Where Is The Diaphragm Located On A Microscope ?
The diaphragm on a microscope is typically located beneath the stage, near the condenser lens. It is a circular or semi-circular disc with several small holes or an adjustable iris that controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen on the slide. By adjusting the diaphragm, the user can regulate the amount and angle of light that illuminates the specimen, which can improve the clarity and contrast of the image. The diaphragm is an important component of the microscope's illumination system and is often used in conjunction with other adjustments, such as the focus and magnification, to optimize the viewing experience.
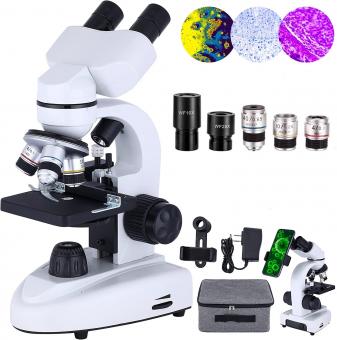
1、 Microscope Anatomy

The diaphragm is an important component of a microscope that controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen. It is located beneath the stage of the microscope and is typically a rotating disk with different sized apertures or holes. By adjusting the size of the aperture, the amount of light that reaches the specimen can be controlled, which can improve the clarity and contrast of the image.
In modern microscopes, the diaphragm is often integrated with other components, such as the condenser, which focuses the light onto the specimen. Some microscopes also have adjustable iris diaphragms, which allow for even more precise control over the amount and angle of light that reaches the specimen.
The location and design of the diaphragm can vary depending on the type of microscope. For example, in a compound microscope, the diaphragm is typically located beneath the stage, while in a stereo microscope, it may be located near the light source. Additionally, some microscopes may have multiple diaphragms or other light control mechanisms, such as polarizers or filters.
Overall, the diaphragm is an essential component of a microscope that plays a critical role in controlling the amount and quality of light that reaches the specimen. By understanding its location and function, microscopists can optimize their imaging conditions and obtain clearer, more detailed images.
2、 Optical Components

The diaphragm is an important component of a microscope that controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen. It is located in the condenser, which is situated beneath the stage of the microscope. The diaphragm is a circular disc with several apertures of varying sizes that can be adjusted to control the amount of light that passes through the specimen.
The diaphragm is an essential component of a microscope as it helps to regulate the amount of light that enters the microscope. This is important because too much light can cause the specimen to appear washed out, while too little light can make it difficult to see the specimen clearly. By adjusting the diaphragm, the user can control the amount of light that enters the microscope, which can help to improve the clarity and contrast of the specimen.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of digital microscopes, which use digital cameras to capture images of the specimen. These microscopes often have built-in software that can automatically adjust the diaphragm to optimize the amount of light that enters the microscope. This can help to improve the quality of the images captured by the microscope, making it easier to see and analyze the specimen. Overall, the diaphragm remains an essential component of the microscope, and its importance is likely to continue to grow as new technologies are developed.
3、 Mechanical Components
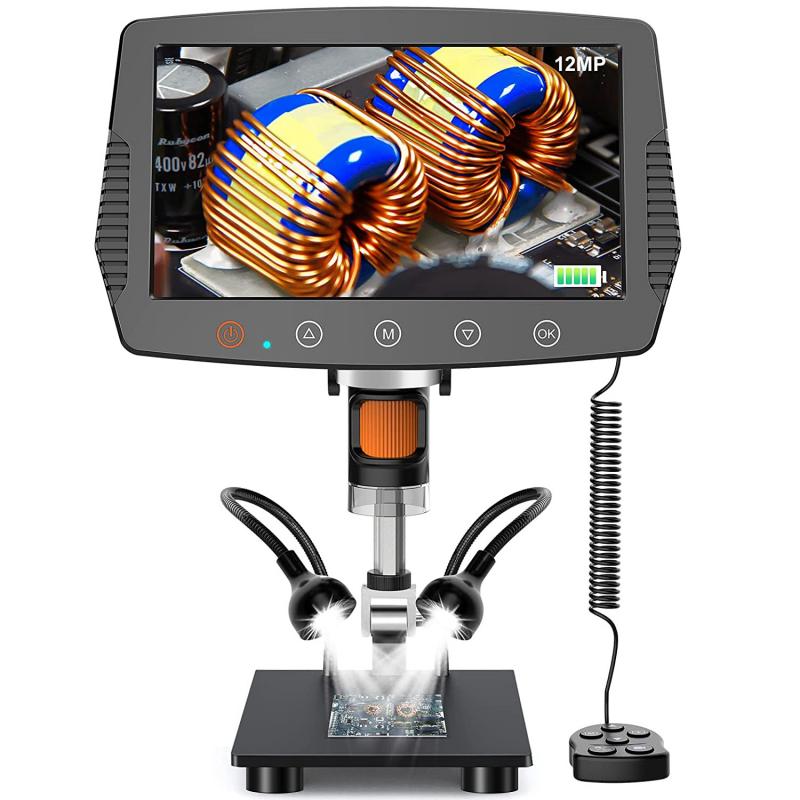

The diaphragm is a mechanical component located on a microscope that controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen being observed. It is typically located beneath the stage of the microscope and is composed of a series of adjustable blades or apertures that can be opened or closed to regulate the amount of light that enters the microscope.
The diaphragm is an essential component of the microscope, as it helps to control the amount of light that reaches the specimen. This is important because too much light can cause the specimen to appear washed out or overexposed, while too little light can make it difficult to see the details of the specimen.
In modern microscopes, the diaphragm is often integrated with other components, such as the condenser and the light source, to provide more precise control over the illumination of the specimen. Some microscopes also feature electronic diaphragms that can be controlled using a computer or other digital device.
Overall, the diaphragm is a critical component of the microscope that helps to ensure accurate and detailed observations of specimens. Its location beneath the stage and its adjustable blades or apertures make it a versatile and essential tool for researchers and scientists in a wide range of fields.
4、 Stage and Focus Mechanism

The diaphragm on a microscope is located within the stage and focus mechanism. It is a circular disk with different sized holes that can be adjusted to control the amount of light that passes through the specimen being viewed. The diaphragm is typically located just below the stage, which is the platform where the specimen is placed for observation.
The purpose of the diaphragm is to regulate the amount of light that passes through the specimen. By adjusting the size of the opening, the user can control the amount of light that reaches the objective lens. This is important because too much light can cause the specimen to appear washed out, while too little light can make it difficult to see the details of the specimen.
In recent years, there has been a trend towards using digital microscopes that do not have a physical diaphragm. Instead, these microscopes use software to adjust the amount of light that is captured by the camera. This allows for more precise control over the lighting conditions and can result in clearer images.
Overall, the location of the diaphragm on a microscope is an important consideration for achieving optimal viewing conditions. Whether using a traditional microscope with a physical diaphragm or a digital microscope with software-based controls, it is essential to have the ability to adjust the lighting conditions to achieve the best possible results.



























There are no comments for this blog.