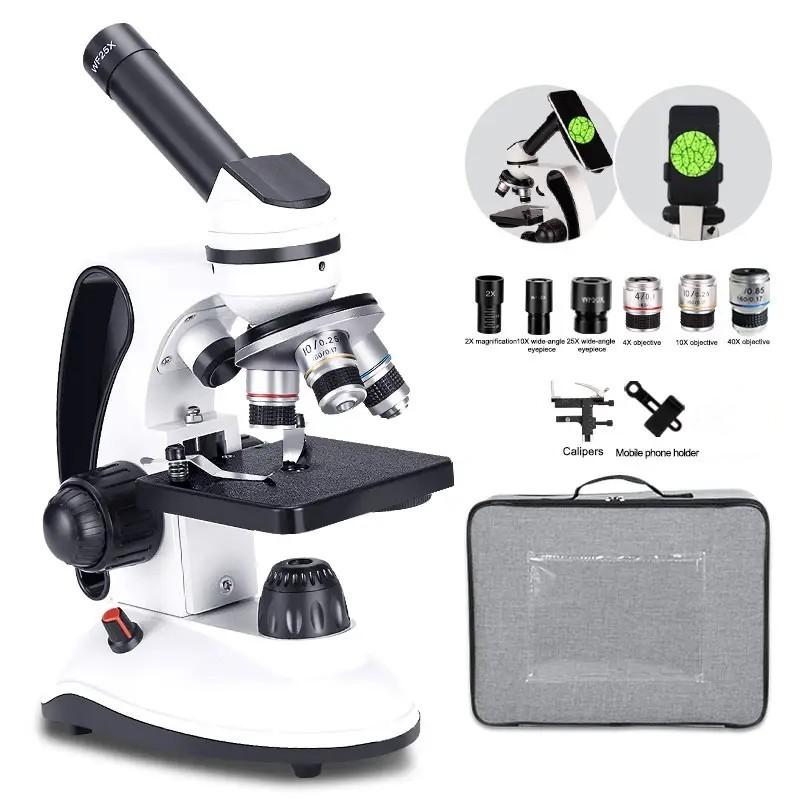
Why Do We Use A Microscope ?
We use a microscope to magnify and observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. It allows us to study the details and structures of microscopic organisms, cells, tissues, and other tiny particles. Microscopes are essential tools in various scientific fields, including biology, medicine, chemistry, and materials science. They enable scientists to make important discoveries, conduct research, and gain a deeper understanding of the microscopic world. Additionally, microscopes are used in industries such as manufacturing and quality control to examine small components and ensure their accuracy and quality.
1、 Magnification: Enlarging objects to see small details.
We use a microscope for various reasons, but the primary purpose is to magnify objects and enable us to see small details that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. Magnification is a crucial aspect of microscopy as it allows us to study and understand the intricate structures and processes occurring at the microscopic level.
Microscopes are extensively used in scientific research, medicine, and various other fields. In biology, for instance, microscopes are indispensable tools for studying cells, tissues, and microorganisms. They enable scientists to observe and analyze the intricate structures and functions of living organisms, aiding in the advancement of knowledge in fields such as genetics, microbiology, and pathology.
Moreover, microscopes have played a pivotal role in medical diagnostics. They allow doctors and pathologists to examine blood samples, identify pathogens, and diagnose diseases. Microscopy has also been instrumental in the development of new drugs and therapies, as it enables researchers to study the effects of drugs on cells and tissues.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have revolutionized the field. The development of electron microscopes has allowed scientists to achieve even higher magnification and resolution, enabling them to observe objects at the atomic level. Additionally, the advent of confocal microscopy has facilitated the study of three-dimensional structures and processes within cells and tissues.
Furthermore, the integration of microscopy with other techniques, such as fluorescence imaging and molecular labeling, has opened up new avenues for research. These techniques enable scientists to visualize specific molecules or structures within cells, providing valuable insights into their functions and interactions.
In conclusion, we use microscopes primarily for magnification, which allows us to see small details. However, the latest advancements in microscopy technology have expanded its applications and capabilities, enabling us to delve deeper into the microscopic world and gain a better understanding of the complex processes occurring at that level.

