Which Lens In Microscope ?
The lens in a microscope is typically a compound lens system that consists of multiple lenses. The most common lenses in a microscope are the objective lens and the eyepiece lens. The objective lens is located near the specimen and is responsible for magnifying the image of the specimen. It typically has a higher magnification power. The eyepiece lens, on the other hand, is located near the viewer's eye and further magnifies the image produced by the objective lens. It is also known as the ocular lens. Together, these lenses work in tandem to produce a magnified image of the specimen for observation.
1、 Objective lens
The objective lens is one of the most important components of a microscope. It is responsible for gathering light from the specimen and forming a magnified image. The objective lens is located close to the specimen and is typically the lens with the highest magnification power in a microscope.
The objective lens is designed to provide high resolution and clarity in the magnified image. It is usually made up of multiple lenses that work together to correct for various optical aberrations and improve the quality of the image. The magnification power of the objective lens can vary depending on the specific microscope, but it is typically in the range of 4x to 100x.
In recent years, there have been advancements in objective lens technology that have further improved the capabilities of microscopes. For example, there are now objective lenses with higher numerical apertures, which allow for increased light-gathering ability and improved resolution. Additionally, there are objective lenses specifically designed for specialized imaging techniques such as fluorescence microscopy or confocal microscopy.
Objective lenses are available in different magnification powers, allowing scientists and researchers to choose the appropriate lens for their specific needs. The choice of objective lens depends on factors such as the type of specimen being observed, the level of detail required, and the specific imaging technique being used.
In conclusion, the objective lens is a crucial component of a microscope, responsible for gathering light and forming a magnified image. Advancements in objective lens technology have improved the resolution and capabilities of microscopes, allowing for more detailed and accurate observations.

2、 Eyepiece lens
The eyepiece lens, also known as the ocular lens, is an essential component of a microscope. It is located at the top of the microscope and is the lens through which the viewer looks to observe the magnified image of the specimen. The primary function of the eyepiece lens is to further magnify the image produced by the objective lens.
The eyepiece lens typically has a magnification power of 10x, although higher magnification options are also available. When combined with the magnification power of the objective lens, the total magnification of the microscope is determined. For example, if the objective lens has a magnification power of 40x and the eyepiece lens has a magnification power of 10x, the total magnification would be 400x.
In recent years, there have been advancements in eyepiece lens technology. Some microscopes now come with digital eyepiece lenses that can capture images and videos of the specimen directly onto a computer or other digital device. This allows for easier documentation and sharing of observations. Additionally, some eyepiece lenses now have built-in reticles or grids that can be used for measuring the size or distance of objects in the field of view.
Overall, the eyepiece lens plays a crucial role in the magnification and observation capabilities of a microscope. It allows for a closer examination of the specimen and provides a clear and detailed image for the viewer. With advancements in technology, the eyepiece lens continues to evolve, offering new features and functionalities to enhance the microscopy experience.

3、 Condenser lens
The condenser lens is an essential component of a microscope that plays a crucial role in focusing and directing light onto the specimen. It is located beneath the stage and above the light source. The main function of the condenser lens is to gather and concentrate light onto the specimen, ensuring optimal illumination and enhancing the quality of the image observed through the microscope.
The condenser lens works by converging the light rays emitted from the light source into a concentrated beam. This concentrated beam of light passes through the specimen and is then magnified by the objective lens, ultimately forming the final image observed by the viewer. Without the condenser lens, the image would appear dim and lack clarity.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards using more advanced condenser lens designs in microscopes. These newer designs incorporate features such as adjustable aperture diaphragms and variable numerical apertures, allowing for greater control over the intensity and angle of the light entering the specimen. This enables researchers to optimize the illumination conditions for different types of specimens and improve image quality.
Additionally, advancements in lens manufacturing technology have led to the development of high-quality condenser lenses with improved optical performance. These lenses are designed to minimize aberrations and maximize light transmission, resulting in sharper and more detailed images.
In conclusion, the condenser lens is a critical component of a microscope that ensures proper illumination and enhances image quality. With advancements in design and manufacturing, modern condenser lenses offer improved control over illumination conditions and superior optical performance, contributing to the advancement of scientific research and discovery.
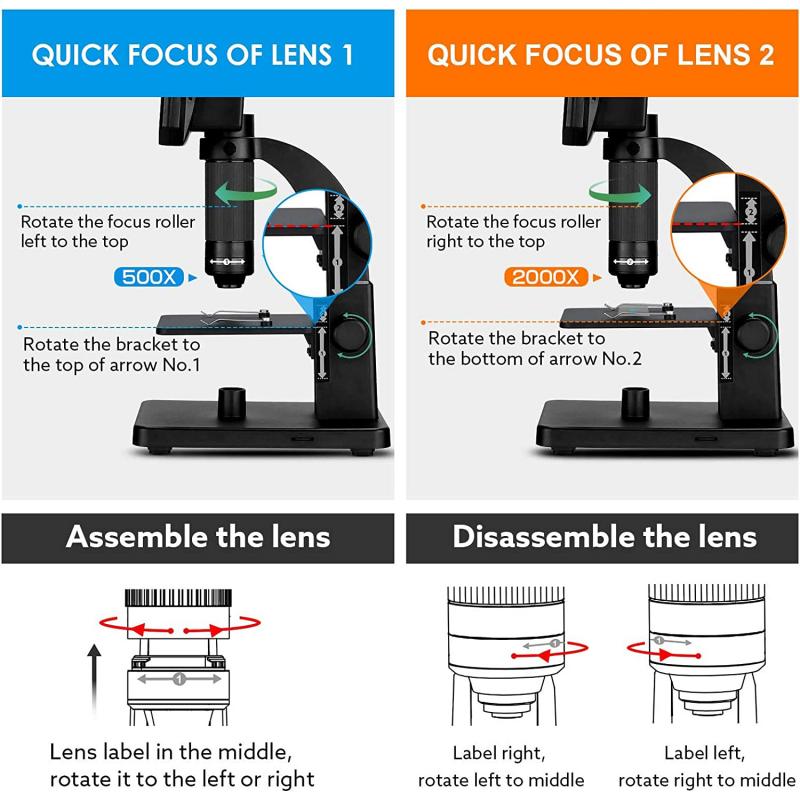
4、 Immersion lens
The immersion lens is a type of lens used in microscopes that is designed to improve the resolution and clarity of the image. It is typically used in high-power objectives, such as the oil immersion lens.
The immersion lens works by reducing the refractive index mismatch between the specimen and the lens. This is achieved by immersing the lens in a liquid with a refractive index similar to that of the specimen. The most commonly used liquid for immersion is oil, hence the name oil immersion lens. By using oil, the light rays passing through the lens are less likely to scatter, resulting in a sharper and more detailed image.
The use of immersion lenses has become increasingly important in modern microscopy techniques, particularly in the field of biological research. With the advancement of technology, researchers are now able to study specimens at a much higher resolution than ever before. Immersion lenses play a crucial role in achieving this level of detail.
In recent years, there have been advancements in immersion lens technology. For example, some microscopes now use water immersion lenses, which offer similar benefits to oil immersion lenses but without the need for oil. Water immersion lenses are particularly useful for live cell imaging, as they are less likely to damage delicate specimens.
Overall, the immersion lens is an essential component of modern microscopy, allowing researchers to observe and study specimens with greater clarity and resolution. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements and innovations in immersion lens design and functionality.