100 Microscope What To Look At ?
A microscope can be used to look at a variety of things, depending on the type of microscope and the level of magnification. With a light microscope, you can look at cells, tissues, and microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. You can also examine small structures such as hair, pollen, and insect parts. With an electron microscope, you can see even smaller structures such as viruses, molecules, and atoms. Additionally, you can use a microscope to observe the behavior of living organisms, such as the movement of cells or the behavior of microorganisms in response to stimuli. Overall, the possibilities of what to look at with a microscope are vast and varied, and depend on the specific interests and goals of the observer.
1、 Microbial life forms
100 microscope what to look at: Microbial life forms
Microbial life forms are microscopic organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. These organisms play a crucial role in the ecosystem, as they are involved in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships with other organisms.
When looking at microbial life forms under a microscope, there are several things to consider. First, it is important to identify the type of microbe being observed. This can be done by examining the shape, size, and other characteristics of the organism. For example, bacteria can be classified based on their shape, such as cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), or spirilla (spiral-shaped).
Another important aspect to consider when observing microbial life forms is their behavior and interactions with other organisms. For example, some bacteria are able to form biofilms, which are communities of microorganisms that adhere to surfaces and can cause infections or other problems.
Recent advances in microscopy technology have allowed scientists to study microbial life forms in greater detail than ever before. For example, confocal microscopy allows for three-dimensional imaging of microorganisms, while super-resolution microscopy can reveal details at the nanoscale level.
Overall, studying microbial life forms under a microscope is a fascinating and important field of research, with implications for fields ranging from medicine to environmental science.
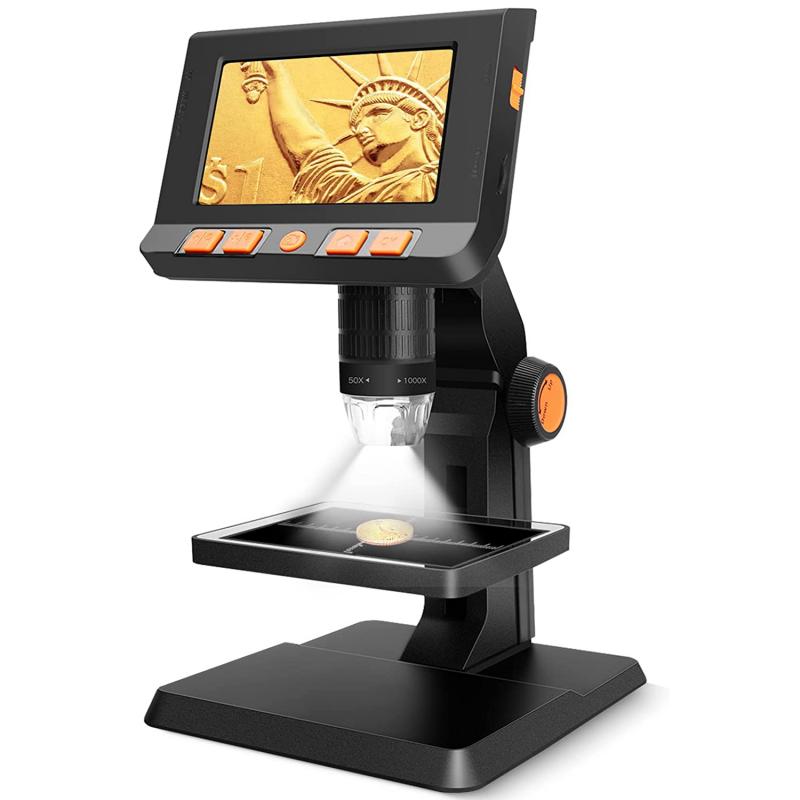

2、 Cellular structures
100 microscope what to look at: Cellular structures.
When using a microscope to observe cellular structures, there are several key features to look for. One of the most important is the cell membrane, which surrounds and protects the cell. This thin, flexible layer is made up of lipids and proteins and is responsible for controlling what enters and exits the cell.
Another important structure to observe is the nucleus, which contains the cell's genetic material. This structure is typically located near the center of the cell and is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. Within the nucleus, you may also be able to observe the nucleolus, which is responsible for producing ribosomes.
Other cellular structures to look for include the endoplasmic reticulum, which is responsible for protein synthesis and lipid metabolism, and the Golgi apparatus, which modifies and packages proteins for transport. You may also be able to observe mitochondria, which are responsible for producing energy for the cell, and lysosomes, which break down and recycle cellular waste.
It's important to note that our understanding of cellular structures is constantly evolving as new research is conducted. For example, recent studies have shed light on the role of the cytoskeleton in maintaining cell shape and movement, and the importance of membraneless organelles in cellular function. As such, it's important to stay up-to-date on the latest research and developments in the field of cell biology.

