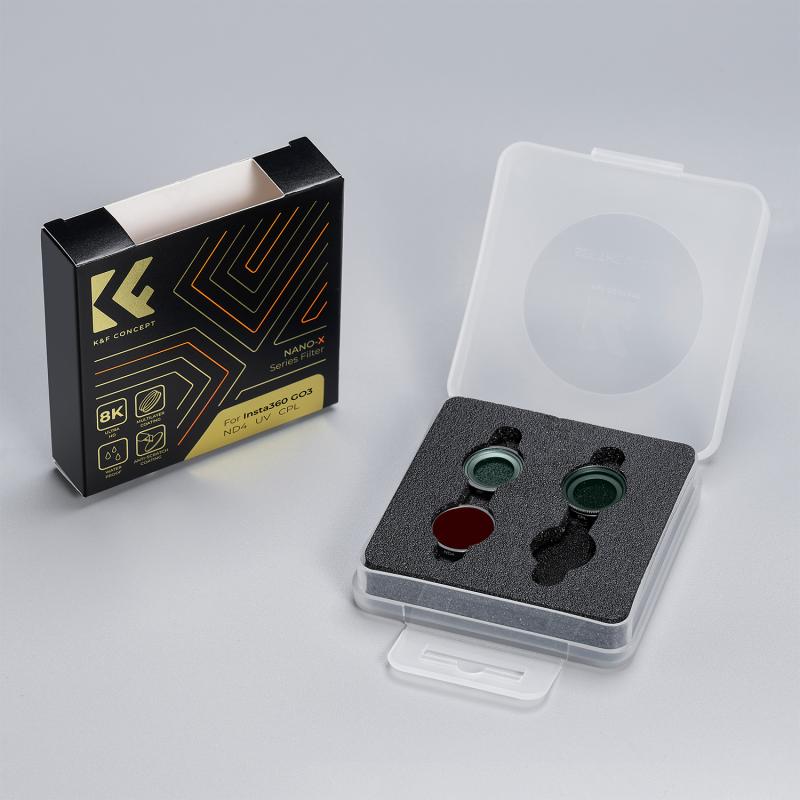
What Are Filters For On Cameras ?
Filters on cameras are accessories that are used to modify the light entering the camera lens. They can serve various purposes, such as enhancing colors, reducing glare, or adding special effects to photographs. Filters are typically made of glass or resin and are attached to the front of the camera lens. They come in different types, including UV filters, polarizing filters, neutral density filters, and color filters. UV filters are primarily used to protect the lens from scratches, dust, and moisture, while also reducing the effects of ultraviolet light. Polarizing filters help to reduce reflections and glare, resulting in more vibrant and saturated colors. Neutral density filters are used to reduce the amount of light entering the camera, allowing for longer exposures or wider apertures in bright conditions. Color filters are used to alter the color balance of the image, creating artistic effects or compensating for different lighting conditions.
1、 Optical Filters: Enhancing or altering light transmission for specific effects.
Filters on cameras are optical devices that are used to enhance or alter light transmission for specific effects. They are typically made of glass or resin and are placed in front of the camera lens. Filters can be used to manipulate the colors, contrast, and overall mood of a photograph, allowing photographers to achieve their desired artistic vision.
One of the most common types of filters is the UV filter, which is primarily used to reduce the amount of ultraviolet light that reaches the camera sensor. UV filters are particularly useful in outdoor photography, as they can help reduce haze and improve overall image clarity. However, with advancements in digital camera technology, the necessity of UV filters has been debated. Some argue that modern camera sensors are already equipped with UV filters, making additional UV filters redundant.
Another popular type of filter is the polarizing filter, which is used to reduce glare and reflections from non-metallic surfaces such as water or glass. Polarizing filters can also enhance color saturation and contrast, resulting in more vibrant and dramatic images. These filters are commonly used in landscape photography to capture clear blue skies and to bring out the colors of foliage.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards digital post-processing techniques, such as using software like Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom, to achieve similar effects that were traditionally achieved with physical filters. This has led some photographers to question the necessity of using filters on cameras. However, it is important to note that while post-processing can be powerful, it cannot always replicate the exact effects achieved with physical filters. Additionally, using filters in-camera can save time and effort in post-processing, allowing photographers to capture their desired effects directly in-camera.
In conclusion, filters on cameras serve the purpose of enhancing or altering light transmission for specific effects. While advancements in digital technology have provided alternative methods for achieving similar effects, physical filters still offer unique advantages and are widely used by photographers to achieve their artistic vision.
