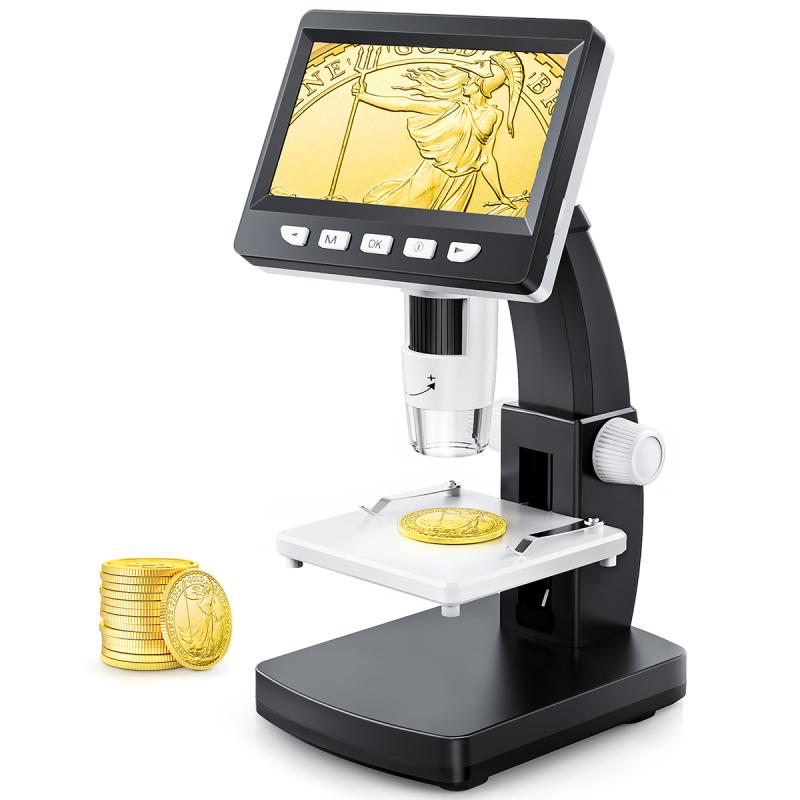
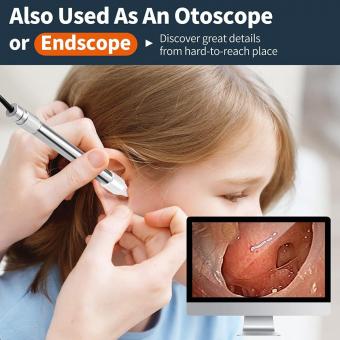
Why Microscope Is Important ?
Microscopes are important tools in various fields of science and medicine. They allow scientists and researchers to observe and study objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. By magnifying the image of the specimen, microscopes enable detailed examination and analysis of cells, tissues, microorganisms, and other tiny structures.
In biology, microscopes are crucial for studying the intricate structures and functions of cells, as well as for conducting research on genetics, microbiology, and pathology. In medicine, microscopes are used for diagnosing diseases by examining tissue samples and identifying abnormalities. They are also essential in fields like forensic science, where they aid in analyzing evidence such as hair, fibers, and fingerprints.
Moreover, microscopes have revolutionized fields like materials science and nanotechnology, enabling scientists to investigate and manipulate materials at the atomic and molecular levels. This has led to advancements in various industries, including electronics, materials engineering, and pharmaceuticals.
Overall, microscopes play a vital role in expanding our understanding of the microscopic world, driving scientific discoveries, and improving our knowledge in numerous disciplines.
1、 Magnification and Resolution
The microscope is an essential tool in the field of science and research, and its importance lies in its ability to magnify and resolve objects that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. Magnification refers to the microscope's ability to enlarge an object, allowing scientists to study its intricate details and structures. Resolution, on the other hand, refers to the microscope's ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects. Both magnification and resolution are crucial aspects of microscopy, and here's why:
Magnification allows scientists to observe and study objects at a much larger scale, enabling them to examine the fine details and structures that are not visible to the naked eye. This is particularly important in fields such as biology, where the study of cells, tissues, and microorganisms requires a high level of magnification. By magnifying these objects, scientists can better understand their functions, interactions, and overall behavior.
Resolution, on the other hand, is equally important as it determines the level of detail that can be observed. A microscope with high resolution can distinguish between closely spaced objects, allowing scientists to study the intricate structures within cells or the fine features of microorganisms. This level of detail is crucial in various scientific disciplines, including medicine, genetics, and materials science.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have further enhanced the importance of magnification and resolution. Techniques such as confocal microscopy, electron microscopy, and super-resolution microscopy have pushed the boundaries of what can be observed and studied. These techniques have allowed scientists to delve deeper into the world of nanoscale structures, unraveling mysteries and discovering new phenomena.
In conclusion, the microscope is important because it enables scientists to magnify and resolve objects, providing a deeper understanding of the natural world. The ability to observe and study objects at a microscopic level has revolutionized various scientific disciplines and continues to drive new discoveries. With ongoing advancements in microscopy technology, the importance of magnification and resolution will only continue to grow.