3、 Tissue samples
100 microscope what to look at: Tissue samples.
Tissue samples are an essential component of medical research and diagnosis. With the help of a microscope, scientists and medical professionals can examine tissue samples at a cellular level to identify abnormalities, diagnose diseases, and develop treatments.
One of the latest advancements in tissue sample analysis is the use of digital pathology. This technology allows for the digitization of tissue samples, making it easier to share and analyze data. It also enables the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to assist in the analysis of tissue samples.
When examining tissue samples under a microscope, there are several things to look for. First, the overall structure of the tissue should be observed, including the arrangement of cells and any abnormalities in shape or size. Next, the presence of any abnormal cells, such as cancer cells, should be identified. The presence of inflammation or infection can also be detected through the examination of tissue samples.
In addition to traditional light microscopy, other types of microscopy can be used to examine tissue samples. Electron microscopy, for example, can provide a higher level of detail and resolution, allowing for the examination of subcellular structures.
Overall, the examination of tissue samples under a microscope remains a crucial tool in medical research and diagnosis. With the latest advancements in technology, the analysis of tissue samples is becoming more efficient and accurate, leading to improved patient outcomes.
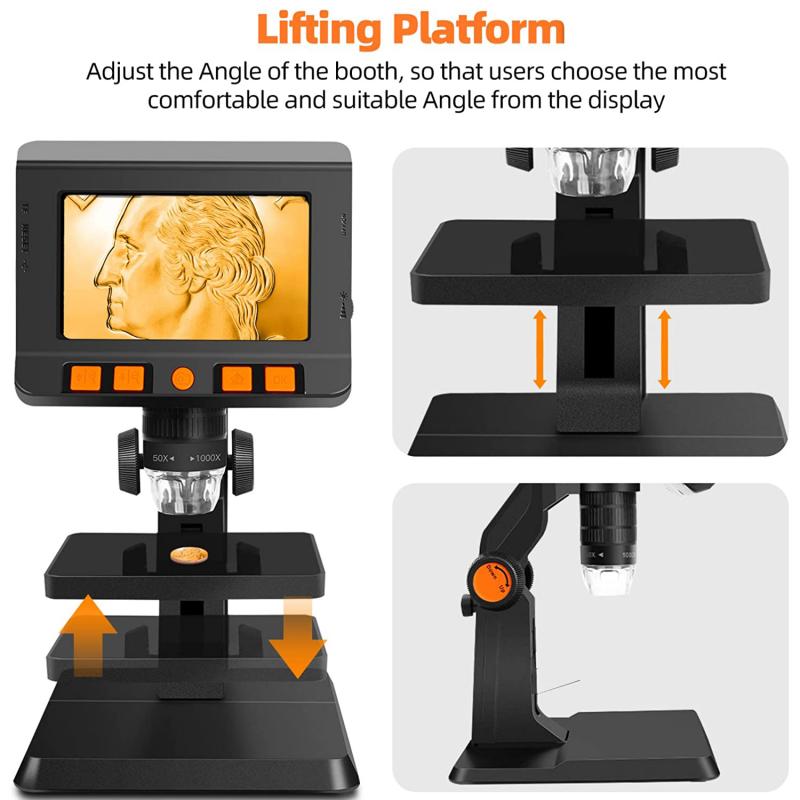

4、 Blood cells
100 microscope what to look at: Blood cells.
When looking at blood cells under a microscope, there are three main types of cells to observe: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. They are small, biconcave discs that lack a nucleus and are filled with hemoglobin. White blood cells, or leukocytes, are part of the immune system and help to fight off infections and diseases. There are several types of white blood cells, each with a specific function. Platelets, or thrombocytes, are responsible for blood clotting and preventing excessive bleeding.
Recent advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for even more detailed observations of blood cells. For example, confocal microscopy allows for the visualization of individual cells in three dimensions, providing a more accurate representation of their structure and function. Additionally, super-resolution microscopy techniques such as stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy and structured illumination microscopy (SIM) have allowed for the visualization of structures within cells that were previously too small to be seen.
Overall, observing blood cells under a microscope can provide valuable information about a person's health and can aid in the diagnosis of various diseases and conditions. With the latest advancements in microscopy technology, researchers and healthcare professionals can gain an even deeper understanding of the complex workings of the human body.