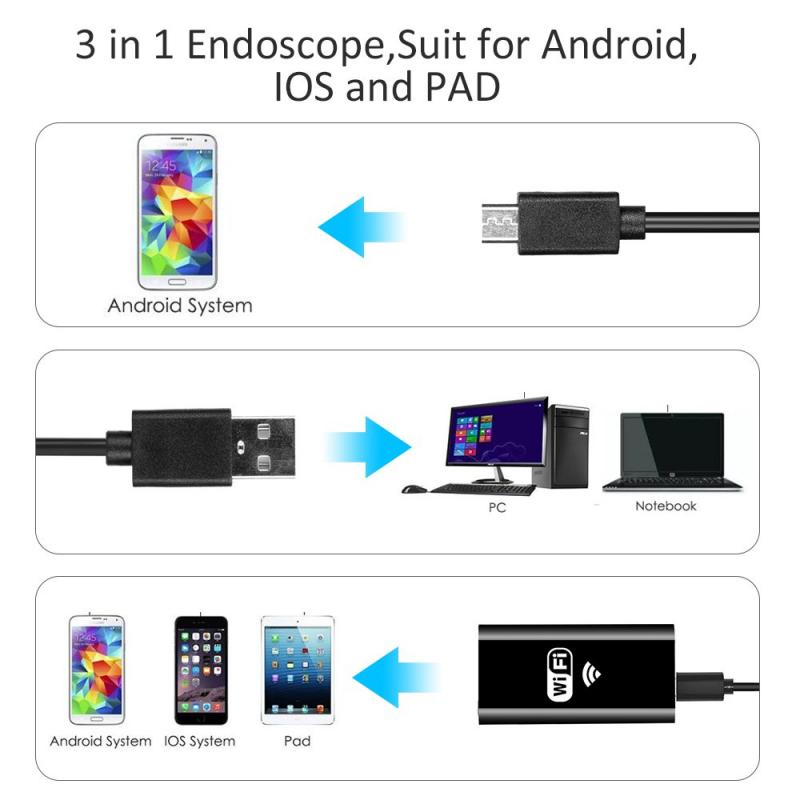
What Size Is An Endoscope ?
The size of an endoscope can vary depending on its specific design and purpose. Endoscopes are medical devices used for visual examination and diagnostic procedures inside the body. They typically consist of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at the tip. The diameter of an endoscope can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters, depending on the area of the body it is intended to be used in and the specific procedure it is designed for. The size of the endoscope is an important consideration to ensure it can be safely inserted into the body and maneuvered within the targeted area.
1、 Diameter of Endoscope
The size of an endoscope can vary depending on its intended use and the specific model. Endoscopes are medical devices used for visualizing and examining internal organs and structures of the body. They are typically long, flexible tubes with a light source and a camera at the tip.
The diameter of an endoscope is an important factor as it determines the size of the instrument that can be inserted into the body. The diameter can range from as small as 1mm to as large as 20mm or more. The choice of diameter depends on the area of the body being examined and the specific procedure being performed.
In recent years, there has been a trend towards the development of smaller and more flexible endoscopes. This is driven by the desire to minimize patient discomfort and improve maneuverability within the body. Advances in technology have allowed for the miniaturization of endoscope components, such as the camera and light source, without compromising image quality.
Additionally, there has been a growing interest in the development of wireless endoscopes, which eliminate the need for a physical connection between the endoscope and the imaging system. These wireless devices are typically smaller in diameter and offer greater flexibility, allowing for easier navigation through the body.
In conclusion, the size of an endoscope can vary depending on its intended use, but there is a trend towards smaller and more flexible devices. The diameter of an endoscope can range from 1mm to 20mm or more, with recent advancements in technology enabling the development of smaller and wireless endoscopes.