2、 Resolution: Enhancing clarity and distinguishing closely spaced objects.
We use a microscope for various reasons, but one of the primary purposes is to enhance clarity and distinguish closely spaced objects. The resolution of a microscope refers to its ability to produce clear and detailed images by magnifying the specimen under observation. This is achieved by using lenses that can magnify the image and improve the level of detail that can be seen.
Microscopes are essential tools in fields such as biology, medicine, and materials science, where the ability to observe and analyze microscopic structures is crucial. By using a microscope, scientists and researchers can study the intricate details of cells, tissues, and microorganisms, leading to a better understanding of their structure and function. This knowledge is vital for advancements in medical research, disease diagnosis, and treatment development.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in microscopy technology, leading to even higher resolution and improved imaging capabilities. For example, the development of super-resolution microscopy techniques has allowed scientists to visualize structures that were previously beyond the limits of traditional microscopes. These techniques, such as stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy and structured illumination microscopy (SIM), have revolutionized the field by enabling the observation of nanoscale structures and processes.
Furthermore, the integration of microscopy with other technologies, such as fluorescence imaging and molecular labeling, has opened up new possibilities for studying biological processes at the molecular level. This has led to breakthroughs in areas such as genetics, neurobiology, and drug discovery.
In conclusion, the use of a microscope is essential for enhancing clarity and distinguishing closely spaced objects. With advancements in microscopy technology, scientists can now observe and analyze structures at unprecedented levels of detail, leading to significant advancements in various scientific disciplines.

3、 Illumination: Providing light to illuminate the specimen.
Why do we use a microscope? One of the main reasons is illumination. Microscopes are designed to provide light that illuminates the specimen being observed. This illumination is crucial because it allows us to see the details and characteristics of the specimen that would otherwise be invisible to the naked eye.
The use of illumination in microscopy has evolved over time. In the early days of microscopy, natural light sources such as sunlight or candles were used to illuminate specimens. However, these light sources were often inconsistent and limited in their ability to provide clear and focused illumination.
With advancements in technology, microscopes now come equipped with various types of illumination sources. One common type is the built-in light source, such as a halogen or LED bulb, which provides a steady and controlled light output. This ensures that the specimen is evenly illuminated, allowing for accurate observation and analysis.
In addition to providing illumination, modern microscopes also offer adjustable lighting options. This allows researchers to control the intensity and direction of the light, enhancing the visibility of specific features or structures within the specimen. For example, darkfield illumination is used to observe transparent or translucent specimens by illuminating them from the side, creating a contrasting background.
Furthermore, the latest advancements in microscopy technology have introduced techniques such as fluorescence microscopy, which utilizes fluorescent dyes to label specific structures or molecules within the specimen. These dyes emit light of a different color when excited by a specific wavelength of light, allowing for the visualization of specific components within the specimen.
In conclusion, the use of a microscope is essential for scientific research, medical diagnostics, and various other fields. Illumination plays a crucial role in microscopy, allowing us to observe and analyze the intricate details of specimens that would otherwise remain hidden. With the latest advancements in illumination techniques, microscopes continue to revolutionize our understanding of the microscopic world.

4、 Observation: Examining microscopic structures and organisms.
We use a microscope for various reasons, but the primary purpose is observation. A microscope allows us to examine microscopic structures and organisms that are not visible to the naked eye. By magnifying these objects, we can gain a deeper understanding of their characteristics, behavior, and interactions.
Observation through a microscope has been crucial in advancing scientific knowledge in fields such as biology, medicine, and materials science. It has enabled us to study the intricate details of cells, tissues, and microorganisms, leading to breakthroughs in disease diagnosis, drug development, and genetic research. Microscopes have also been instrumental in exploring the world of nanotechnology, where scientists manipulate and study materials at the atomic and molecular level.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have further expanded our capabilities. For instance, the development of electron microscopes has allowed us to visualize structures with even higher resolution, providing unprecedented insights into the nanoscale world. Additionally, techniques like confocal microscopy and super-resolution microscopy have enabled scientists to study living cells and dynamic processes in real-time, revolutionizing our understanding of biological systems.
Moreover, microscopes are not limited to scientific research. They are also widely used in industries such as manufacturing, forensics, and quality control. Microscopic examination helps identify defects, analyze materials, and ensure product quality and safety.
In summary, we use microscopes for observation because they allow us to explore and understand the microscopic world. From unraveling the mysteries of life to advancing technological innovations, microscopes continue to play a vital role in expanding our knowledge and pushing the boundaries of scientific discovery.