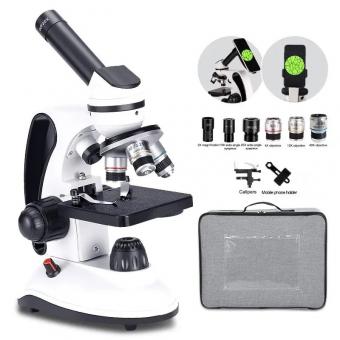
Why Use A Light Microscope ?
A light microscope is used to observe and study small objects or organisms that are not visible to the naked eye. It uses visible light to illuminate the specimen and magnify it, allowing for detailed examination of its structure and characteristics. Light microscopes are widely used in various scientific fields, including biology, medicine, and materials science. They are relatively simple to use, affordable, and versatile, making them accessible to researchers, students, and professionals. Additionally, light microscopes can provide real-time imaging, allowing for dynamic observations and analysis.
1、 Magnification: Enlarging the image of small objects for better visibility.
Why use a light microscope? One of the main reasons is magnification. Light microscopes are designed to enlarge the image of small objects, allowing us to see them more clearly and in greater detail. By using lenses to focus light, these microscopes can magnify objects up to a thousand times their original size. This is particularly useful when studying tiny organisms, cells, or structures that are not visible to the naked eye.
Magnification is crucial in various scientific fields, such as biology, medicine, and materials science. In biology, for example, researchers use light microscopes to study the intricate structures of cells and tissues. By magnifying these structures, scientists can observe and analyze their functions, interactions, and abnormalities. In medicine, light microscopes are used to diagnose diseases by examining blood samples, biopsies, and other bodily fluids. The ability to magnify these samples allows doctors to identify pathogens, abnormal cells, and other indicators of illness.
Moreover, light microscopes are relatively affordable and easy to use compared to other types of microscopes. They do not require complex sample preparation techniques or expensive equipment, making them accessible to a wide range of users. This accessibility has contributed to their widespread use in educational settings, where students can learn about the microscopic world and conduct their own experiments.
In recent years, advancements in technology have further enhanced the capabilities of light microscopes. For instance, the development of digital imaging has allowed for the capture and analysis of high-resolution images. This has opened up new possibilities for research and has facilitated the sharing of findings among scientists worldwide. Additionally, the integration of fluorescence microscopy techniques with light microscopes has enabled the visualization of specific molecules and cellular processes, providing valuable insights into various biological phenomena.
In conclusion, the use of light microscopes is essential for magnifying small objects and improving visibility. Their affordability, ease of use, and recent technological advancements have made them indispensable tools in scientific research, education, and medical diagnostics. By enabling us to see the microscopic world in greater detail, light microscopes continue to contribute to our understanding of the natural world and the advancement of various fields of study.

2、 Resolution: Ability to distinguish fine details and separate closely spaced objects.
Why use a light microscope? Resolution: Ability to distinguish fine details and separate closely spaced objects.
The light microscope has been a fundamental tool in the field of biology for centuries. One of its key advantages is its ability to provide high resolution, allowing scientists to observe and study fine details of biological specimens. Resolution refers to the microscope's ability to distinguish between closely spaced objects and reveal intricate structures that may not be visible to the naked eye.
The light microscope achieves this resolution through the use of visible light, which has a shorter wavelength compared to other forms of radiation such as electron beams. The shorter wavelength of light allows for greater detail to be captured, enabling scientists to study cellular structures, microorganisms, and other biological specimens with precision.
In recent years, advancements in light microscopy techniques have further enhanced the resolution capabilities of the light microscope. Techniques such as confocal microscopy, which uses laser scanning to eliminate out-of-focus light, and super-resolution microscopy, which surpasses the diffraction limit of light, have revolutionized the field. These techniques have allowed scientists to visualize cellular processes at the nanoscale level, providing insights into the intricate workings of living organisms.
Furthermore, the light microscope is a versatile and accessible tool. It is relatively affordable, easy to use, and can be used to observe living specimens in real-time. This makes it an invaluable tool for a wide range of scientific disciplines, from cell biology to microbiology, and even in medical diagnostics.
In conclusion, the light microscope remains a crucial tool in the field of biology due to its ability to provide high resolution. With advancements in microscopy techniques, it continues to play a vital role in unraveling the mysteries of the microscopic world and advancing our understanding of life itself.
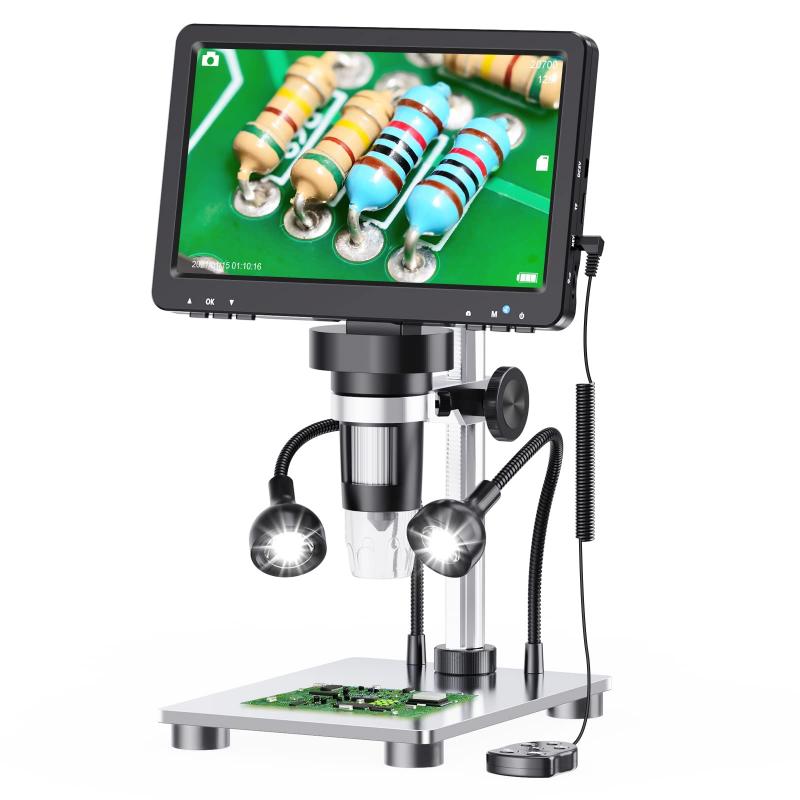