2、 Length of Endoscope
The size of an endoscope can vary depending on its intended use and the specific model. Endoscopes are medical devices used for visualizing and examining internal organs and cavities of the body. They are typically long, flexible tubes with a light source and a camera at the tip.
The length of an endoscope can range from a few millimeters to several meters. The size of the endoscope is determined by the area of the body it needs to access and the specific procedure it is designed for. For example, an endoscope used for gastrointestinal procedures may be around 1.5 meters long, while an endoscope used for nasal or ear examinations may be much shorter.
Advancements in technology have led to the development of smaller and more compact endoscopes. Miniaturized endoscopes, known as microendoscopes, have become increasingly popular in recent years. These devices are typically less than 1 millimeter in diameter and can be used for minimally invasive procedures.
The size of an endoscope is an important consideration as it affects the ease of insertion, patient comfort, and the quality of the images captured. Smaller endoscopes can be less invasive and more comfortable for patients, but they may have limitations in terms of image quality and maneuverability.
In conclusion, the size of an endoscope can vary greatly depending on its intended use. From long, flexible tubes for gastrointestinal procedures to miniaturized devices for minimally invasive examinations, endoscopes come in a range of sizes to suit different medical applications.

3、 Working Channel Size of Endoscope
The size of an endoscope can vary depending on its intended use and the specific model. Endoscopes are medical devices used for visualizing and examining internal organs and structures. They consist of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera at the tip. The size of the endoscope is determined by the diameter of the tube, which is measured in millimeters (mm).
The working channel size of an endoscope refers to the diameter of the channel through which instruments can be passed. This channel allows for various procedures to be performed, such as taking biopsies, removing polyps, or delivering therapeutic interventions. The working channel size typically ranges from 2.8 mm to 4.2 mm, although larger channels are available for specialized procedures.
Advancements in technology have led to the development of smaller and more flexible endoscopes. Miniaturized endoscopes with diameters as small as 1 mm have been developed for certain applications, such as examining the small intestine or navigating through narrow passages. These smaller endoscopes offer improved patient comfort and can access areas that were previously difficult to reach.
It is important to note that the size of the endoscope should be chosen based on the specific procedure and patient characteristics. Factors such as the patient's anatomy, the target organ, and the desired intervention will influence the selection of the appropriate endoscope size.
In conclusion, the size of an endoscope can vary, but the working channel size typically ranges from 2.8 mm to 4.2 mm. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of smaller endoscopes with diameters as small as 1 mm for specialized applications. The selection of the appropriate endoscope size should be based on the specific procedure and patient characteristics.

4、 Field of View of Endoscope
The size of an endoscope can vary depending on its specific design and purpose. Generally, endoscopes are slender, flexible tubes that range in diameter from 2.8mm to 12mm. The length of an endoscope can vary as well, typically ranging from 25cm to 150cm. The size of the endoscope is determined by the area of the body it needs to access and the specific procedure it is intended for.
The field of view of an endoscope refers to the range of vision it provides during a procedure. The field of view can vary depending on the type of endoscope being used. Traditional endoscopes typically have a field of view ranging from 70 to 120 degrees. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of wide-angle endoscopes with a field of view of up to 170 degrees.
These wide-angle endoscopes provide a broader view of the internal organs or structures being examined, allowing for better visualization and potentially reducing the need for additional procedures. The wider field of view can be particularly beneficial in complex procedures such as laparoscopic surgeries or gastrointestinal examinations.
It is important to note that the field of view of an endoscope is not solely determined by its size, but also by the optics and imaging technology used. The quality of the image produced by the endoscope can also impact the effectiveness of the procedure. Therefore, advancements in imaging technology play a crucial role in improving the field of view and overall performance of endoscopes.
In conclusion, the size of an endoscope can vary depending on its design and purpose, with diameters ranging from 2.8mm to 12mm and lengths ranging from 25cm to 150cm. The field of view of an endoscope can range from 70 to 170 degrees, with wider angles providing a more comprehensive view. Advancements in technology continue to enhance the field of view and overall performance of endoscopes, leading to improved diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities.