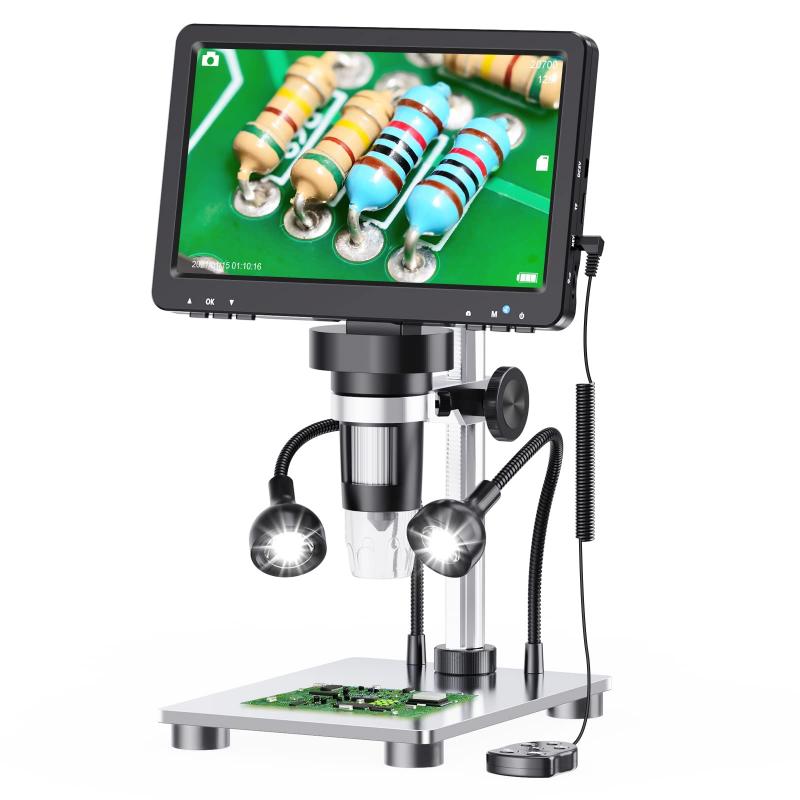
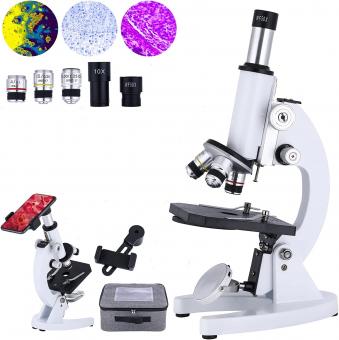
What Can You See With 1200x Microscope ?
With a 1200x microscope, you can see highly magnified details of various objects and specimens. This level of magnification allows you to observe intricate structures and features that are not visible to the naked eye. For example, you can examine the cellular structures of plants and animals, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and cell walls. Additionally, you can explore the world of microorganisms, observing bacteria, fungi, and protozoa in great detail. With this microscope, you can also study the fine details of minerals, crystals, and other small objects. Overall, a 1200x microscope provides a powerful tool for scientific research, education, and exploration of the microscopic world.
1、 Cellular Structures and Organelles
With a 1200x microscope, you can observe cellular structures and organelles in great detail. This level of magnification allows for a closer examination of the intricate components that make up a cell.
One of the first things you may notice is the cell membrane, a thin barrier that encloses the cell and controls the movement of substances in and out. You can observe its phospholipid bilayer structure and any proteins embedded within it.
Moving inside the cell, you can see the nucleus, which contains the genetic material of the cell in the form of DNA. With a 1200x microscope, you can observe the nuclear envelope, nucleolus, and chromatin fibers within the nucleus.
Other organelles that become visible at this magnification include the mitochondria, responsible for energy production through cellular respiration. You can observe their double membrane structure and the presence of cristae, which increase the surface area for energy production.
Additionally, you can see the endoplasmic reticulum, a network of membranes involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. With a 1200x microscope, you may be able to distinguish between rough endoplasmic reticulum (with ribosomes attached) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (without ribosomes).
Golgi apparatus, involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins, can also be observed. You can see its stacked membrane structure and vesicles budding off from its edges.
Furthermore, you may be able to observe lysosomes, which contain digestive enzymes for breaking down waste materials, and peroxisomes, involved in detoxification processes.
It is important to note that the latest advancements in microscopy techniques, such as super-resolution microscopy, have pushed the boundaries of what can be observed. These techniques allow for even higher magnification and resolution, enabling scientists to study cellular structures and organelles in even greater detail.

