How Do Optical Rangefinders Work ?
Optical rangefinders work by measuring the distance between the observer and a target using optical principles. They typically use a combination of lenses, mirrors, and sensors to determine the range. One common method is the time-of-flight principle, where a laser or infrared beam is emitted towards the target, and the time it takes for the beam to bounce back is measured. By knowing the speed of light or infrared radiation, the distance can be calculated. Another method is triangulation, where the rangefinder uses two optical sensors to observe the target from slightly different angles. By comparing the images captured by the sensors, the device can calculate the distance based on the parallax effect. Optical rangefinders are commonly used in various applications, including photography, surveying, and military targeting.
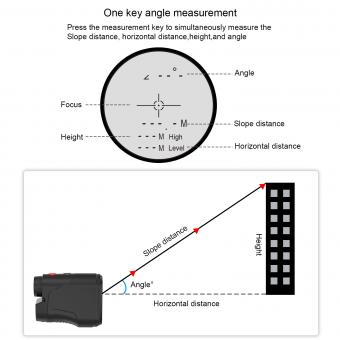
1、 Triangulation method in optical rangefinders
Optical rangefinders are devices used to measure the distance between the observer and a target object. One common method employed by optical rangefinders is the triangulation method. This method relies on the principles of geometry and trigonometry to calculate the distance.
In the triangulation method, the rangefinder emits a beam of light towards the target object. This beam of light is either a laser or an infrared signal. The light beam is then reflected off the target object and detected by a sensor in the rangefinder. The sensor measures the angle at which the light beam is received.
By knowing the angle at which the light beam was emitted and the angle at which it was received, the rangefinder can calculate the distance to the target object using trigonometric calculations. The distance is determined by the principle of triangulation, which involves forming a triangle with the observer, the target object, and the rangefinder.
The latest advancements in optical rangefinders have focused on improving the accuracy and speed of distance measurements. This has been achieved through the use of advanced sensors and algorithms. For example, some rangefinders now employ multiple sensors to capture a wider field of view and improve accuracy.
Additionally, the use of digital signal processing techniques has allowed for faster and more precise calculations. These advancements have made optical rangefinders more reliable and efficient in various applications, such as surveying, hunting, and military operations.
In conclusion, optical rangefinders work based on the triangulation method, which involves emitting a light beam towards a target object and measuring the angles to calculate the distance. The latest advancements in technology have further enhanced the accuracy and speed of distance measurements in optical rangefinders.

2、 Time-of-flight principle in optical rangefinders
Optical rangefinders are devices used to measure the distance between the device and a target object. They utilize various principles to achieve accurate distance measurements. One commonly used principle is the time-of-flight principle.
The time-of-flight principle in optical rangefinders involves emitting a laser or infrared beam towards the target object and measuring the time it takes for the beam to travel to the object and back to the rangefinder. By knowing the speed of light, the rangefinder can calculate the distance based on the time it took for the beam to make the round trip.
To measure the time-of-flight accurately, optical rangefinders use advanced timing circuits and sensors. These sensors detect the reflected beam and provide precise timing information. The rangefinder then calculates the distance by multiplying the time by the speed of light and dividing it by two.
In recent years, there have been advancements in optical rangefinder technology. One notable development is the use of advanced algorithms and signal processing techniques to improve accuracy and reliability. These algorithms can compensate for factors such as atmospheric conditions, target surface properties, and interference from other light sources.
Additionally, some optical rangefinders now incorporate multiple beams or use pulsed lasers to enhance accuracy. By emitting multiple beams or pulses, the rangefinder can measure the time-of-flight for each beam and average the results to obtain a more precise distance measurement.
Overall, optical rangefinders based on the time-of-flight principle provide accurate distance measurements by utilizing advanced timing circuits, sensors, and algorithms. These devices have applications in various fields, including surveying, construction, and robotics, where precise distance measurements are crucial.

3、 Laser-based distance measurement in optical rangefinders
Optical rangefinders are devices used to measure the distance between the observer and a target. They utilize various techniques, including laser-based distance measurement, to accurately determine the range.
Laser-based distance measurement in optical rangefinders works by emitting a laser beam towards the target and measuring the time it takes for the beam to travel to the target and back. This time measurement is then used to calculate the distance based on the speed of light. By knowing the speed of light and accurately measuring the time of flight, the distance can be determined with high precision.
In recent years, there have been advancements in laser technology that have improved the performance of optical rangefinders. For instance, the development of solid-state lasers has made them more compact, reliable, and energy-efficient. These lasers emit short pulses of light, allowing for precise time-of-flight measurements.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced signal processing algorithms has enhanced the accuracy and reliability of laser-based distance measurement. These algorithms can compensate for factors such as atmospheric conditions, target reflectivity, and background noise, ensuring more accurate distance calculations.
Additionally, some optical rangefinders now incorporate multiple laser beams or use scanning techniques to measure distances to multiple points simultaneously. This enables the creation of three-dimensional maps or the tracking of moving targets in real-time.
Overall, laser-based distance measurement in optical rangefinders has evolved to provide highly accurate and reliable range measurements. The latest advancements in laser technology and signal processing algorithms have further improved their performance, making them invaluable tools in various applications, including surveying, construction, and military operations.

4、 Phase-shift measurement technique in optical rangefinders
Optical rangefinders are devices used to measure the distance between the device and a target object. One common technique used in optical rangefinders is the phase-shift measurement technique.
In the phase-shift measurement technique, a laser beam is emitted from the rangefinder towards the target object. The laser beam reflects off the object and returns to the rangefinder. By measuring the phase shift of the laser beam, the distance between the rangefinder and the object can be calculated.
The phase shift is determined by comparing the phase of the emitted laser beam with the phase of the received laser beam. This phase difference is caused by the difference in the path length traveled by the laser beam during emission and reception. By accurately measuring this phase difference, the distance can be calculated using the known speed of light.
The latest point of view in optical rangefinders is the advancement in technology, particularly in the development of more precise and sensitive detectors. These detectors are capable of accurately measuring the phase shift of the laser beam, allowing for more accurate distance measurements.
Additionally, advancements in signal processing algorithms have improved the accuracy and reliability of optical rangefinders. These algorithms can compensate for environmental factors such as atmospheric conditions or surface reflectivity, which can affect the accuracy of distance measurements.
Overall, the phase-shift measurement technique in optical rangefinders provides a reliable and accurate method for measuring distances. With the latest advancements in technology, optical rangefinders are becoming increasingly precise and versatile, finding applications in various fields such as surveying, construction, and robotics.