2、 UV Filters: Reducing ultraviolet light and protecting the lens.
UV filters are an essential accessory for cameras that serve multiple purposes. One of the primary functions of UV filters is to reduce the amount of ultraviolet (UV) light that enters the camera lens. UV light is invisible to the human eye but can cause a hazy or bluish cast in photographs, especially in outdoor settings. By using a UV filter, photographers can effectively minimize this unwanted effect and achieve more accurate and vibrant colors in their images.
In addition to improving image quality, UV filters also serve as a protective barrier for the camera lens. They act as a shield against dust, moisture, and scratches, safeguarding the lens from potential damage. This is particularly important when shooting in challenging environments such as sandy beaches or dusty landscapes. By using a UV filter, photographers can ensure the longevity of their lens and avoid costly repairs or replacements.
However, it is worth noting that the necessity of UV filters has been a topic of debate among photographers in recent years. With advancements in lens coatings and digital post-processing techniques, some argue that the impact of UV light on image quality is minimal and can be easily corrected in editing software. Additionally, high-quality lenses often come with built-in coatings that effectively reduce UV light without the need for an additional filter.
Ultimately, the decision to use a UV filter depends on personal preference and shooting conditions. While some photographers choose to rely on post-processing techniques, others still find value in using UV filters for their protective properties. It is important for photographers to weigh the benefits and drawbacks and make an informed decision based on their specific needs and shooting style.

3、 Polarizing Filters: Minimizing reflections and enhancing color saturation.
Filters on cameras serve various purposes, but one common type is the polarizing filter. These filters are designed to minimize reflections and enhance color saturation in photographs. By selectively blocking certain light waves, polarizing filters help to reduce glare and unwanted reflections from non-metallic surfaces such as water, glass, and foliage.
When photographing a scene with a polarizing filter, the filter can be rotated to achieve the desired effect. By adjusting the angle of the filter, photographers can control the amount of polarized light that enters the camera, resulting in a reduction of reflections and an increase in color saturation. This can be particularly useful when shooting landscapes, as it helps to bring out the vibrant colors of the sky, water, and foliage.
In addition to reducing reflections and enhancing colors, polarizing filters can also improve overall image quality. By reducing glare, they can increase the clarity and sharpness of the photograph. This is especially beneficial when shooting in bright sunlight or when capturing images through glass.
It is worth noting that with advancements in digital photography and post-processing software, some photographers argue that the need for polarizing filters has diminished. They argue that many of the effects achieved with a polarizing filter can be replicated or enhanced in post-processing. However, others still find value in using polarizing filters, as they allow for immediate results in-camera and can help to reduce the amount of post-processing required.
Ultimately, the use of polarizing filters on cameras remains a personal choice for photographers. While they may not be essential in every situation, they can still be a valuable tool for minimizing reflections and enhancing color saturation in certain photographic scenarios.

4、 Neutral Density Filters: Reducing the amount of light entering the camera.
Neutral density filters are an essential tool in a photographer's arsenal, serving the purpose of reducing the amount of light that enters the camera. These filters are particularly useful in situations where the available light is too bright, such as when shooting in broad daylight or capturing long exposures. By limiting the amount of light, neutral density filters allow photographers to achieve creative effects that would otherwise be challenging or impossible to achieve.
One of the primary applications of neutral density filters is in landscape photography. When shooting landscapes, photographers often want to capture a wide depth of field, which requires using a small aperture. However, in bright lighting conditions, this can result in overexposed images. By using a neutral density filter, photographers can reduce the amount of light entering the camera, allowing them to use longer shutter speeds and smaller apertures without overexposing the image. This enables them to capture stunning landscapes with sharp details throughout the frame.
Neutral density filters are also commonly used in long exposure photography. By using a filter with a high density, photographers can achieve longer exposure times, resulting in smooth and silky waterfalls, rivers, or clouds. This technique can create a sense of motion and tranquility in the image, adding a unique and artistic touch.
In recent years, neutral density filters have become even more popular with the rise of drone photography. Drones often have fixed apertures, limiting the control over exposure settings. By using neutral density filters, drone photographers can effectively control the amount of light entering the camera, allowing them to capture well-exposed images even in bright conditions.
In conclusion, neutral density filters play a crucial role in photography by reducing the amount of light entering the camera. They enable photographers to overcome challenges posed by bright lighting conditions and achieve creative effects such as long exposures and wide depth of field. With the increasing popularity of landscape and drone photography, neutral density filters have become an indispensable tool for photographers seeking to capture stunning and unique images.