2、 Microorganisms and Bacteria
With a 1200x microscope, you can observe a wide range of microorganisms and bacteria that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. This level of magnification allows for detailed examination of their structures, behaviors, and interactions.
Microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and algae can be observed in great detail with a 1200x microscope. Bacteria, for example, can be classified into different shapes (cocci, bacilli, spirilla) and arrangements (clusters, chains, pairs) based on their microscopic appearance. This level of magnification also enables the observation of their cellular structures, such as cell walls, cytoplasm, and flagella. Additionally, it allows for the identification of specific features like pili, capsules, and endospores, which are crucial for their survival and pathogenicity.
Furthermore, a 1200x microscope can reveal the intricate world of microorganisms in their natural habitats. For instance, you can observe the complex biofilms formed by bacteria on surfaces, which play a significant role in various processes such as disease development and water treatment. Additionally, you can study the interactions between microorganisms, such as symbiotic relationships or competition for resources, which are essential for understanding ecological dynamics.
It is important to note that the latest advancements in microscopy techniques, such as fluorescence microscopy and confocal microscopy, can enhance the visualization of microorganisms. Fluorescent dyes and tags can be used to selectively label specific structures or molecules within microorganisms, providing valuable insights into their functions and activities. Confocal microscopy, on the other hand, allows for the imaging of microorganisms in three dimensions, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of their spatial organization and behavior.
In conclusion, a 1200x microscope offers a powerful tool for studying microorganisms and bacteria. It allows for the observation of their structures, behaviors, and interactions, providing valuable insights into their roles in various biological processes. The latest advancements in microscopy techniques further enhance our ability to explore the microscopic world and deepen our understanding of these fascinating organisms.

3、 Tissue and Cell Morphology
With a 1200x microscope, one can observe and study various aspects of tissue and cell morphology in great detail. This level of magnification allows for the visualization of structures that are not visible to the naked eye, providing valuable insights into the intricate world of cells and tissues.
At this magnification, one can observe the general morphology of cells, including their shape, size, and arrangement. Different types of cells, such as epithelial cells, muscle cells, and nerve cells, can be distinguished based on their unique characteristics. The microscope enables the examination of cellular organelles, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, which play crucial roles in cell function and metabolism.
Furthermore, the 1200x microscope allows for the observation of tissue architecture and organization. Tissues are composed of specialized cells that work together to perform specific functions. By examining tissues at this level of magnification, one can identify different tissue types, such as epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues. Additionally, the microscope enables the visualization of tissue components, such as blood vessels, collagen fibers, and extracellular matrix, which contribute to tissue structure and function.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy techniques have expanded our understanding of tissue and cell morphology. For instance, the use of fluorescent dyes and immunohistochemistry allows for the visualization of specific molecules and proteins within cells and tissues. This provides researchers with the ability to study cellular processes, such as cell division, apoptosis, and protein localization, at a higher resolution.
In conclusion, a 1200x microscope offers a detailed view of tissue and cell morphology, allowing for the examination of cellular structures, tissue organization, and the latest advancements in the field. This level of magnification provides researchers with valuable insights into the complex world of cells and tissues, contributing to our understanding of various biological processes and diseases.

4、 Blood Cells and Circulatory System
With a 1200x microscope, you can observe various components of the blood cells and the circulatory system in great detail. The high magnification power allows for a closer examination of the intricate structures and functions of these vital elements.
When observing blood cells, you can clearly see the different types of cells present in the blood, including red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Red blood cells appear as small, biconcave discs, responsible for carrying oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide. White blood cells, on the other hand, come in various shapes and sizes, and they play a crucial role in the immune response, defending the body against infections and diseases. Platelets, the smallest of the blood cells, are involved in blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding.
Furthermore, a 1200x microscope allows for a closer examination of the circulatory system. You can observe the intricate network of blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body's tissues, while veins transport deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, facilitate the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and surrounding tissues.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy techniques have enabled scientists to delve even deeper into the study of blood cells and the circulatory system. For instance, fluorescent labeling techniques can be used to visualize specific molecules or proteins within the cells, providing insights into their functions and interactions. Additionally, live-cell imaging techniques allow for the observation of dynamic processes, such as blood flow and cell migration, in real-time.
Overall, a 1200x microscope offers a detailed view of blood cells and the circulatory system, providing valuable information for medical research, diagnostics, and understanding the complexities of the human body.