3、 Versatility: Suitable for observing a wide range of specimens and materials.
Why use a light microscope? One of the main reasons is its versatility, as it is suitable for observing a wide range of specimens and materials. Light microscopes use visible light to illuminate the sample, allowing for detailed examination of various biological and non-biological samples.
In the field of biology, light microscopes are commonly used to study cells, tissues, and microorganisms. They provide valuable information about cell structure, cellular processes, and the interactions between different components of living organisms. Light microscopes are also used in medical research and diagnostics, enabling the identification and analysis of diseases and abnormalities at the cellular level.
Moreover, light microscopes are not limited to biological samples. They can be used to examine materials in fields such as materials science, geology, and forensics. For example, light microscopes can analyze the composition and structure of minerals, study the properties of different materials, and aid in the identification of trace evidence in criminal investigations.
Additionally, light microscopes are relatively affordable and easy to use compared to other types of microscopes. They do not require extensive sample preparation or specialized training, making them accessible to a wide range of users. Furthermore, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated light microscopes, such as confocal and fluorescence microscopes, which offer enhanced imaging capabilities and allow for the visualization of specific molecules or structures within a sample.
In conclusion, the versatility of light microscopes makes them an indispensable tool in various scientific disciplines. Their ability to observe a wide range of specimens and materials, coupled with their accessibility and affordability, ensures that they remain a fundamental instrument in scientific research and discovery.

4、 Cost-effectiveness: Relatively affordable compared to other microscopy techniques.
Why use a light microscope? One of the main reasons is cost-effectiveness. Light microscopes are relatively affordable compared to other microscopy techniques. This makes them accessible to a wide range of researchers, educators, and students.
Light microscopes use visible light to illuminate the sample and magnify it, allowing for detailed observation of cells, tissues, and other small structures. They are widely used in various fields such as biology, medicine, materials science, and forensics. The affordability of light microscopes makes them an essential tool for many researchers and educators who may not have the budget for more advanced microscopy techniques.
In addition to being cost-effective, light microscopes also offer other advantages. They are easy to use and require minimal training, making them suitable for educational purposes. They provide real-time imaging, allowing researchers to observe dynamic processes in living cells. Light microscopes also have a wide range of available techniques and accessories, such as phase contrast, fluorescence, and polarized light, which can enhance the visualization of specific structures or molecules.
Furthermore, advancements in technology have improved the capabilities of light microscopes. For example, the development of confocal microscopy has allowed for the imaging of thick samples with high resolution and reduced background noise. Super-resolution techniques, such as stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy and structured illumination microscopy (SIM), have pushed the limits of resolution beyond the diffraction limit of light.
In conclusion, the cost-effectiveness of light microscopes makes them a popular choice for researchers, educators, and students. They provide a versatile and accessible tool for studying a wide range of samples and have benefited from technological advancements that have expanded their capabilities.