2、 Scientific Research and Discovery
The microscope is an essential tool in scientific research and discovery due to its ability to magnify and visualize objects that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. It has revolutionized various fields of study, including biology, medicine, chemistry, and materials science, by enabling scientists to observe and understand the intricate details of the microscopic world.
One of the primary reasons why microscopes are important is their role in advancing our knowledge of the natural world. By allowing scientists to observe and study cells, microorganisms, and other tiny structures, microscopes have played a crucial role in the development of the cell theory, the discovery of bacteria and viruses, and the understanding of complex biological processes. Microscopes have also been instrumental in the field of medicine, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases by enabling the visualization of pathogens and abnormalities at the cellular level.
Moreover, microscopes have facilitated breakthroughs in materials science by allowing scientists to examine the atomic and molecular structures of materials. This has led to the development of new materials with enhanced properties, such as stronger metals, more efficient semiconductors, and advanced polymers. In addition, microscopes have been instrumental in the field of nanotechnology, where scientists manipulate and study materials at the nanoscale to create innovative devices and technologies.
The importance of microscopes in scientific research continues to grow with advancements in technology. The latest point of view emphasizes the development of high-resolution imaging techniques, such as electron microscopy and super-resolution microscopy, which provide even greater detail and clarity. These techniques have enabled scientists to visualize structures at the atomic level and observe dynamic processes in real-time, opening up new avenues for research and discovery.
In conclusion, the microscope is a vital tool in scientific research and discovery. Its ability to magnify and visualize the microscopic world has revolutionized various fields of study, leading to significant advancements in our understanding of biology, medicine, chemistry, and materials science. With the continuous development of high-resolution imaging techniques, the microscope will undoubtedly continue to play a crucial role in pushing the boundaries of scientific knowledge.

3、 Medical Diagnostics and Pathology
The microscope is an essential tool in the field of medical diagnostics and pathology. It allows healthcare professionals to examine and analyze various specimens at a microscopic level, providing valuable insights into the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
One of the primary reasons why microscopes are important in medical diagnostics is their ability to visualize and identify cellular and tissue abnormalities. By examining blood, urine, or tissue samples under a microscope, doctors can detect the presence of pathogens, abnormal cells, or other indicators of disease. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Moreover, microscopes enable pathologists to study the structure and function of tissues and organs in detail. This helps in identifying the nature and extent of diseases, such as cancer, infections, or autoimmune disorders. Microscopic examination also aids in determining the stage of a disease, which is vital for prognosis and selecting the most effective treatment options.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy techniques have further enhanced its importance in medical diagnostics. For instance, the development of digital microscopy allows for the capture and storage of high-resolution images, enabling remote consultation and collaboration among healthcare professionals. Additionally, techniques like fluorescence microscopy and confocal microscopy have revolutionized the visualization of specific cellular components and molecular processes, providing deeper insights into disease mechanisms.
Furthermore, the integration of microscopy with other diagnostic technologies, such as molecular biology and genetic testing, has expanded its applications. Microscopes are now used in conjunction with techniques like polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and immunohistochemistry to analyze genetic mutations, gene expression patterns, and protein markers. This multidisciplinary approach has significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnostics.
In conclusion, the microscope plays a crucial role in medical diagnostics and pathology. Its ability to visualize and analyze specimens at a microscopic level provides valuable information for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease monitoring. With ongoing advancements in microscopy techniques, it continues to be an indispensable tool in the field of medicine.

4、 Industrial Quality Control and Inspection
Microscopes play a crucial role in industrial quality control and inspection processes. They provide a magnified view of objects, allowing for detailed analysis and examination of various materials and components. Here are several reasons why microscopes are important in industrial quality control:
1. Defect detection: Microscopes enable inspectors to identify and analyze defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. This is particularly important in industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace, where even minor defects can have significant consequences.
2. Precision measurement: Microscopes equipped with measurement tools, such as calibrated scales or digital imaging software, allow for accurate measurement of dimensions and tolerances. This ensures that products meet the required specifications and standards.
3. Material analysis: Microscopes enable inspectors to examine the composition and structure of materials, helping to identify impurities, defects, or inconsistencies. This is crucial in industries where the quality and integrity of materials directly impact product performance and safety.
4. Surface inspection: Microscopes with advanced imaging techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), can provide detailed surface analysis. This helps in detecting surface irregularities, scratches, cracks, or contamination, which are critical factors in ensuring product quality.
5. Research and development: Microscopes are essential tools in research and development processes, allowing scientists and engineers to study new materials, analyze their properties, and develop innovative products. They aid in understanding the microstructure and behavior of materials, leading to improved product design and performance.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have further enhanced its importance in industrial quality control. For example, the development of digital microscopy has enabled real-time imaging, image analysis, and data sharing, facilitating faster decision-making and collaboration among inspectors and quality control teams. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms with microscopes has the potential to automate defect detection and analysis, improving efficiency and accuracy in quality control processes.
In conclusion, microscopes are indispensable tools in industrial quality control and inspection. They enable defect detection, precise measurement, material analysis, surface inspection, and support research and development efforts. With the continuous advancements in microscopy technology, their importance in ensuring product quality and safety is only expected to grow.