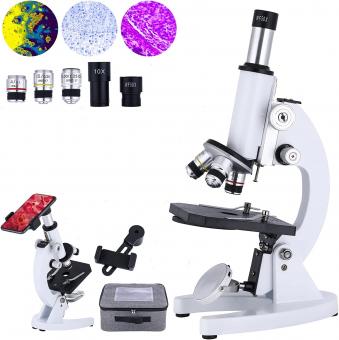
Which Part Of The Microscope ?
The microscope consists of several parts, including the eyepiece, objective lenses, stage, focus knobs, and light source. The eyepiece is the part that the viewer looks through to see the magnified image. The objective lenses are located near the stage and are responsible for magnifying the specimen. The stage is where the specimen is placed for observation. The focus knobs are used to adjust the focus of the image. The light source provides illumination for the specimen.
1、 Eyepiece
The eyepiece, also known as the ocular lens, is the part of the microscope that is responsible for magnifying the image produced by the objective lens. It is located at the top of the microscope and is the part that the viewer looks through to observe the specimen.
The eyepiece typically contains a set of lenses that work together to magnify the image. The magnification power of the eyepiece is usually indicated on the lens itself, and can range from 5x to 30x or more. The eyepiece is also adjustable, allowing the viewer to focus the image to their liking.
In recent years, there has been a trend towards using digital eyepieces, which allow the user to view the specimen on a computer screen rather than through the eyepiece itself. This can be particularly useful for sharing images with others or for capturing images for later analysis.
Another recent development in eyepiece technology is the use of eyepieces with built-in cameras. These cameras can capture high-resolution images and videos of the specimen, which can be saved and shared electronically. This technology has revolutionized the way that scientists and researchers study specimens, allowing for more detailed and accurate analysis than ever before.
Overall, the eyepiece is a critical component of the microscope, allowing the viewer to observe and analyze specimens at high magnification. With the latest advancements in technology, the eyepiece continues to evolve and improve, making it an essential tool for scientific research and discovery.

2、 Objective lenses
Objective lenses are an essential part of the microscope that plays a crucial role in magnifying the specimen. These lenses are located at the bottom of the microscope's body tube and are responsible for producing a magnified image of the specimen. The objective lenses come in different magnification powers, ranging from 4x to 100x, and are interchangeable to provide different levels of magnification.
The quality of the objective lenses is critical in determining the clarity and resolution of the image produced. The latest advancements in objective lens technology have led to the development of high-quality lenses that provide sharper and clearer images. These lenses are made using advanced materials and manufacturing techniques that reduce aberrations and distortions, resulting in a more accurate image.
Another recent development in objective lens technology is the use of specialized lenses for specific applications. For example, there are objective lenses designed for use in fluorescence microscopy, which emit light of a specific wavelength to excite fluorescent molecules in the specimen. These lenses are essential in studying the behavior of cells and tissues in living organisms.
In conclusion, objective lenses are a crucial part of the microscope that plays a vital role in producing a magnified image of the specimen. The latest advancements in objective lens technology have led to the development of high-quality lenses that provide sharper and clearer images, as well as specialized lenses for specific applications.

3、 Stage
Which part of the microscope is the stage?
The stage is an essential part of the microscope that holds the specimen being observed. It is a flat platform that is usually located below the objective lenses and above the light source. The stage has a hole in the center that allows light to pass through and illuminate the specimen. The stage also has clips or clamps that hold the slide in place, preventing it from moving during observation.
In recent years, the stage has undergone significant improvements to enhance its functionality. For instance, some microscopes now have motorized stages that allow for precise movement of the specimen in the x, y, and z-axis. This feature is particularly useful in advanced microscopy techniques such as confocal microscopy, where the specimen needs to be scanned in multiple planes.
Additionally, some stages now have heating and cooling capabilities, which enable the observation of live specimens at different temperatures. This feature is particularly useful in studying biological processes that are temperature-dependent, such as enzyme activity.
In conclusion, the stage is a crucial part of the microscope that holds the specimen being observed. Its functionality has been enhanced in recent years with the introduction of motorized stages and heating/cooling capabilities, making it easier to observe specimens in advanced microscopy techniques.

4、 Focus knobs
The focus knobs are an essential part of the microscope that allows the user to adjust the focus of the specimen being observed. These knobs are typically located on the side or underneath the microscope and are used to move the stage up and down, which in turn adjusts the focus of the objective lens.
The focus knobs are crucial for obtaining clear and sharp images of the specimen being observed. Without proper focus, the image will appear blurry and difficult to interpret. Therefore, it is important to use the focus knobs to adjust the focus until the image is clear and in focus.
In recent years, there have been advancements in microscope technology that have led to the development of automated focus systems. These systems use advanced algorithms and sensors to automatically adjust the focus of the microscope, eliminating the need for manual adjustments. This technology has made it easier for researchers and scientists to obtain high-quality images and has reduced the risk of human error.
Overall, the focus knobs are an essential part of the microscope that allows for precise adjustments of the focus of the objective lens. While automated focus systems have become more prevalent in recent years, the focus knobs remain an important tool for obtaining clear and sharp images of the specimen being observed.